In practice, the three most significant disadvantages of using biomass as a fuel are its lower energy density compared to fossil fuels, the high costs associated with its collection and processing, and the substantial land and resource requirements that can compete with food production and lead to environmental degradation. These factors create considerable economic and logistical hurdles that challenge its viability as a large-scale energy solution.
While biomass is a renewable resource, its physical properties and the logistics of its supply chain make it fundamentally less efficient and more complex to utilize than the dense, concentrated energy found in fossil fuels.

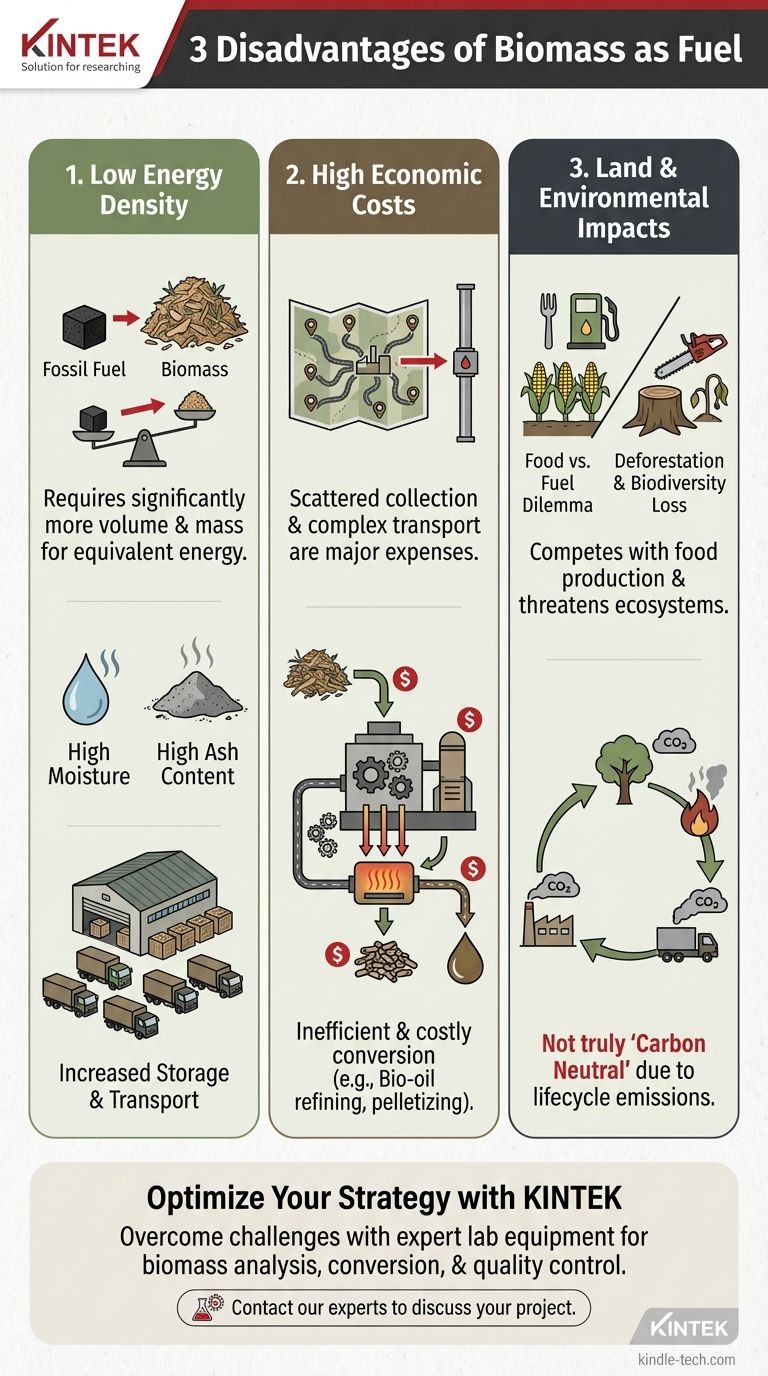
The Challenge of Energy Density
A primary technical disadvantage of biomass is its low energy density. This means that a given volume or mass of biomass contains significantly less energy than the same amount of coal, oil, or natural gas.
