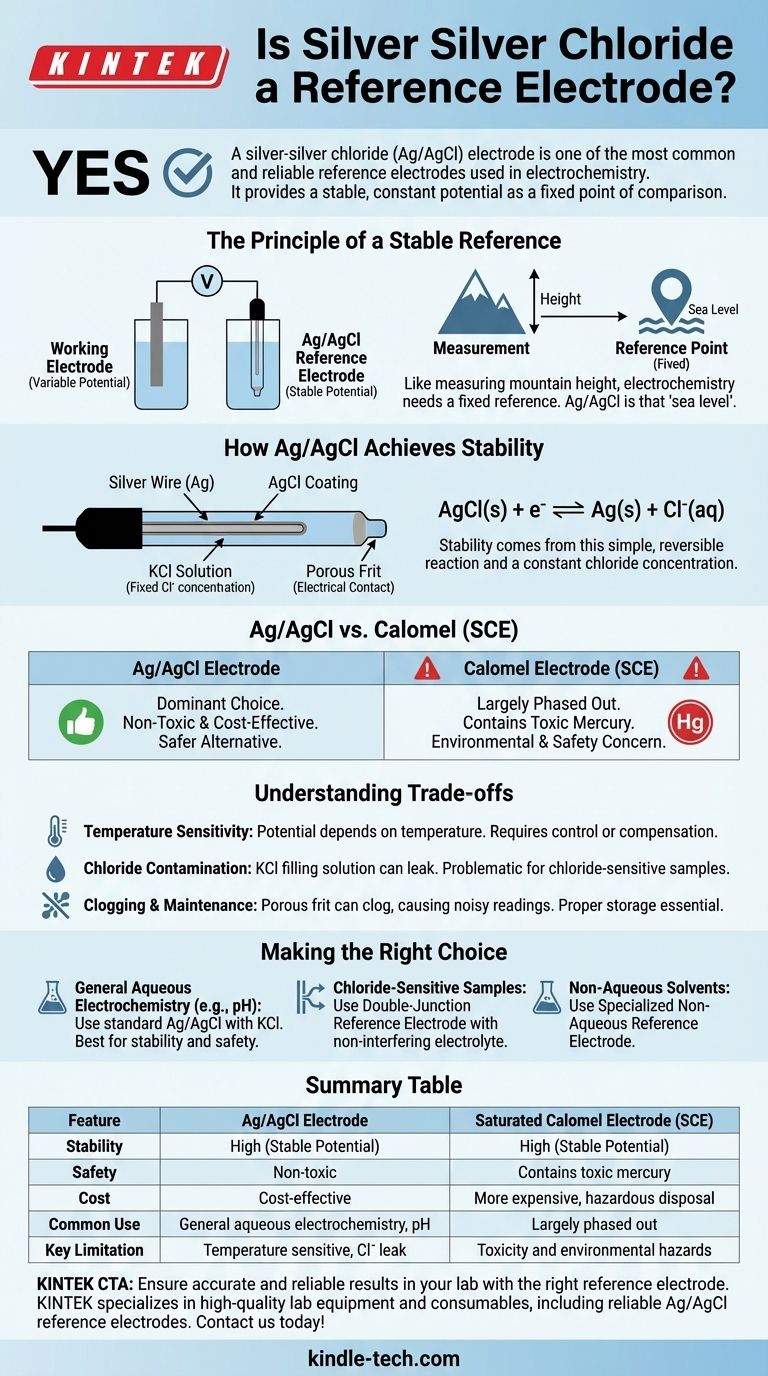
Yes, a silver-silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode is one of the most common and reliable reference electrodes used in electrochemistry. It provides a stable, constant potential that acts as a fixed point of comparison, allowing you to accurately measure the potential of another electrode (the working electrode) within an electrochemical cell. This stability makes it indispensable for applications ranging from pH measurement to cyclic voltammetry.
The core function of a reference electrode is to provide an unchanging voltage baseline. The Ag/AgCl electrode achieves this through a specific, stable chemical equilibrium, making it a trusted and cost-effective standard in modern electrochemistry.

The Principle of a Stable Reference
To understand why the Ag/AgCl electrode is so effective, we must first understand what makes a good reference. An electrochemical measurement is always a comparison of potential between two points.
