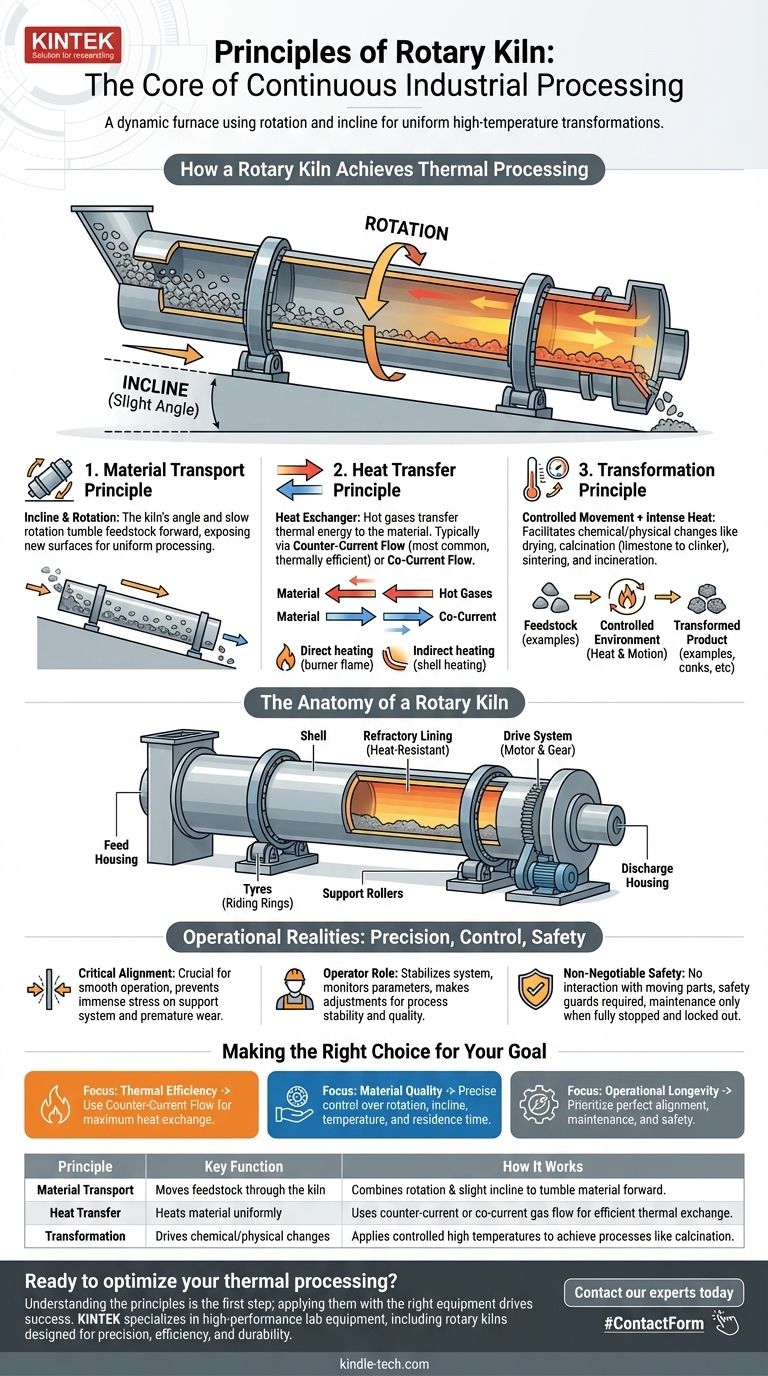
At its core, a rotary kiln is a continuously processing industrial furnace that uses a combination of slow rotation and a slight horizontal incline to move solid materials through a high-temperature environment. This controlled movement ensures the material tumbles and mixes, allowing for uniform heat transfer from hot gases to induce a required chemical reaction or physical change.
The fundamental principle of a rotary kiln is its ability to create a dynamic, controlled environment where mechanical motion and thermal energy work in concert. It continuously tumbles bulk solids down an incline through a heated zone to efficiently drive high-temperature transformations.
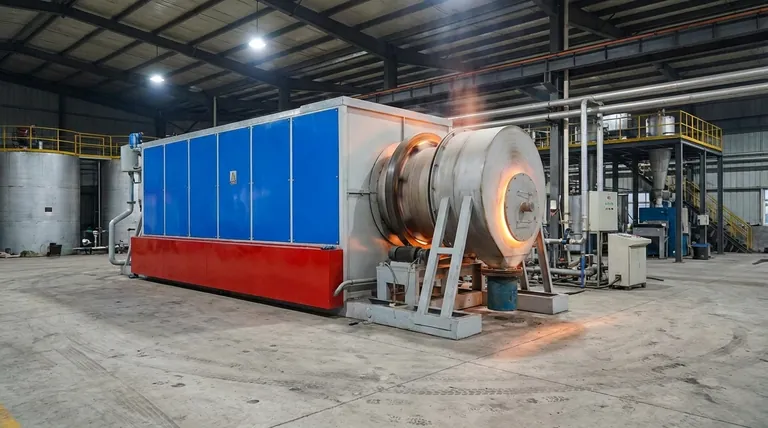

How a Rotary Kiln Achieves Thermal Processing
A rotary kiln's design is deceptively simple, but its effectiveness comes from the interplay of a few key mechanical and thermal principles.
