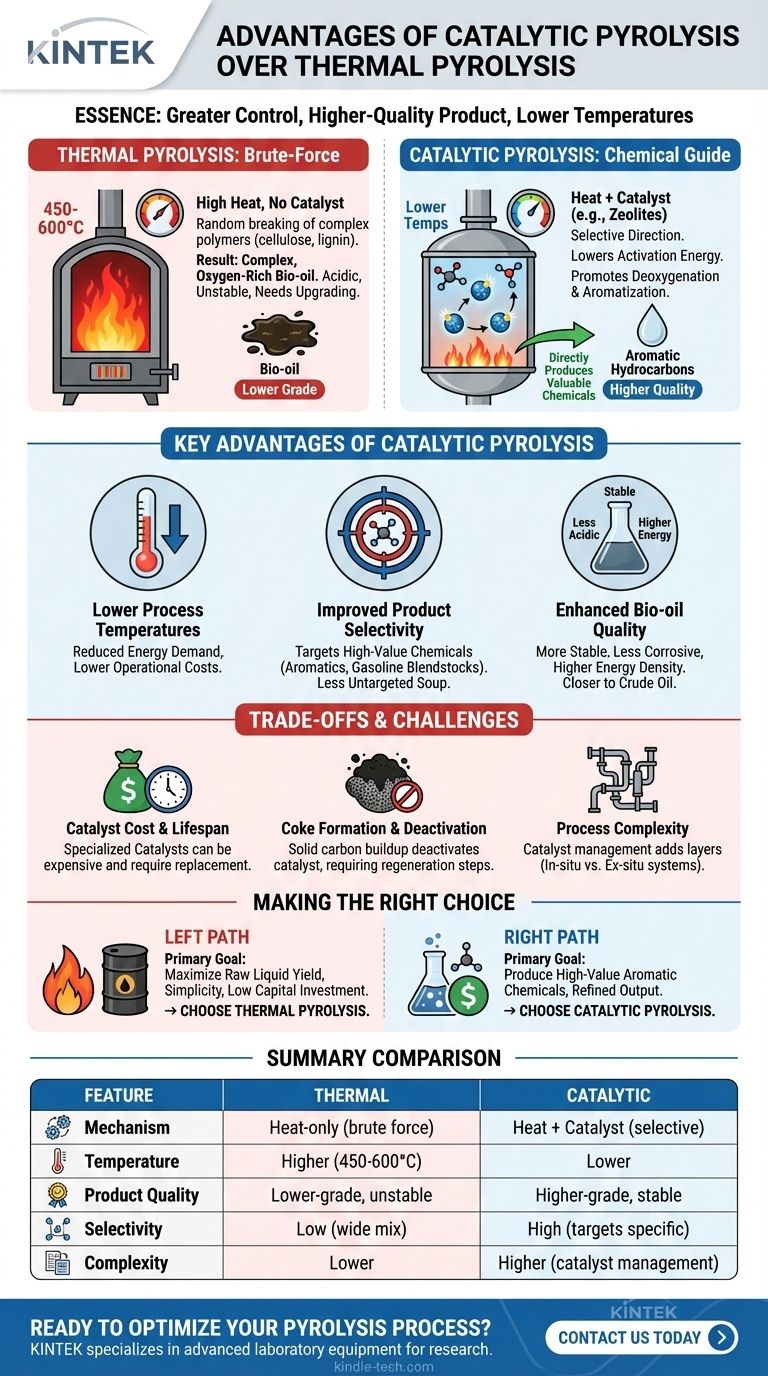
In essence, the primary advantage of catalytic pyrolysis is its ability to exert greater control over the chemical reaction, resulting in a higher-quality and more refined final product. Unlike thermal pyrolysis, which relies on heat alone, the addition of a catalyst selectively steers the process toward desired outcomes, such as producing valuable aromatic hydrocarbons directly, while operating at lower temperatures.
Choosing between thermal and catalytic pyrolysis is a strategic decision based on your end goal. Catalytic pyrolysis prioritizes product quality and specificity, while thermal pyrolysis often prioritizes simplicity and maximum liquid yield, albeit of a lower grade.

The Fundamental Difference: The Role of the Catalyst
To understand the advantages, it's crucial to first distinguish the two processes at a chemical level. They both use high heat in the absence of oxygen, but the mechanism is entirely different.
