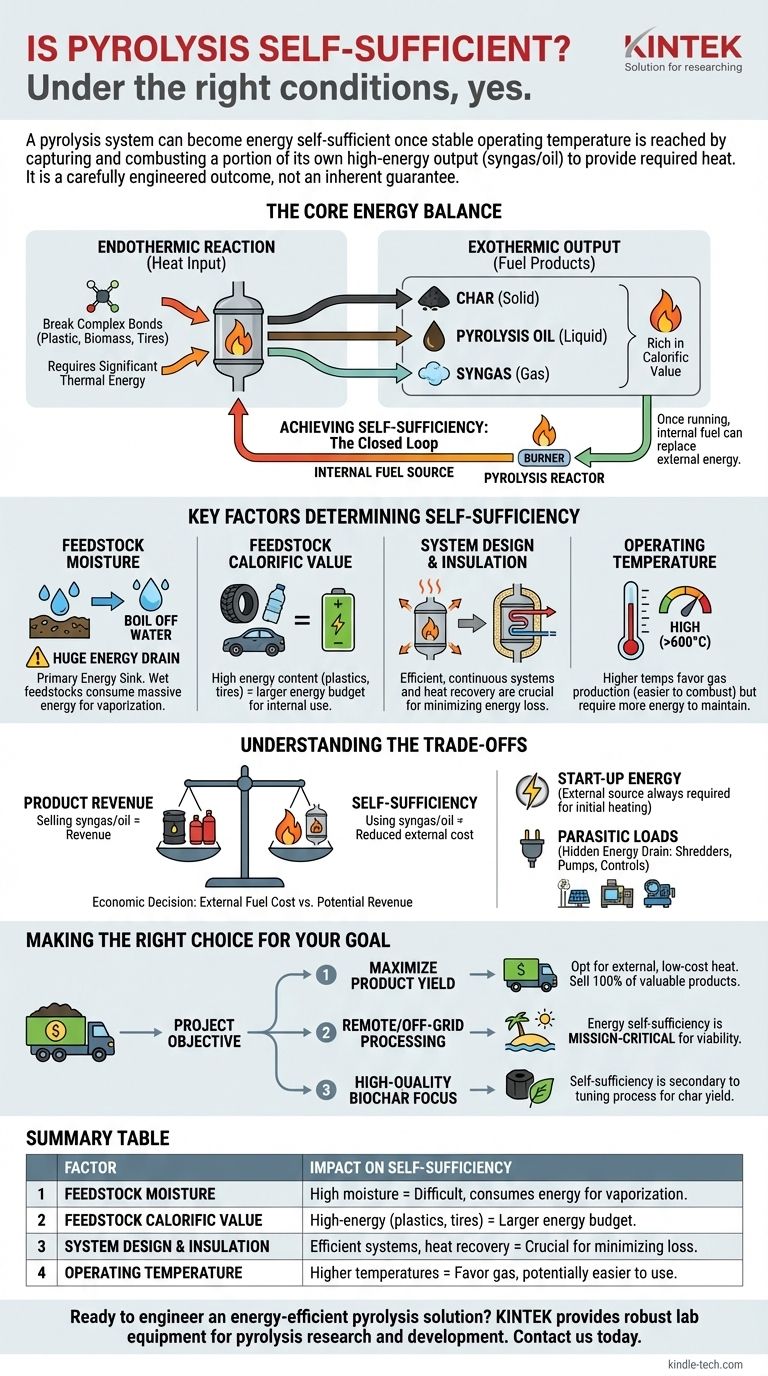
Under the right conditions, yes. A pyrolysis system can become energy self-sufficient once it reaches its stable operating temperature. This is achieved by capturing and combusting a portion of the high-energy gas (syngas) or oil it produces to provide the heat required to sustain the reaction. However, this self-sufficiency is not an inherent guarantee; it is a carefully engineered outcome that depends entirely on the feedstock, system design, and operational efficiency.
While the core chemical reaction of pyrolysis is endothermic (requiring energy input), a well-designed plant can achieve a net-zero or even net-positive energy balance. Self-sufficiency is an engineering goal, not an intrinsic property, achieved by using a fraction of the valuable fuel products to power the process itself.
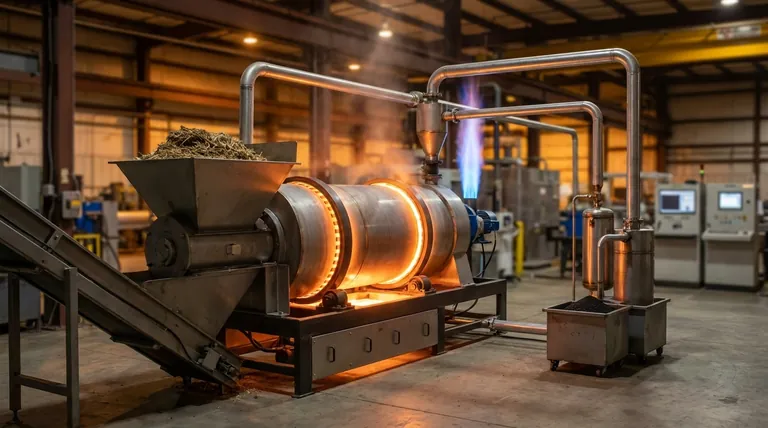

The Core Energy Balance of Pyrolysis
To understand self-sufficiency, you must first understand the fundamental energy equation of the process. Pyrolysis is not a single event but a balance of energy consumption and energy production.