Lower Calorific Value
Biomass, whether as raw wood or processed into forms like bio-oil, has a lower heating or calorific value. You simply need to burn a much larger quantity of it to generate the same amount of heat or electricity as you would with fossil fuels.
High Moisture and Ash Content
Raw biomass often contains a high percentage of water, which must be removed through an energy-intensive drying process before it can be burned efficiently. It also produces more ash after combustion, which creates disposal challenges and can reduce boiler efficiency.
Implications for Storage and Transport
Because it is less dense and requires larger quantities, biomass demands significantly more space for storage. This also means more trucks or trains are needed for transportation, increasing logistical complexity, costs, and the overall carbon footprint of the fuel cycle.
The Economic Hurdles of Biomass
Converting a bulky, dispersed resource into a usable fuel is an expensive and complex undertaking that often struggles to compete with established energy sources on cost.
High Collection and Transportation Costs
Unlike fossil fuels, which are extracted from concentrated deposits, biomass is geographically scattered. The process of harvesting, collecting, and transporting it from fields and forests to a central processing plant is a major operational expense.
Complex and Costly Processing
Raw biomass is rarely used directly. It must be converted into a more uniform and stable fuel, such as wood pellets or liquid bio-oil. These conversion processes can be inefficient and expensive.
As an example, refining bio-oil is complicated by its high viscosity (making it difficult to pump), its tendency to deteriorate over time, and a general lack of mature, economically viable refining technologies.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Land and Environmental Impacts
While often promoted as "green," the large-scale use of biomass carries significant environmental trade-offs that must be carefully managed.
The "Food vs. Fuel" Dilemma
Dedicating large tracts of arable land to grow energy crops (like corn for ethanol or switchgrass) can directly compete with land used for food production. This can lead to increased food prices and concerns about food security.
Risk of Deforestation and Biodiversity Loss
If demand for wood biomass outstrips the supply from sustainably managed forests, it can lead to deforestation. This destroys natural habitats, reduces biodiversity, and releases massive amounts of stored carbon into the atmosphere.
The Question of Carbon Neutrality
The idea that biomass is "carbon neutral" is an oversimplification. While a new plant can reabsorb the CO2 released from burning one, this cycle takes time. Furthermore, the entire lifecycle—including emissions from harvesting machinery, transportation, and processing—contributes a significant carbon footprint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Energy Strategy
Understanding these disadvantages is crucial for deploying biomass energy effectively and sustainably. Your ideal approach depends entirely on your specific goals and available resources.
- If your primary focus is utilizing local waste: Biomass from agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, or municipal solid waste is an excellent choice, as it solves a disposal problem while generating energy.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, consistent power generation: Be prepared for major logistical and financial commitments to secure a stable, affordable, and sustainable fuel supply chain.
- If your primary focus is maximum environmental benefit: Prioritize biomass sourced exclusively from waste streams or certified sustainable operations to avoid negative impacts on land use, food supply, and forests.
Ultimately, viewing biomass not as a universal replacement for fossil fuels, but as a specialized tool for specific situations, is the key to leveraging its benefits responsibly.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Issue | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Low Energy Density | High moisture/ash content, low calorific value | Requires more fuel volume, increases storage/transport costs |
| High Economic Cost | Expensive collection, transport, and processing | Struggles to compete with fossil fuels on price |
| Land & Environmental Impact | Food vs. fuel dilemma, deforestation risk | Can threaten food security and biodiversity |
Optimize your biomass energy strategy with KINTEK.
Navigating the complexities of biomass fuel—from sourcing sustainable materials to managing processing efficiency—requires expert support and reliable equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for biomass analysis, conversion process development, and quality control.
Whether you're researching alternative feedstocks, optimizing bio-oil refinement, or ensuring the sustainability of your supply chain, our solutions help you overcome the key disadvantages of biomass and make informed, efficient decisions.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific biomass energy projects and enhance your research capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process





