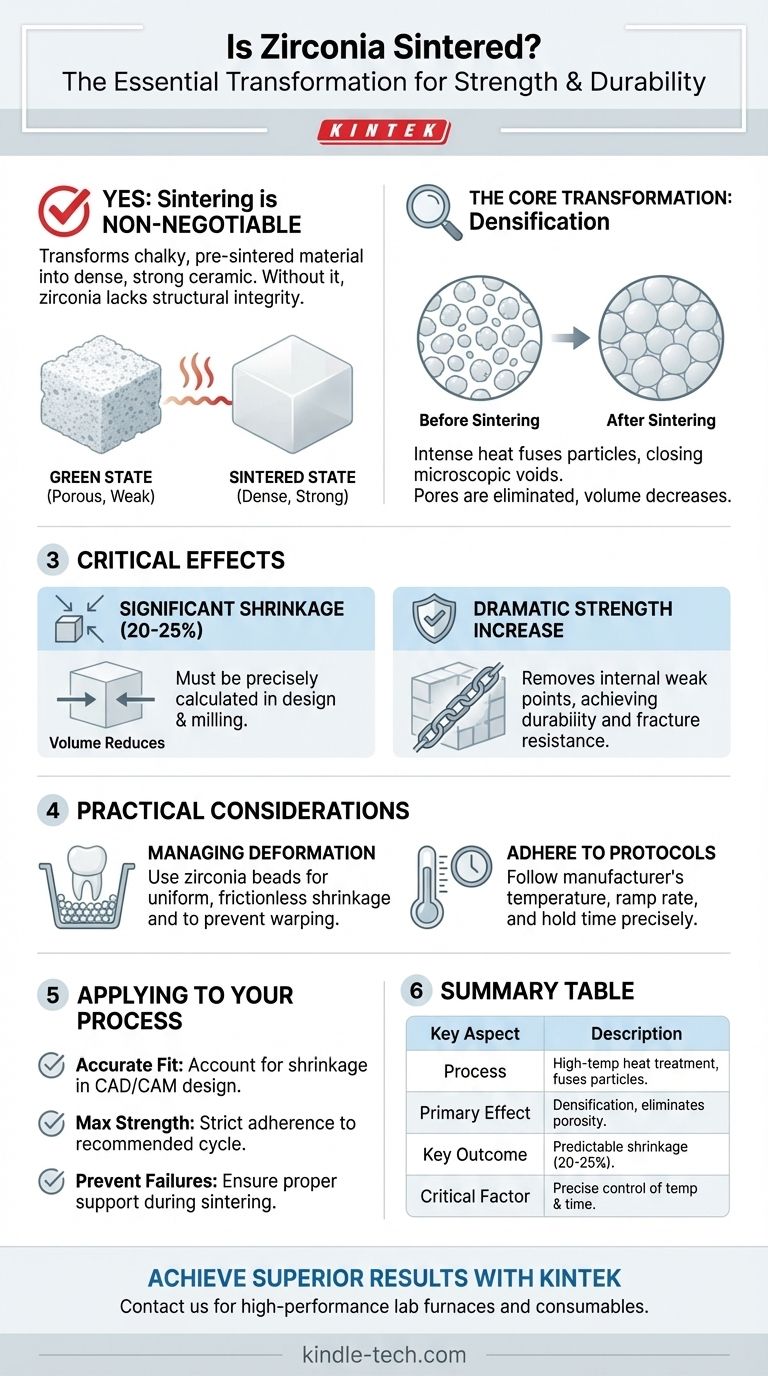
Yes, sintering is an essential and non-negotiable step in the processing of zirconia. This high-temperature heat treatment is the fundamental process that transforms the chalky, pre-sintered material into the dense, incredibly strong ceramic used in demanding applications. Without sintering, zirconia would lack the structural integrity and durability for which it is known.
Sintering is not merely a step in making a zirconia part; it is the definitive process that creates its final properties. By applying heat and pressure, sintering eliminates internal porosity, which dramatically increases the material's density and strength.