The Principle of Material Transport
The entire system is built around moving feedstock from the entry point to the exit point. This is achieved through two main factors: inclination and rotation.
The kiln itself is a long, cylindrical shell positioned at a slight angle to the ground. As it rotates slowly on its axis, the feedstock fed into the higher end gently tumbles and slides forward, gradually making its way toward the lower, discharge end.
This tumbling action is critical. It constantly exposes new surfaces of the material to the hot gases inside, ensuring thorough and uniform processing.
The Principle of Heat Transfer
The kiln functions as a massive heat exchanger. Hot gases are passed through the cylinder to transfer thermal energy to the material.
This is typically done in one of two ways:
- Counter-Current Flow: Hot gases are introduced at the discharge end and travel up toward the feed end, moving in the opposite direction of the material. This is the most common and thermally efficient method.
- Co-Current Flow: Hot gases enter at the same end as the feedstock and move in the same direction.
The heat itself can be generated by a flame projected from a burner inside the kiln (direct heating) or by heating the kiln shell from the outside (indirect heating).
The Principle of Transformation
The combination of controlled movement and intense heat is what facilitates the desired change in the material.
Rotary kilns are versatile tools used for a wide range of thermal processes, including drying, calcination (like creating cement clinker from limestone), sintering, induration, and incineration.
The Anatomy of a Rotary Kiln
The operational principles are brought to life by a few essential components working together.
The Shell and Refractory Lining
The shell is the main cylindrical steel body of the kiln.
Inside the shell is a refractory lining, a brick-like layer of heat-resistant material that protects the steel shell from the extreme internal temperatures and any chemical reactions.
The Support and Drive System
The massive weight of the kiln is supported by steel tyres (also called riding rings) that encircle the shell.
These tyres rest on support rollers, which allow the entire assembly to rotate smoothly.
A large drive gear is attached to the shell, which is turned by a motor to provide the slow, consistent rotation required for processing.
Feed and Discharge Housings
At either end of the rotating cylinder are stationary housings. The process feedstock is introduced through the upper feed housing, and the finished product exits through the lower discharge housing.
Understanding the Operational Realities
While the principles are straightforward, successful operation depends on precision, control, and an unwavering focus on safety.
Why Alignment is Critical
The construction, position, and alignment of the kiln are paramount for smooth operation. Even a slight misalignment can cause immense stress on the support rollers, tyres, and drive system, leading to premature wear and potential failure.
The Role of the Operator
A skilled operator is essential for stabilizing the kiln's thermodynamic system. They must constantly monitor parameters from a central control room, pay close attention to field conditions, and make appropriate adjustments to maintain process stability and product quality.
Non-Negotiable Safety Protocols
Operating a high-temperature rotary kiln involves inherent risks. It is strictly forbidden to perform any inspection or repair on moving parts. Safety guards must always be in place, and any maintenance requires the kiln to be fully stopped with a "no start" sign on the motor switch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of these principles varies depending on the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is thermal efficiency: You will likely use a counter-current gas flow to maximize the heat exchange between the hot gases and the cooler incoming material.
- If your primary focus is material quality: You must maintain precise control over the rotation speed, kiln incline, and temperature profile to ensure the material has the correct residence time to complete its transformation.
- If your primary focus is operational longevity: You must prioritize perfect alignment, consistent maintenance of the drive and support systems, and strict adherence to safety and operational procedures.
By understanding these core principles, the rotary kiln is revealed as a highly engineered and controllable industrial tool.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Key Function | How It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Material Transport | Moves feedstock through the kiln | Combines rotation and a slight incline to tumble material forward |
| Heat Transfer | Heats material uniformly | Uses counter-current or co-current gas flow for efficient thermal exchange |
| Transformation | Drives chemical/physical changes | Applies controlled high temperatures to achieve processes like calcination |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing?
Understanding the principles is the first step; applying them with the right equipment is what drives success. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including rotary kilns designed for precision, efficiency, and durability.
Whether your goal is superior material quality, maximum thermal efficiency, or long-term operational reliability, our solutions are engineered to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your high-temperature processing challenges and help you achieve your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What temperature is a carbon regeneration kiln? Master the 650°C-800°C Range for Optimal Results
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















