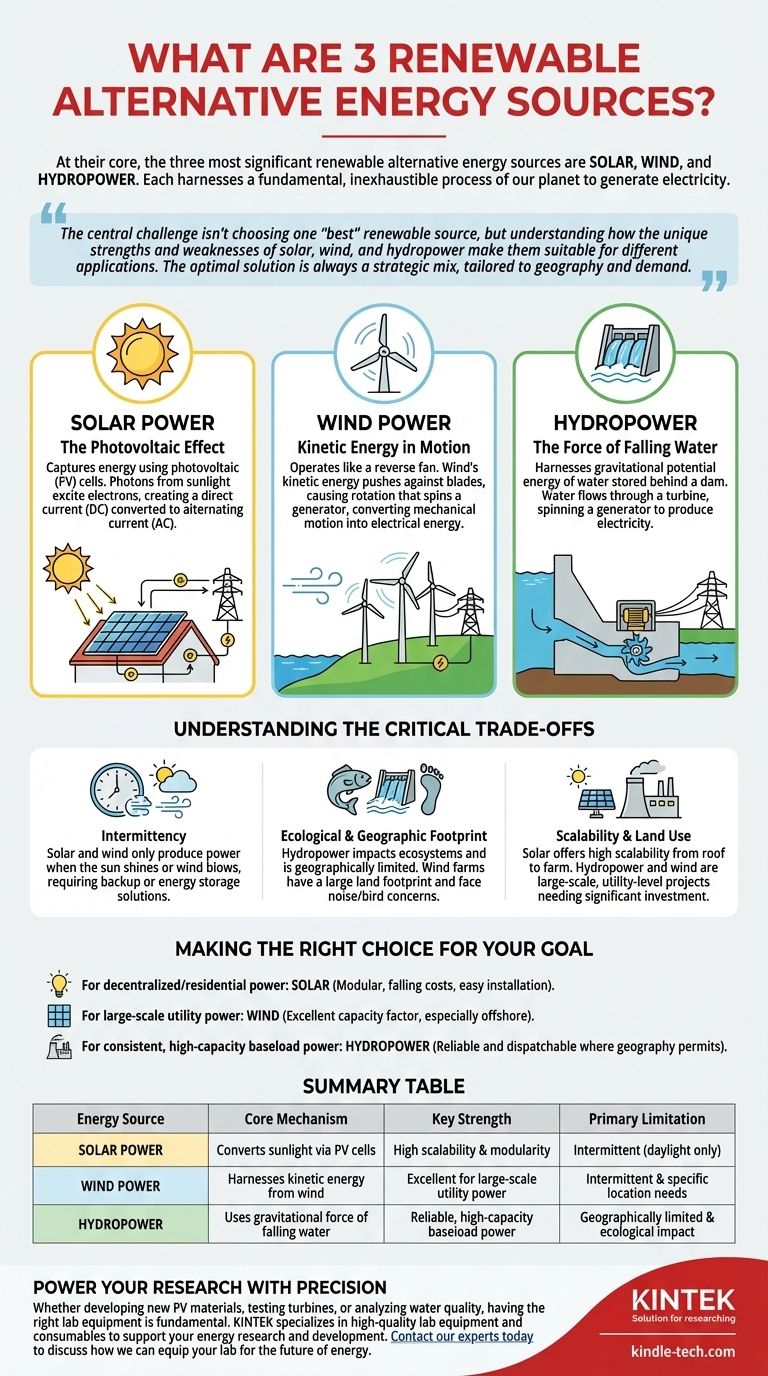
At their core, the three most significant renewable alternative energy sources are solar, wind, and hydropower. Each harnesses a fundamental, inexhaustible process of our planet—the sun's radiation, the movement of air, and the flow of water—to generate electricity without consuming finite fossil fuels. These technologies form the foundation of the global transition to sustainable energy.
The central challenge isn't choosing one "best" renewable source, but understanding how the unique strengths and weaknesses of solar, wind, and hydropower make them suitable for different applications. The optimal solution is always a strategic mix, tailored to geography and demand.

How Each Source Generates Power
To understand their applications, you must first understand their fundamental mechanisms. Each converts a different form of natural energy into electrical energy.
Solar Power: The Photovoltaic Effect
Solar panels capture energy using the photovoltaic (PV) effect. PV cells, typically made from silicon, absorb photons from sunlight.
This absorption of energy excites electrons, allowing them to break free from their atoms. This flow of electrons creates a direct current (DC), which is then converted into the alternating current (AC) used by our power grid.
Wind Power: Kinetic Energy in Motion
Wind turbines operate like a reverse fan. Instead of using electricity to make wind, they use wind to make electricity.
The wind's kinetic energy pushes against the turbine's blades, causing them to rotate. This rotation spins a central shaft connected to a generator, which converts the mechanical motion into electrical energy.
Hydropower: The Force of Falling Water
Hydropower, or hydroelectric energy, harnesses the gravitational potential energy of water stored behind a dam.
When water is released, it flows downward through a channel called a penstock, spinning the blades of a massive turbine. Just like in a wind turbine, this turbine is connected to a generator that produces electricity.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
No energy source is without its limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging the distinct challenges associated with each of the leading renewables.
The Challenge of Intermittency
The most significant drawback for solar and wind is intermittency. They only produce power when the sun is shining or the wind is blowing.
This variability creates challenges for grid stability, requiring backup power sources or large-scale energy storage solutions like batteries to ensure a consistent supply.
The Ecological and Geographic Footprint
Hydropower, while highly reliable, has a major ecological impact. Damming rivers alters ecosystems, disrupts fish migration, and can displace communities. Its potential is also geographically limited to regions with suitable river systems.
Wind farms also have a large land footprint, although the land between turbines can often be used for other purposes like agriculture. They also face concerns about noise and their impact on bird populations.
Scalability and Land Use
Solar offers incredible scalability, from a single panel on a roof to massive desert solar farms. This makes it ideal for decentralized, distributed power generation.
Hydropower and wind are inherently large-scale, utility-level projects. They require significant upfront investment and specific geographic conditions to be viable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best choice is dictated entirely by your objective. There is no single winner, only the right tool for the right job.
- If your primary focus is decentralized or residential power: Solar is the undisputed leader due to its modularity, falling costs, and ease of installation on existing structures.
- If your primary focus is large-scale utility power in open regions: Wind energy offers an excellent capacity factor and efficiency, especially in offshore or vast plains environments.
- If your primary focus is consistent, high-capacity baseload power: Hydropower remains a dominant force where geography permits, providing a reliable and dispatchable source of energy.
Ultimately, building a resilient and sustainable energy future depends on intelligently combining these technologies to balance their strengths and mitigate their weaknesses.
Summary Table:
| Energy Source | Core Mechanism | Key Strength | Primary Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Power | Converts sunlight via photovoltaic cells | High scalability & modularity | Intermittent (daylight only) |
| Wind Power | Harnesses kinetic energy from wind | Excellent for large-scale utility power | Intermittent & specific location needs |
| Hydropower | Uses gravitational force of falling water | Reliable, high-capacity baseload power | Geographically limited & ecological impact |
Power Your Research with Precision
Whether you're developing new photovoltaic materials, testing turbine blade composites, or analyzing water quality for hydropower projects, having the right lab equipment is fundamental to advancing renewable energy.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your energy research and development. We help you achieve accurate, reliable results that drive innovation.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can equip your lab for the future of energy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Wall Mounted Water Distillation Unit
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the principles of a rotary kiln? Master the Mechanics of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy




