At a technical level, yes, it is possible to turn plastic into fuel, but its overall efficiency is highly debatable and complex. The process, most commonly pyrolysis, can convert hard-to-recycle plastic waste into usable liquid oil. However, claims of efficiency must be weighed against significant energy inputs, potential for harmful emissions, and economic challenges that are often overlooked.
The core issue is not whether plastic can be turned into fuel, but whether it is an energy-positive, environmentally sound, and economically viable solution at scale. The evidence suggests that while it can address a specific waste problem, it is far from a universally efficient or clean process.
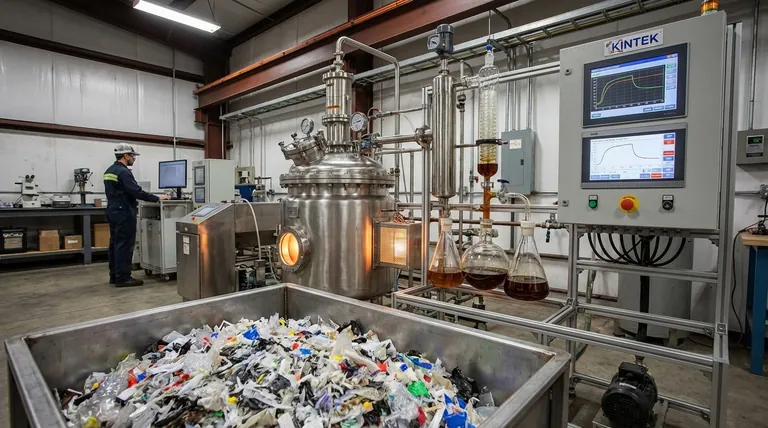

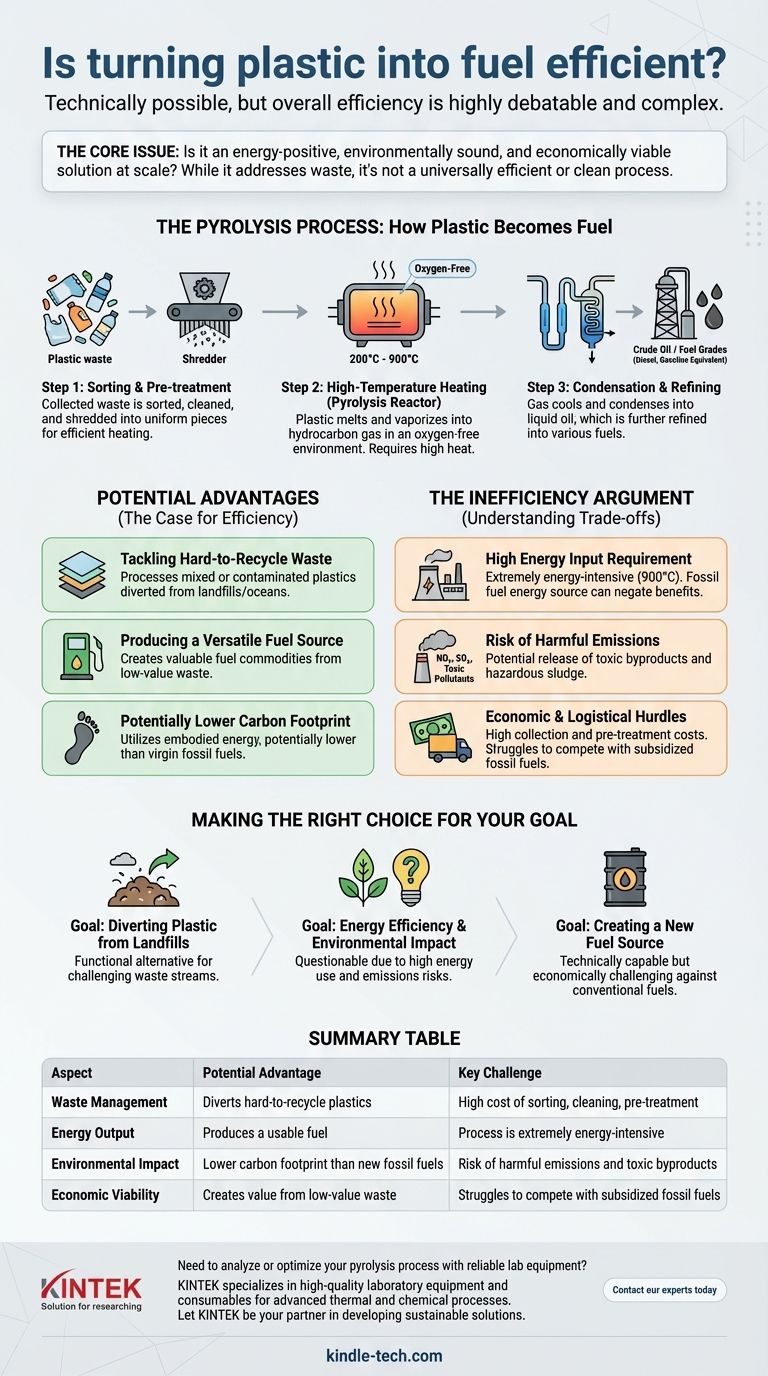
How Plastic is Converted to Fuel: The Pyrolysis Process
Pyrolysis is the most common method for converting plastic waste into fuel. It is a thermochemical process that breaks down the long polymer chains of plastic into smaller, useful hydrocarbons using high heat in an oxygen-free environment.