What is Thermal Pyrolysis?
Thermal pyrolysis is a brute-force method. Biomass is subjected to intense heat (typically 450-600°C), causing its complex polymers—like cellulose and lignin—to violently and randomly break apart.
The result is a complex, oxygen-rich mixture known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil. This oil is acidic, unstable, and requires significant and costly upgrading before it can be used as a transportation fuel.
How Catalytic Pyrolysis Changes the Game
Catalytic pyrolysis introduces a "chemical guide" into the reaction. The catalyst provides a surface with active sites that lower the activation energy needed for specific chemical reactions to occur.
Instead of random cracking, the process is directed. The catalyst selectively promotes reactions like deoxygenation (removing oxygen) and aromatization (forming stable ring structures), fundamentally changing the output from the very beginning.
Key Advantages of Catalytic Pyrolysis
The introduction of a catalyst creates several distinct operational and product-related benefits.
Lower Process Temperatures
Because catalysts lower the energy barrier for reactions, catalytic pyrolysis can often be run at lower temperatures than its thermal counterpart. This reduces the overall energy demand of the system, potentially lowering operational costs.
Improved Product Selectivity
This is the most significant advantage. Catalysts can be chosen to specifically target the production of high-value chemicals. For example, using zeolite catalysts can directly convert biomass into aromatic hydrocarbons (like benzene, toluene, and xylene), which are precursors for plastics and gasoline blendstocks.
Thermal pyrolysis, by contrast, produces a wide, untargeted soup of hundreds of different oxygenated compounds.
Enhanced Bio-oil Quality
Catalytic processes actively remove oxygen from the biomass vapors. This deoxygenation results in a bio-oil that is:
- More stable and less prone to aging.
- Less acidic and corrosive.
- Higher in energy density.
- Closer in composition to conventional crude oil, reducing the need for extensive hydrotreating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While advantageous, catalytic pyrolysis is not a universally superior solution. It introduces its own set of complexities and costs that must be considered.
Catalyst Cost and Lifespan
Catalysts, particularly specialized ones like zeolites, can be expensive. They also do not last forever and require eventual replacement, which adds to the long-term operational cost of the process.
Coke Formation and Deactivation
A major technical hurdle is the formation of coke (a solid carbon byproduct) on the catalyst surface. This coke blocks the active sites, rapidly deactivating the catalyst and halting its effectiveness.
This requires the process to include a regeneration step where the coke is burned off, adding complexity and cost to the reactor design and operation.
Process Complexity
Managing the catalyst adds layers of complexity. As the references note, this can be done in two main ways, each with its own trade-offs:
- In-situ: The catalyst is mixed directly with the biomass. This offers excellent heat and mass transfer but makes separating the spent catalyst from the char for regeneration difficult.
- Ex-situ: The pyrolysis vapors pass through a separate, secondary reactor containing the catalyst bed. This allows for easier catalyst regeneration but requires a more complex dual-reactor system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use thermal or catalytic pyrolysis depends entirely on your technical and economic objectives.
- If your primary focus is producing high-value aromatic chemicals or gasoline-range hydrocarbons: Catalytic pyrolysis is the superior and often necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing raw liquid yield for creating a bio-crude or for direct combustion: Thermal pyrolysis is often more robust, simpler, and more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational complexity and initial capital investment: Thermal pyrolysis is the clear winner due to its simpler reactor design and lack of catalyst management systems.
Ultimately, your choice is dictated by whether you prioritize the upfront simplicity of thermal processing or the refined, high-value output of a catalytically-controlled reaction.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Pyrolysis | Catalytic Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Heat-only (brute force) | Heat + Catalyst (selective) |
| Typical Temperature | Higher (450-600°C) | Lower |
| Product Quality | Lower-grade, unstable bio-oil | Higher-grade, stable bio-oil |
| Product Selectivity | Low (wide mix of compounds) | High (targets specific chemicals) |
| Process Complexity | Lower | Higher (catalyst management) |
| Best For | Maximizing raw liquid yield | Producing high-value chemicals |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Choosing the right pyrolysis method is critical for achieving your specific product and efficiency goals. KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Our experts can help you select the right tools to explore catalytic or thermal processes for your biomass conversion needs.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and drive your research forward. Let's turn your biomass into valuable products together!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs



















