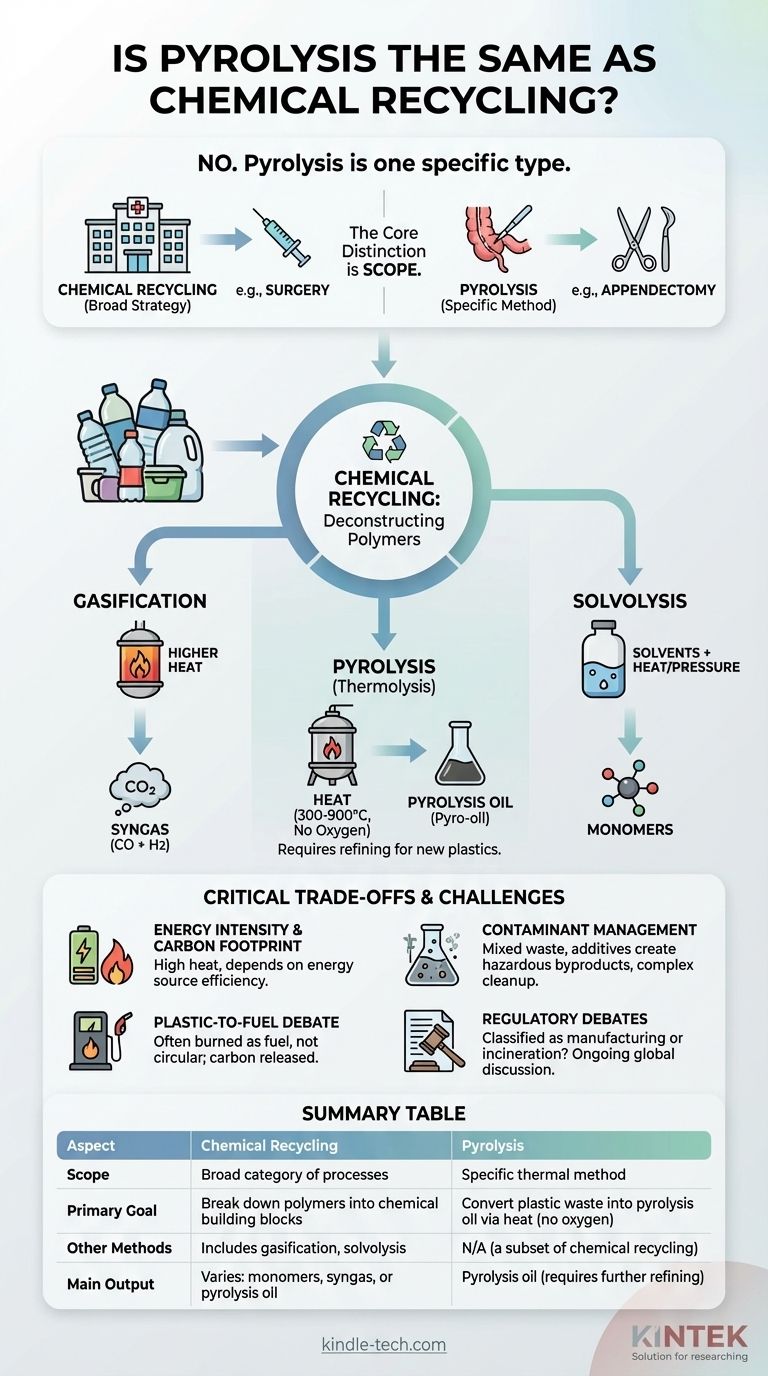
No, pyrolysis is not the same as chemical recycling—rather, it is one specific type of it. Chemical recycling is a broad category of technologies designed to break down plastics into their basic chemical components. Pyrolysis is a specific thermal method used to accomplish this, but it is not the only one.
The core distinction is one of scope: Chemical recycling is the broad strategy of breaking down polymers into their chemical building blocks, while pyrolysis is a specific thermal technology used to achieve that goal. Confusing the two is like confusing the general concept of "surgery" with the specific procedure of an "appendectomy."

What is Chemical Recycling?
The Goal: Deconstructing Polymers
At its core, chemical recycling, often called "advanced recycling," refers to any process that uses chemical reactions to break down long, complex polymer chains (plastics) into smaller, simpler molecules.
The objective is to convert plastic waste back into valuable chemical feedstocks. These feedstocks can then, in theory, be used to create new plastics, chemicals, or fuels.
