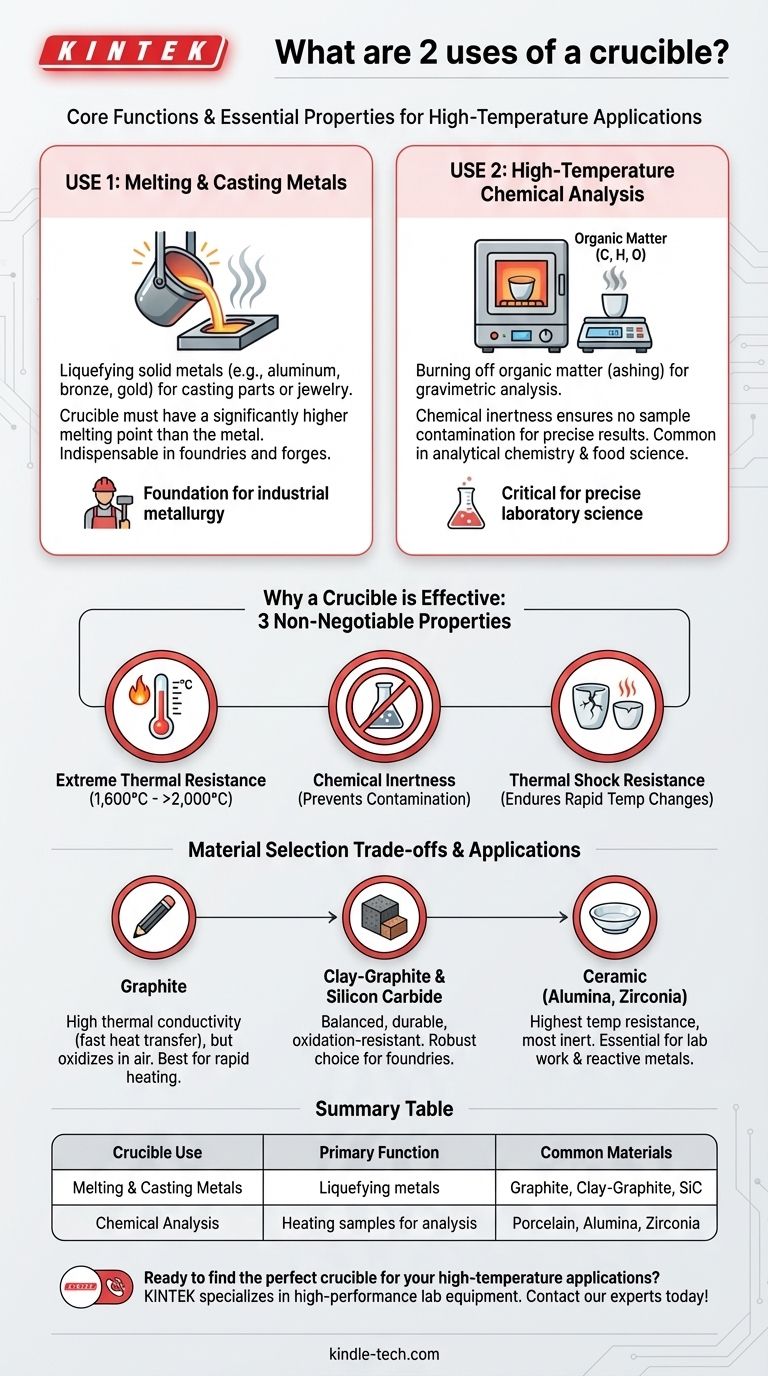
At its core, a crucible has two primary functions: holding materials for melting or heating at extremely high temperatures and conducting chemical analysis where samples must be heated without contamination. These seemingly simple uses are critical in fields ranging from industrial metallurgy to precise laboratory science.
A crucible is not merely a container; it is a high-performance tool engineered to withstand extreme conditions—intense heat, thermal shock, and chemical attack—while remaining inert and preserving the purity of its contents.