What is a Reference Electrode?
A reference electrode is a half-cell with a known, stable electrode potential. Its job is to remain constant, regardless of changes occurring in the other half of the cell (the working electrode and the sample solution).
Think of it like measuring the height of a mountain. You need a fixed reference point, like sea level, to get a meaningful measurement. In electrochemistry, the reference electrode is sea level.
How Ag/AgCl Achieves Stability
The stability of the Ag/AgCl electrode comes from a simple, reversible chemical reaction. It consists of a silver wire coated with a thin layer of silver chloride (AgCl), all immersed in a solution with a fixed concentration of chloride ions (Cl⁻), typically potassium chloride (KCl).
The potential is established by the equilibrium between the solid silver metal and its salt:
AgCl(s) + e⁻ ⇌ Ag(s) + Cl⁻(aq)
Because the concentration of the chloride solution inside the electrode is kept constant, the potential of this half-reaction remains exceptionally stable.
Ag/AgCl vs. Other Reference Electrodes
The Ag/AgCl electrode is not the only option, but its advantages have made it a dominant choice over older standards like the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE).
The Rise of Ag/AgCl
The primary reason for the widespread adoption of Ag/AgCl is its safety and performance. It is relatively inexpensive to produce and, most importantly, non-toxic.
The Decline of the Calomel Electrode (SCE)
The Calomel electrode, which uses a mercury/mercurous chloride paste, was once a common standard. However, it has been largely phased out in many labs.
The key reason is toxicity. Mercury is a hazardous material, making the use, storage, and disposal of Calomel electrodes a significant environmental and safety concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the Ag/AgCl electrode is an excellent general-purpose choice, it is not without limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for accurate measurements.
Temperature Sensitivity
The potential of an Ag/AgCl electrode is dependent on temperature. For highly precise work, the temperature of the cell must be controlled and reported, or a temperature-compensating probe must be used.
Chloride Contamination
The electrode is filled with a concentrated KCl solution. A small amount of this solution can leak out of the porous frit at the electrode tip and into your sample. If your experiment is sensitive to chloride ions, this can be a source of error.
Clogging and Maintenance
The porous frit that allows electrical contact with the sample can become clogged, leading to noisy or drifting potential readings. Proper storage (with the tip immersed in its filling solution) and regular maintenance are essential for long life and accurate results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct reference electrode and filling solution is critical for experimental success. Your choice depends entirely on the chemistry of your sample.
- If you are performing general aqueous electrochemistry (like most pH or ion measurements): An Ag/AgCl electrode with a standard KCl filling solution is almost always the best choice due to its stability and safety.
- If your sample reacts with or is sensitive to chloride ions: You must use a "double-junction" reference electrode, where an outer chamber with a non-interfering electrolyte (like potassium nitrate) isolates the inner Ag/AgCl element from your sample.
- If you are working in non-aqueous solvents: You will need a specialized non-aqueous reference electrode, as standard aqueous electrodes will not function properly and will contaminate your solvent.
Ultimately, choosing the right reference electrode is about ensuring it remains an inert, stable observer of the chemical reaction you wish to study.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ag/AgCl Electrode | Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) |
|---|---|---|
| Stability | High (stable potential) | High (stable potential) |
| Safety | Non-toxic | Contains toxic mercury |
| Cost | Cost-effective | More expensive, hazardous disposal |
| Common Use | General aqueous electrochemistry, pH measurement | Largely phased out due to safety concerns |
| Key Limitation | Temperature sensitive, potential chloride contamination | Toxicity and environmental hazards |
Ensure accurate and reliable results in your lab with the right reference electrode. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable Ag/AgCl reference electrodes tailored for your electrochemical applications. Our experts can help you select the perfect electrode to maintain stability and avoid contamination in your experiments. Contact us today to enhance your lab's precision and safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
People Also Ask
- Which type of electrode can be used as a reference point? Select the Right One for Accurate Measurements
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercury chloride? Discover the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE)
- Why and how should the electrodes of an electrolytic cell be calibrated? Ensure Reliable Results
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercurous sulfate? A Guide to Chloride-Free Electrochemistry
- Which electrode is used as a reference? A Guide to Accurate Electrochemical Measurements

















