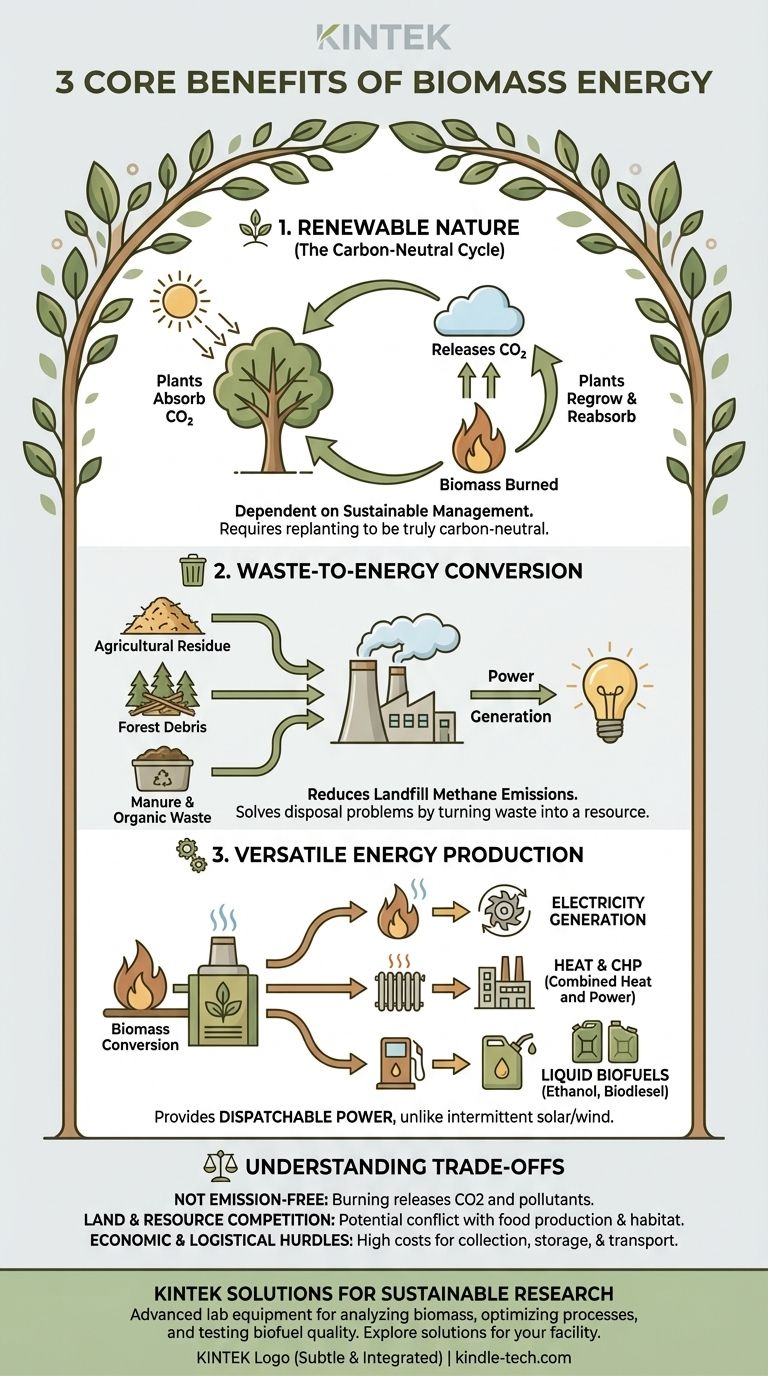
The three primary benefits of biomass energy are its renewable nature, its ability to convert waste into fuel, and its versatility in producing heat, electricity, and biofuels. While it is often sourced from dedicated crops, its greatest potential lies in using organic waste materials like agricultural residue or forest debris, which simultaneously solves a disposal problem while generating power.
Biomass energy occupies a unique space in the renewable landscape. Its core advantage is not just being renewable, but its ability to provide consistent, dispatchable power from organic materials—often from waste streams—unlike intermittent sources like solar or wind.

