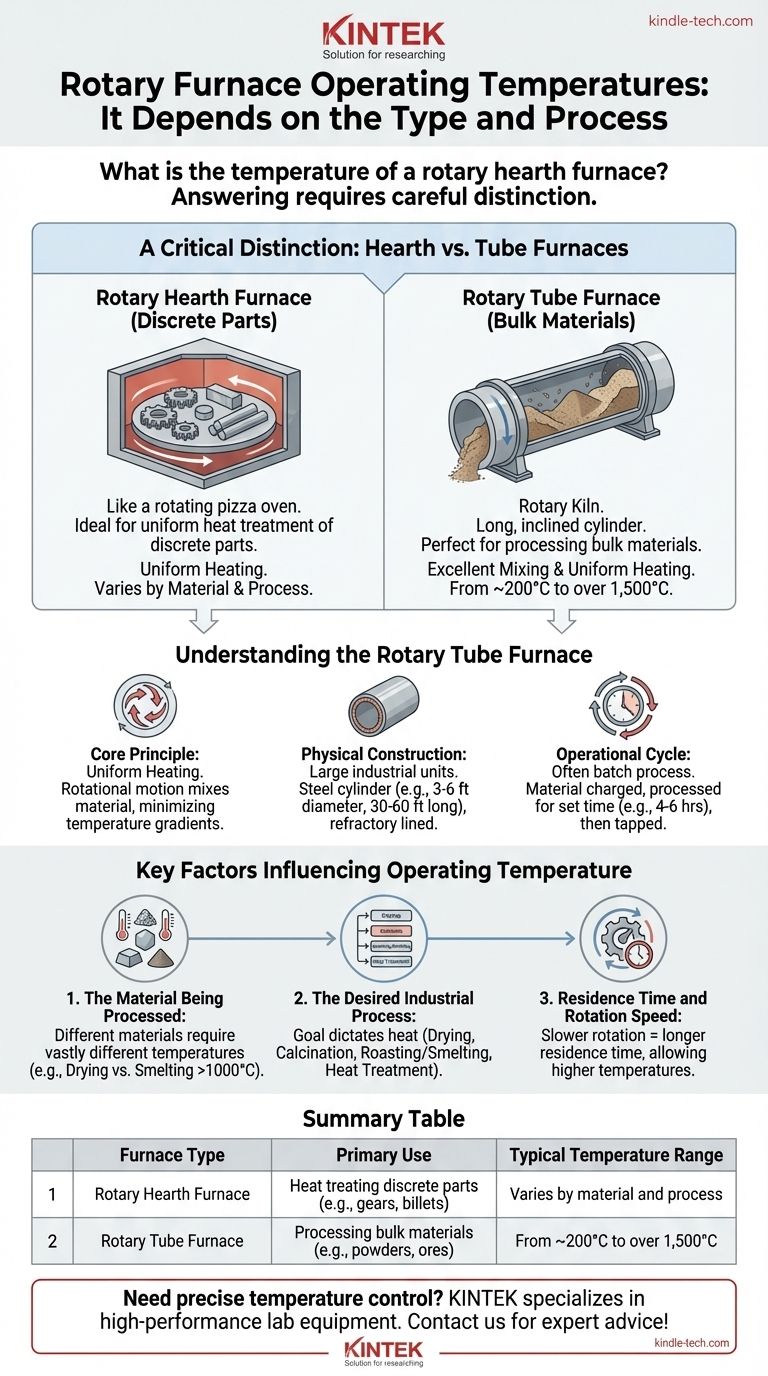
Answering this question requires careful distinction, as the operating temperature of a rotary furnace is entirely dependent on its specific type and industrial application. While a single temperature cannot be given, the design of these furnaces allows for precise control across a wide range, from relatively low drying temperatures to extreme smelting heat.
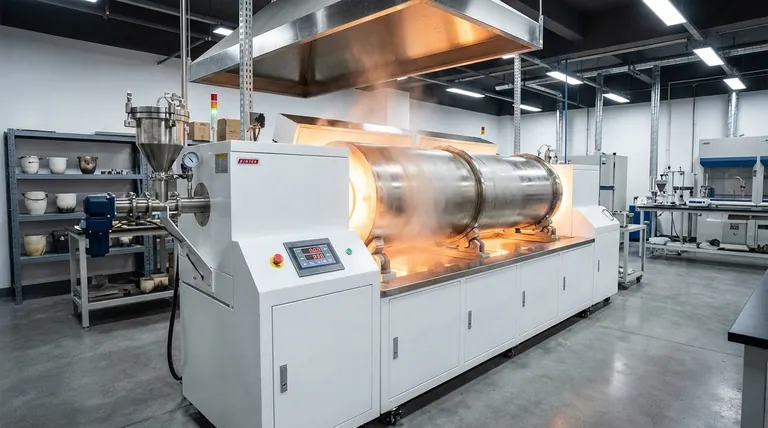
The term "rotary furnace" is often used ambiguously. Your first step must be to distinguish between a rotary hearth furnace (for discrete parts) and a rotary tube furnace (for bulk materials), as their designs and operating temperatures are fundamentally different.