The "Advanced Recycling" Label
This group of technologies is positioned as a solution for plastic waste that is difficult or impossible to manage with traditional mechanical recycling. This includes mixed plastics, multi-layer films, and contaminated materials.
Where Does Pyrolysis Fit In?
The Process: Intense Heat Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is a specific chemical recycling technique known as thermolysis. It involves heating plastic waste to very high temperatures (typically 300-900°C) in an environment with little to no oxygen.
The absence of oxygen is critical. It prevents the plastic from burning (combustion) and instead causes its long polymer chains to break apart, or "crack," into smaller hydrocarbon molecules.
The Primary Output: Pyrolysis Oil
The main product of plastic pyrolysis is a liquid substance commonly called pyrolysis oil or pyro-oil. This oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons that resembles crude oil.
To become a useful feedstock for creating new plastics, this pyrolysis oil must undergo significant, energy-intensive purification and upgrading at a refinery or steam cracker.
Understanding the Key Differences and Overlaps
A Matter of Scope: The Category and the Tool
Think of chemical recycling as a library of different techniques for deconstructing polymers.
Pyrolysis is just one important book on that library's shelf. It sits alongside other methods that achieve a similar goal through different means.
Other Chemical Recycling Methods
To fully grasp the context, it's helpful to know about other major chemical recycling processes:
- Gasification: Uses even higher temperatures than pyrolysis to convert plastics into a mixture of gases called synthesis gas (syngas), primarily carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
- Solvolysis: Uses solvents (like water, methanol, or glycols) along with heat and pressure to selectively break down specific types of polymers, such as PET, back into their original monomer building blocks.
The Critical Trade-offs and Challenges
Objectively evaluating these technologies requires understanding their significant operational challenges.
Energy Intensity and Carbon Footprint
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process requiring high, sustained heat. The overall carbon footprint depends heavily on the energy source used to power the facility and the efficiency of the subsequent oil upgrading process.
Contaminant Management
Mixed plastic waste is rarely pure. Contaminants like food residue, labels, and additives (such as flame retardants or PVC) can create hazardous byproducts in the pyrolysis oil or syngas. These contaminants must be carefully managed and removed, adding complexity and cost.
The "Plastic-to-Fuel" Debate
A significant portion of pyrolysis oil produced today is not used to make new plastics but is instead burned as fuel. Critics argue that classifying this "plastic-to-fuel" pathway as recycling is misleading, as the carbon in the plastic is released into the atmosphere, representing a one-time use, not a circular solution.
Regulatory and Definitional Debates
There is an ongoing global debate about how to classify these facilities. The chemical industry often prefers they be regulated as manufacturing plants, while environmental groups argue they should be regulated as waste incinerators due to their emissions and process similarities.
How to Interpret These Terms
When you encounter these terms, your interpretation should depend on your objective.
- If your primary focus is evaluating environmental claims: Look past the generic "chemical recycling" label and ask what specific process is being used and what the final output is—new plastic or fuel.
- If your primary focus is understanding technology: Remember that pyrolysis is a specific method, and "chemical recycling" is the overarching category of processes that alter a polymer's chemical structure.
- If your primary focus is assessing waste solutions: Recognize that the value of pyrolysis hinges on its ability to handle difficult mixed plastics and whether its output genuinely re-enters the manufacturing supply chain as a circular material.
Understanding this distinction empowers you to cut through the marketing and critically assess the true circularity of any plastic recycling claim.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Chemical Recycling | Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad category of processes | Specific thermal method |
| Primary Goal | Break down polymers into chemical building blocks | Convert plastic waste into pyrolysis oil via heat (no oxygen) |
| Other Methods | Includes gasification, solvolysis | N/A (a subset of chemical recycling) |
| Main Output | Varies: monomers, syngas, or pyrolysis oil | Pyrolysis oil (requires further refining) |
Need Reliable Lab Equipment for Your Recycling Research?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored for chemical recycling and pyrolysis processes. Whether you're developing new recycling methods or analyzing pyrolysis oil, our solutions ensure precision, safety, and efficiency. Enhance your R&D with trusted tools—contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does an industrial tube furnace ensure the required process conditions for supercritical fluid experimental devices?
- What is the primary function of quartz tubes in halide electrolyte synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses



