The Endothermic Reaction
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of material in an oxygen-free environment. Breaking the complex chemical bonds within a feedstock—whether it's plastic, biomass, or tires—requires a significant input of thermal energy. This makes the core reaction endothermic.
The Exothermic Output
The process transforms the solid feedstock into three primary products: char (a solid), pyrolysis oil (a liquid), and syngas (a non-condensable gas). Both the syngas and oil are rich in hydrocarbons and have significant calorific (heat) value. They are fuels.
How Self-Sufficiency is Achieved
A self-sufficient system creates a closed loop. A portion of the syngas produced is redirected from the output stream back to a burner that heats the main pyrolysis reactor. Once the system is running, this internal fuel source can completely replace the external energy (like natural gas or electricity) that was used to start the process.
Key Factors Determining Self-Sufficiency
Achieving a positive energy balance is a technical challenge where several variables are critical. A failure in any one of these areas can make self-sufficiency impossible.
Feedstock Moisture: The Primary Energy Sink
This is the single most important factor. If the feedstock is wet (e.g., food waste, sludge, green biomass), a massive amount of energy is consumed just to boil off the water before the material can even reach pyrolysis temperature. This "latent heat of vaporization" is an enormous energy drain and is the most common reason a system fails to be self-sufficient.
Dry feedstocks like plastics, tires, or kiln-dried wood are far better candidates for energy self-sufficiency.
Feedstock Composition and Calorific Value
The energy content of the feedstock itself matters. Materials with a high calorific value, such as plastics and tires, produce more energetic gases and oils. This provides a larger "energy budget" to work with, making it easier to divert a fraction for internal heating while still having a high net product yield.
System Design: Heat Recovery and Insulation
A poorly designed reactor bleeds heat to the environment, demanding constant energy input. Continuous-process systems are generally more efficient than batch-process systems, which cool down between loads, wasting vast amounts of energy on reheating.
Effective insulation is non-negotiable. Furthermore, advanced designs use heat exchangers to pre-heat the incoming feedstock using the hot output products (char and syngas), recovering and recycling thermal energy that would otherwise be lost.
Operating Temperature
Higher pyrolysis temperatures (e.g., >600°C) tend to produce more syngas and less oil and char. This can be beneficial for self-sufficiency, as gas is often easier to combust on-site. However, reaching and maintaining these higher temperatures also requires more energy, creating a complex optimization problem for engineers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Pursuing self-sufficiency introduces critical trade-offs that impact the overall business case of a pyrolysis project.
Energy Self-Sufficiency vs. Product Revenue
The syngas used to power the reactor is syngas you cannot sell or upgrade into other valuable products like electricity or hydrogen. Every cubic meter of gas burned is a direct reduction in potential revenue. The decision to be self-sufficient is therefore an economic one: is the cost of external fuel higher than the potential revenue from the syngas?
The Reality of Start-Up Energy
No pyrolysis plant is self-sufficient from a cold start. An external energy source is always required to bring the reactor up to its initial operating temperature. For large industrial plants, this pre-heating phase can take several hours and consume a significant amount of energy.
Parasitic Loads: The Hidden Energy Drain
A pyrolysis plant is more than just a reactor. The total energy consumption must account for parasitic loads, which include the power needed for:
- Shredders and grinders for feedstock preparation
- Conveyors and feeding systems
- Pumps for moving liquids
- Condensers and gas scrubbers
- The electronic control system itself
These loads can be substantial and may require a separate electrical connection, even if the heating process itself is self-sustaining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether to design a pyrolysis system for self-sufficiency depends entirely on your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum product yield for revenue: You may opt for an external, low-cost heat source (like natural gas) to ensure 100% of the valuable syngas and oil can be sold.
- If your primary focus is waste processing in a remote or off-grid location: Energy self-sufficiency is mission-critical to ensure operational viability and minimize reliance on expensive transported fuel.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar: Your process will be tuned for char yield, which dictates a specific temperature and residence time; self-sufficiency becomes a secondary optimization goal within those constraints.
Ultimately, achieving an energy-positive pyrolysis operation is a deliberate engineering decision driven by your specific economic and logistical framework.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Self-Sufficiency |
|---|---|
| Feedstock Moisture | High moisture consumes energy for vaporization, making self-sufficiency difficult. |
| Feedstock Calorific Value | High-energy feedstocks (e.g., plastics, tires) provide a larger energy budget for internal use. |
| System Design & Insulation | Efficient, continuous systems with heat recovery are crucial for minimizing energy loss. |
| Operating Temperature | Higher temperatures favor gas production, which can be easier to use for internal heating. |
Ready to engineer an energy-efficient pyrolysis solution for your lab or facility?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you are optimizing feedstock, testing reactor designs, or analyzing product yields, our solutions help you achieve precise thermal processing and reliable data.
Contact us today to discuss how our equipment can support your journey toward a sustainable, energy-positive operation.
Get in touch with our experts to find the right tools for your pyrolysis project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