Step 1: Sorting and Pre-treatment
First, the collected plastic waste must be sorted and cleaned. Any non-plastic materials, dirt, and other impurities must be removed to prevent contamination of the final product.
The cleaned plastic is then often shredded or ground into smaller, uniform pieces. This increases the surface area, allowing the material to heat more evenly and efficiently in the next stage.
Step 2: High-Temperature Heating
The prepared plastic is loaded into a sealed, oxygen-free reactor chamber, often with a catalyst to speed up the reaction.
The reactor is then heated to extremely high temperatures, typically between 200°C and 900°C. This intense heat causes the plastic to melt and then vaporize into a hydrocarbon gas without combusting.
Step 3: Condensation and Refining
The hot gas is then channeled out of the reactor and into a cooling system. As the gas cools, it condenses into a liquid, which is a raw, crude-like oil.
This liquid oil often requires further refining to separate it into different fuel grades, such as a diesel or gasoline equivalent, and to remove any remaining impurities.
The Case for Efficiency: Potential Advantages
Proponents of plastic-to-fuel technology point to several key benefits that frame it as an efficient solution to a specific environmental problem.
Tackling Hard-to-Recycle Waste
The primary advantage is the ability to process plastic waste that is difficult or impossible to recycle through traditional mechanical means. This includes mixed, contaminated, or multi-layered plastics that would otherwise end up in a landfill or the ocean.
Producing a Versatile Fuel Source
The process can be calibrated to produce different types of fuel tailored for specific needs, including transportation. This creates a valuable commodity from a low-value waste stream.
A Potentially Lower Carbon Footprint
When compared to extracting and refining new fossil fuels, using waste plastic as a feedstock can result in a lower overall carbon footprint. It utilizes the embodied energy already present in the plastic, creating a form of circularity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Inefficiency Argument
Despite the potential benefits, significant drawbacks challenge the overall efficiency and sustainability of turning plastic into fuel.
The High Energy Input Requirement
The pyrolysis process is extremely energy-intensive. Heating a reactor to 900°C requires a substantial amount of external energy. If that energy comes from fossil fuels, it can negate the environmental benefits and make the process a net energy loser.
The Risk of Harmful Emissions
While the process occurs in an oxygen-free chamber, it is not free from harmful byproducts. The potential release of nitrous oxides, sulfur dioxides, and other toxic pollutants is a major concern. Incomplete conversion can also create a hazardous sludge that requires careful disposal.
Economic and Logistical Hurdles
The economic viability is often precarious. The cost of collecting, transporting, and pre-treating plastic waste can be high. Furthermore, the resulting fuel must compete with a highly optimized and subsidized global fossil fuel market, making profitability a challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating plastic-to-fuel technology requires a clear understanding of your primary objective. It is a technology of trade-offs, not a perfect solution.
- If your primary focus is diverting non-recyclable plastic from landfills: Plastic-to-fuel offers a functional alternative to incineration or landfilling for specific, challenging waste streams.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and environmental impact: The significant energy required and the risk of toxic emissions make this a questionable choice compared to reducing plastic consumption and improving traditional recycling systems.
- If your primary focus is creating a new fuel source: The process is technically capable, but its economic competitiveness against conventional fossil fuels remains a major barrier to widespread adoption.
Ultimately, viewing plastic-to-fuel as a niche, transitional technology rather than a silver bullet for our plastic or energy problems provides the most accurate and responsible perspective.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Potential Advantage | Key Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Management | Diverts hard-to-recycle plastics from landfills | High cost of sorting, cleaning, and pre-treatment |
| Energy Output | Produces a usable fuel from waste | Process is extremely energy-intensive |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint than new fossil fuels | Risk of harmful emissions and toxic byproducts |
| Economic Viability | Creates value from a low-value waste stream | Struggles to compete with subsidized fossil fuels |
Need to analyze or optimize your pyrolysis process with reliable lab equipment?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables for advanced thermal and chemical processes. Whether you're researching pyrolysis efficiency, analyzing fuel outputs, or scaling up your operations, our precise and durable instruments provide the accurate data you need to make informed decisions.
Let KINTEK be your partner in developing sustainable solutions. Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can support your specific project goals and help you navigate the complexities of plastic-to-fuel conversion.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