What is Sintering? The Core Transformation
Sintering is a thermal process applied to a powdered material to create a dense, solid object. For a material like zirconia, this is where its final, robust characteristics are born.
From a "Green State" to a Final Form
Before sintering, a zirconia part exists in a porous, chalk-like condition known as the "green state." While it can be easily milled and shaped in this phase, it is mechanically weak.
The sintering process applies intense heat, causing the individual zirconia particles to bond and fuse.
The Mechanism of Densification
This fusion closes the microscopic voids between the particles, a process called densification. The goal is to reduce porosity as much as possible.
As the pores are eliminated, the overall volume of the material decreases, leading to a more compact and solid structure.
The Critical Effects of Sintering Zirconia
The changes that occur during sintering are not subtle. They are dramatic, predictable, and absolutely critical to the performance of the final component.
Significant, Predictable Shrinkage
The most noticeable result of sintering zirconia is significant shrinkage. As the material densifies, it can shrink by 20-25% in volume.
This shrinkage is a known variable that must be precisely calculated and compensated for during the initial design and milling phase.
A Dramatic Increase in Strength
The primary reason for sintering is to achieve exceptional strength. By eliminating porosity, the process removes the internal weak points where fractures could initiate.
This transformation is what gives zirconia its renowned durability and fracture resistance, making it suitable for high-stress applications like dental crowns and industrial components.
Understanding the Practical Considerations
Successfully sintering zirconia requires a clear understanding of the physical changes involved and the precise control needed to manage them.
Managing Deformation During Shrinkage
Because the material shrinks substantially, there is a risk of warping or deformation. To ensure uniform transformation, parts are often placed in a crucible filled with zirconia beads.
These beads act as a supportive, frictionless bed, allowing the component to move and shrink evenly in all directions without being constrained.
The Importance of Manufacturer Protocols
Different formulations of zirconia have unique sintering requirements. The specific temperature, heating rate, and hold time are all critical parameters.
Following the manufacturer's instructions precisely is paramount. Deviating from the recommended cycle can result in an under-sintered (weak) or over-sintered (brittle) part, compromising the final outcome.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Understanding the role of sintering allows you to control the quality and predictability of your zirconia components.
- If your primary focus is achieving an accurate fit: You must account for the manufacturer's specified shrinkage rate with extreme precision during the initial CAD/CAM design.
- If your primary focus is maximizing material strength: Adhering strictly to the recommended sintering cycle—temperature, ramp rate, and duration—is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is preventing processing failures: Ensure the part is properly supported, often with zirconia beads, to allow for uniform shrinkage and prevent warping.
Mastering the sintering process is the key to unlocking the full potential of zirconia and achieving consistently superior results.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | High-temperature heat treatment that fuses zirconia particles. |
| Primary Effect | Densification: Eliminates porosity, increasing strength dramatically. |
| Key Outcome | Predictable shrinkage (20-25%) that must be accounted for in design. |
| Critical Factor | Precise control of temperature and time per manufacturer's protocol. |
Achieve Superior Zirconia Results with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of your zirconia components with precise and reliable sintering. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables designed specifically for dental labs, research institutions, and industrial manufacturers.
Our sintering furnaces ensure the exact temperature control and uniform heating required for consistent, high-strength results, batch after batch. Let us help you master this critical process.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sintering needs and find the perfect equipment solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Is ceramic the same as porcelain teeth? A Guide to Choosing the Right Dental Material
- What does a porcelain furnace do? Create Durable, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is low fusing porcelain? Achieve Superior Esthetics and Metal Integrity in PFM Restorations
- Why are porcelain fired under vacuum? To Eliminate Porosity for Superior Strength & Translucency
- What are the disadvantages of ceramic restoration? Weighing Aesthetics Against Durability and Cost
- What temperature is porcelain fired at? A Guide to Precise Dental Firing Cycles
- What is a dental furnace? The Essential Tool for High-Quality Dental Restorations
- Are zirconia crowns biocompatible? The Ultimate Guide to Safe, Metal-Free Dental Restorations



