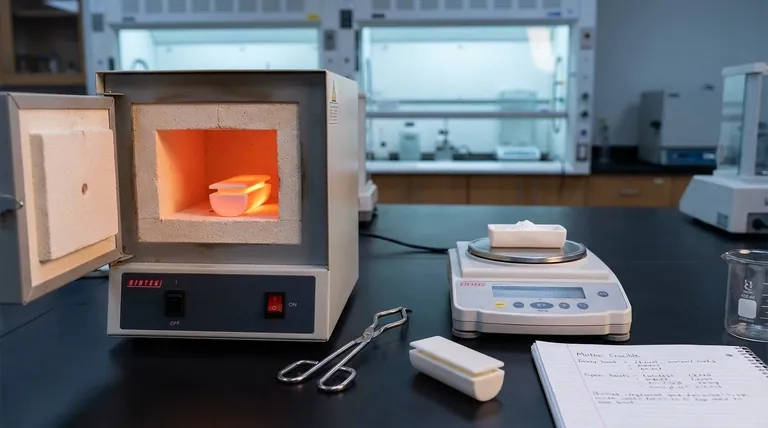

The Fundamental Purpose: Containing Extreme Heat
A crucible’s main job is to act as a stable vessel when temperatures soar far beyond the capabilities of standard glass or metal containers. This enables foundational processes across science and industry.
Use 1: Melting and Casting Metals
In foundries and forges, crucibles are indispensable for liquefying metals. Solid metals like aluminum, bronze, steel, gold, and platinum are placed into a crucible, which is then heated in a furnace.
The crucible must have a melting point significantly higher than the metal inside. This allows the metal to become fully molten for casting into molds, creating everything from engine parts to jewelry.
Use 2: High-Temperature Chemical Analysis
In analytical chemistry, crucibles are used for processes like gravimetric analysis and ashing. For example, a food sample might be placed in a porcelain crucible and heated to over 500°C.
This process burns off all the organic matter (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen), leaving only the inorganic mineral content behind for analysis. The crucible's chemical inertness ensures that it does not react with the sample and alter the results.
Beyond the Basics: Material Synthesis
Crucibles are also central to creating new materials. Scientists and engineers use them to melt and mix elements to form new alloys, synthesize high-purity crystals for semiconductors, and produce specialty glass compositions.
What Makes a Crucible Effective?
The function of a crucible is defined by the properties of the material it is made from. Three characteristics are non-negotiable.
Extreme Thermal Resistance
A crucible's most obvious requirement is an exceptionally high melting point. Materials like graphite, silicon carbide, and ceramics like alumina and zirconia can withstand temperatures from 1,600°C to well over 2,000°C (3,000-4,000°F).
Chemical Inertness
The crucible material cannot react with the substance it holds. Contamination from the crucible walls can ruin a metal alloy or invalidate a sensitive chemical analysis. This is why highly stable ceramic and graphite compositions are used.
Thermal Shock Resistance
A crucible must endure rapid and extreme temperature changes without cracking. Being removed from a white-hot furnace and exposed to cooler air creates immense stress. Materials are specifically engineered to handle this thermal shock.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material Selection
No single crucible is perfect for every task. The choice of material involves balancing performance, longevity, and cost.
Graphite Crucibles
These offer excellent thermal conductivity, meaning they transfer heat to the contents very quickly. However, pure graphite can oxidize (burn away) in the presence of air at high temperatures, limiting its lifespan.
Clay-Graphite and Silicon Carbide Crucibles
These are composite materials that blend the heat transfer of graphite with the durability and oxidation resistance of other materials. They represent a robust, all-around choice for many foundries and are more durable than pure graphite.
Ceramic Crucibles
Materials like alumina, zirconia, and porcelain offer the highest temperature resistance and are the most chemically inert. This makes them essential for laboratory work and for melting highly reactive metals like titanium, but they are typically more brittle and expensive.
Selecting the Right Crucible for Your Application
Choosing the correct crucible is a critical first step for ensuring the success and purity of any high-temperature process.
- If your primary focus is melting common non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible provides the best balance of cost, durability, and performance.
- If your primary focus is high-purity lab analysis or melting reactive metals: A high-purity ceramic crucible, such as one made from alumina, is necessary to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is rapidly heating small batches of precious metals: A pure graphite crucible can be effective due to its high thermal conductivity, but you must manage its exposure to oxygen.
Ultimately, understanding the demands of your specific task is key to selecting a tool that will perform reliably under extreme conditions.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Use | Primary Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Melting & Casting Metals | Liquefying metals for casting parts or jewelry | Graphite, Clay-Graphite, Silicon Carbide |
| Chemical Analysis | Heating samples for gravimetric analysis or ashing | Porcelain, Alumina, Zirconia |
Ready to find the perfect crucible for your high-temperature applications? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including a wide range of crucibles designed for extreme conditions. Whether you're melting metals or conducting precise chemical analysis, our experts can help you select the right crucible material—graphite, ceramic, or silicon carbide—to ensure purity, durability, and accurate results. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of high-purity alumina crucibles for molten ZnNaK//Cl salts? Ensure Experimental Purity
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible preferred for high-temperature oxidation? Ensure Unmatched Data Integrity
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data



