A Closer Look at the Core Benefits
Biomass energy is derived from organic matter, such as plants, wood, and waste. This material, or "feedstock," is burned or converted to generate energy.
A Renewable Resource (with a Caveat)
Biomass is considered a renewable energy source because its core component—plant life—can be regrown. Through photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere.
When this biomass is burned, it releases that same amount of CO2 back, creating what is known in principle as a carbon-neutral cycle.
However, this benefit is entirely dependent on sustainable management. If forests are cleared without being replanted, or if land is mismanaged, biomass ceases to be renewable and can contribute to deforestation.
Turning Waste into Energy
One of the most powerful benefits of biomass is its ability to create value from materials that would otherwise be discarded. This is a key advantage over other energy sources.
Common feedstocks include agricultural crop residues, forest debris from logging, manure, and even the organic components of municipal solid waste.
Using these materials for energy generation helps reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills, which in turn cuts down on the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas produced during decomposition.
Versatility in Energy Production
Biomass is not limited to a single form of energy output. This flexibility allows it to be adapted to a wide range of needs.
It can be burned directly in a boiler to create high-pressure steam, which then spins a turbine to generate electricity. The excess heat from this process can also be captured and used to warm buildings in a system known as Combined Heat and Power (CHP), greatly increasing overall efficiency.
Furthermore, biomass can be converted into liquid biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel, providing a renewable alternative to gasoline and diesel for the transportation sector.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The benefits of biomass are significant, but they must be weighed against considerable challenges. The references you provided correctly highlight that its viability is highly dependent on context and proper management.
The Question of "Clean" Energy
While theoretically carbon-neutral, the combustion of biomass is not emission-free. It releases CO2, and inefficient burning can produce other harmful air pollutants like particulate matter and carbon monoxide.
The environmental benefit hinges entirely on using waste streams or ensuring that any dedicated crops are grown and harvested sustainably without depleting soil or water resources.
Land Use and Resource Competition
Developing large-scale biomass facilities requires a significant amount of land. This creates a potential conflict with other essential land uses.
There is a major risk of competing with food production, driving up food prices, or contributing to deforestation if natural habitats are cleared to grow energy crops. This is the central sustainability challenge facing the biomass industry.
Economic and Logistical Hurdles
Biomass is a low-density fuel. It is bulky and expensive to collect, store, and transport compared to the ease of piping natural gas or transmitting electricity.
The initial construction and ongoing maintenance of a biomass plant are also costly. These economic factors often make it less competitive than fossil fuels or even other renewables like utility-scale solar and wind, especially without subsidies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Biomass is not a universal solution, but rather a specialized tool for specific energy and environmental goals.
- If your primary focus is Waste Management: Biomass is an excellent solution for converting local agricultural, forest, or municipal organic waste into a reliable energy source.
- If your primary focus is Energy Independence: Locally sourced biomass can provide a consistent, dispatchable power source that is not dependent on weather or distant supply chains.
- If your primary focus is Scalable, Low-Impact Energy: Solar or wind are often more suitable due to the significant land use, logistical, and potential emissions complexities of large-scale biomass.
Ultimately, the value of biomass energy is unlocked when it is applied thoughtfully, at a scale appropriate to the local supply of sustainable feedstock.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Advantage | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Resource | Carbon-neutral cycle from regrown plants | Requires sustainable management to avoid deforestation |
| Waste to Energy | Converts agricultural residue, forest debris, and manure into fuel | Reduces landfill methane and solves disposal problems |
| Versatile Production | Generates electricity, heat (CHP), and liquid biofuels like biodiesel | Offers dispatchable power unlike intermittent solar/wind |
Ready to explore sustainable energy solutions for your laboratory or facility? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables that support renewable energy research and development. Whether you're analyzing biomass feedstocks, optimizing conversion processes, or testing biofuel quality, our precision instruments can help you achieve accurate and reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your biomass energy projects and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- 5L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output











