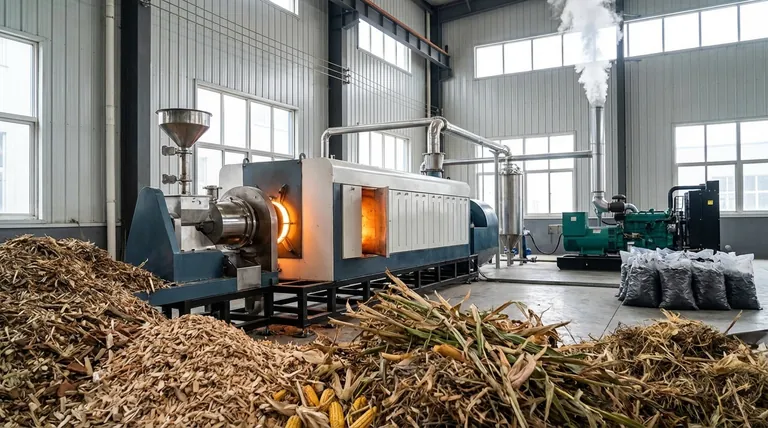
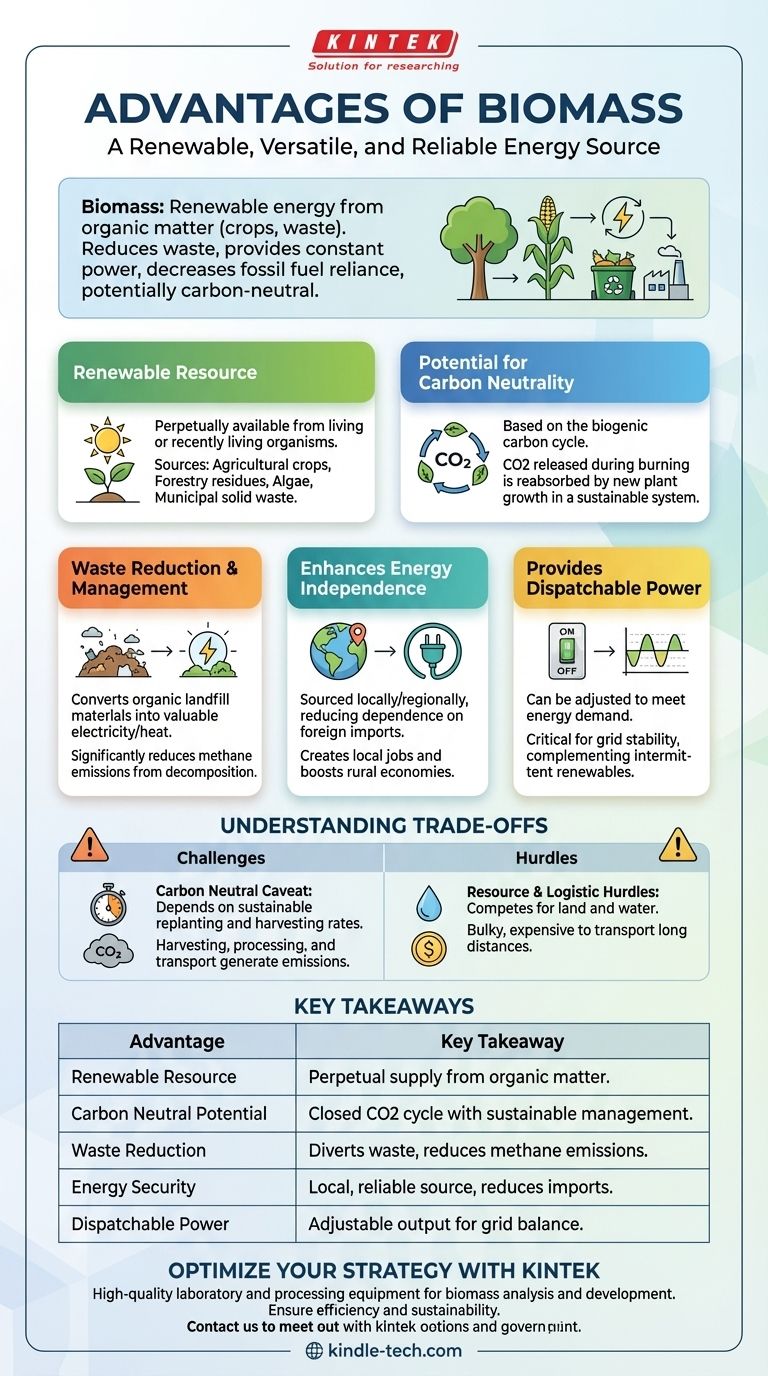
At its core, biomass is a renewable energy source derived from organic matter. Its main advantages are its ability to reduce waste, provide a constant and reliable power source, and decrease reliance on fossil fuels, all while operating within a potentially carbon-neutral cycle.
While often discussed as a "green" alternative, the true advantage of biomass lies in its versatility. It can be a tool for waste management, a source of reliable grid power, and a driver for local economies, but its environmental benefit is entirely dependent on sustainable sourcing and responsible management.