A Critical Distinction: Hearth vs. Tube Furnaces
The most common point of confusion is the difference between two distinct furnace designs that both use rotation. Your process requirements will dictate which one is appropriate.
What is a Rotary Hearth Furnace?
A rotary hearth furnace functions like a large, heated carousel or a rotating pizza oven. A circular platform, or "hearth," rotates slowly inside a stationary, heated chamber.
Parts are loaded onto the hearth at one point, travel through the heating zones, and are unloaded at another. This design is ideal for the uniform heat treatment of discrete, individual parts like engine components or metal billets.
What is a Rotary Tube Furnace?
A rotary tube furnace, often called a rotary kiln, is a long, cylindrical barrel that is slightly inclined and rotates on its axis. This is the type described in the reference materials.
Material is fed into the higher end and tumbles its way to the lower end as the furnace rotates. This constant mixing is perfect for processing bulk materials like powders, granules, or aggregates, ensuring every particle is heated uniformly.
Understanding the Rotary Tube Furnace
Based on the provided information, we can detail the characteristics of the rotary tube furnace specifically.
Core Operating Principle
The defining feature is its ability to achieve uniform heating. The rotational motion thoroughly mixes the material, which minimizes temperature gradients and leads to a more consistent and efficient heat treatment process.
Physical Construction
These are typically large industrial units. A common construction involves a steel cylinder, often 3 to 6 feet in diameter and 30 to 60 feet long, lined with refractory material to withstand high temperatures.
Operational Cycle
Many rotary tube furnaces operate in batches. A load of material is charged into the furnace, processed for a set time (e.g., 4-6 hours for some smelting applications), and then tapped to remove the finished product and byproducts.
Key Factors Influencing Operating Temperature
No single temperature defines a rotary furnace because the target temperature is a function of the process, not the equipment itself.
The Material Being Processed
Different materials require vastly different temperatures. Drying organic matter may only require a few hundred degrees, while calcining limestone for cement production or smelting metal ores requires temperatures well over 1,000°C (1,832°F).
The Desired Industrial Process
The goal dictates the heat. Processes include:
- Drying: Removing moisture at low temperatures.
- Calcination: Decomposing materials through heat, like in cement manufacturing.
- Roasting/Smelting: Chemical reactions to extract metals from ores at very high temperatures.
- Heat Treatment: Altering the physical properties of a material.
Residence Time and Rotation Speed
The speed of rotation controls how long the material stays inside the furnace. A slower rotation increases residence time, allowing the material to reach a higher temperature with the same energy input. This is a critical parameter for process control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the correct furnace and temperature, you must first clarify your specific industrial objective.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating individual parts like forgings or gears: You should investigate a rotary hearth furnace, as its stationary platform prevents damage to the components.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk materials like powders, ores, or granules: A rotary tube furnace is the correct tool due to its excellent mixing and uniform heating capabilities.
- If your primary focus is determining a specific temperature: You must first define the exact material and process (e.g., iron ore reduction, hazardous waste incineration), which will then dictate the required thermal profile.
Ultimately, defining your material and process is the critical first step to determining the correct furnace technology and its operating parameters.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use | Typical Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Rotary Hearth Furnace | Heat treating discrete parts (e.g., gears, billets) | Varies by material and process |
| Rotary Tube Furnace | Processing bulk materials (e.g., powders, ores) | From ~200°C to over 1,500°C |
Need precise temperature control for your lab or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces tailored for materials research, heat treatment, and chemical processing. Our experts will help you select the right furnace to achieve uniform heating and optimal results for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover the KINTEK advantage in laboratory solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of calcination process? Achieve Precise Material Transformation for Your Industrial Needs
- What is calcination a burning process? Discover the Key Differences in Thermal Processing
- What is the mechanism of pyrolysis of biomass materials? A Guide to Converting Biomass into Bio-Oil, Char, and Gas
- What are the types of feedstock for biochar? Choose the Right Material for Your Needs
- How does biomass break down during pyrolysis? A Guide to Controlled Thermal Decomposition
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is the role of a Rotary Furnace in recycling nickel-based superalloys? Unlocking Critical Metal Recovery
- How does a tilting furnace work? A Guide to Hydraulic & Mechanical Pouring Systems



