The Core Advantages of Biomass Energy
Understanding the specific benefits of biomass energy requires looking at its role within the broader energy and waste ecosystems. Each advantage comes with its own context.
It's a Renewable Resource
Unlike finite resources like coal, oil, and natural gas, biomass is perpetually available. It is derived from living or recently living organisms.
Sources include agricultural crops (like corn or switchgrass), forestry residues (wood chips, sawdust), algae, and even municipal solid waste (MSW). As long as these organic materials can be regrown or collected, the fuel source is sustainable.
Potential for Carbon Neutrality
The concept of biomass being carbon neutral is based on the biogenic carbon cycle. When plants grow, they absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere.
When that biomass is burned for energy, it releases the same amount of CO2 back into the atmosphere. In a perfectly balanced, sustainable system, new plant growth reabsorbs this CO2, creating a closed loop.
Waste Reduction and Management
This is one of the most powerful and often overlooked advantages. Biomass energy facilities can convert materials that would otherwise end up in landfills into valuable electricity or heat.
Using agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and the organic portion of municipal waste reduces landfill volume. This also significantly cuts down on the release of methane, a greenhouse gas far more potent than CO2, which is produced as organic matter decomposes in landfills.
Enhancing Energy Independence and Security
Biomass resources are typically sourced locally or regionally. This reduces a nation's or community's dependence on foreign energy imports, which are often subject to price volatility and geopolitical instability.
Developing local biomass supply chains also creates jobs in agriculture, forestry, transportation, and power plant operation, boosting rural economies.
It Provides Dispatchable Power
Unlike intermittent renewables like solar and wind, which only generate power when the sun is shining or the wind is blowing, biomass power plants are dispatchable.
This means they can be turned on and off or have their output adjusted to meet energy demand. This reliability is critical for maintaining a stable and resilient electricity grid, especially as more intermittent sources are added.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
To make an informed decision, you must weigh the advantages against the significant challenges and potential downsides. The "green" label on biomass is not absolute.
The "Carbon Neutral" Caveat
The claim of carbon neutrality is highly conditional. If forests are clear-cut for biomass fuel and not replanted, or if the regrowth rate is slower than the harvest rate, the process becomes a net source of carbon emissions. This creates a "carbon debt" that can take decades to repay.
Furthermore, the energy used to harvest, process, and transport the bulky biomass material generates its own fossil fuel emissions, which must be factored into its total lifecycle carbon footprint.
Land and Water Use Concerns
Dedicating large tracts of land to growing "energy crops" for biomass can create competition with land needed for food production, potentially impacting food prices and availability.
Additionally, some biomass crops can be very water-intensive, which poses a significant challenge in water-scarce regions.
Air Quality and Emissions
While cleaner than coal, burning biomass still releases air pollutants, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and particulate matter. Modern biomass plants require advanced emissions control technologies to mitigate these impacts on local air quality.
Economic and Logistical Hurdles
Biomass fuel is bulky, has a low energy density, and can have high moisture content. This makes it expensive to transport over long distances. As a result, biomass facilities are often only economically viable when located very close to a consistent and abundant fuel source.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Biomass is not a universal solution, but a specific tool. Its value depends entirely on the problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is reducing landfill waste and associated methane: Utilizing municipal solid waste and agricultural residues for a waste-to-energy biomass plant is an extremely effective strategy.
- If your primary focus is grid stability and reliability: Dispatchable biomass power is a valuable complement to intermittent renewables like solar and wind, helping to balance supply and demand.
- If your primary focus is decarbonization: Relying on biomass is only effective if you can guarantee a sustainable, local fuel supply chain where regrowth rates match or exceed harvest rates.
- If your primary focus is economic development in rural areas: A biomass facility using local forestry or agricultural waste can create jobs and provide a stable market for byproducts that would otherwise be considered waste.
Ultimately, the advantage of biomass is unlocked when it is applied thoughtfully to solve a specific, localized problem rather than being treated as a one-size-fits-all green energy source.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Renewable Resource | Derived from organic matter like crops and waste, ensuring a perpetual supply. |
| Carbon Neutral Potential | Operates in a closed CO2 cycle when sourced and managed sustainably. |
| Waste Reduction | Diverts organic waste from landfills, reducing methane emissions. |
| Energy Security | Provides a local, reliable energy source, reducing dependence on imports. |
| Dispatchable Power | Can be adjusted to meet demand, unlike intermittent solar or wind power. |
Optimize Your Energy and Waste Management Strategy with KINTEK
Biomass energy offers a powerful, sustainable solution for reliable power generation and effective waste reduction. Whether you're a facility manager looking to handle organic waste, a utility planner aiming to stabilize the grid, or a community leader focused on local economic development, the right equipment is key to success.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory and processing equipment for analyzing and developing biomass feedstocks. Our solutions help you accurately assess fuel properties, optimize conversion processes, and ensure the efficiency and sustainability of your biomass operations.
Ready to harness the advantages of biomass for your specific needs? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's equipment can support your renewable energy goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success






