At its core, a rotary kiln is an industrial furnace for processing bulk solids at extremely high temperatures. Its applications span a vast range of industries, from producing the cement in our buildings to recycling hazardous waste and refining the metals used in modern technology. The kiln achieves this by tumbling material through a heated, rotating cylinder, ensuring uniform exposure to heat that drives specific chemical reactions or physical changes.
The versatility of a rotary kiln stems not from a single function, but from its ability to combine multiple thermal processes—drying, heating, chemical transformation, and cooling—into one continuous, high-volume operation. This makes it the industrial workhorse for transforming bulk solids with heat.

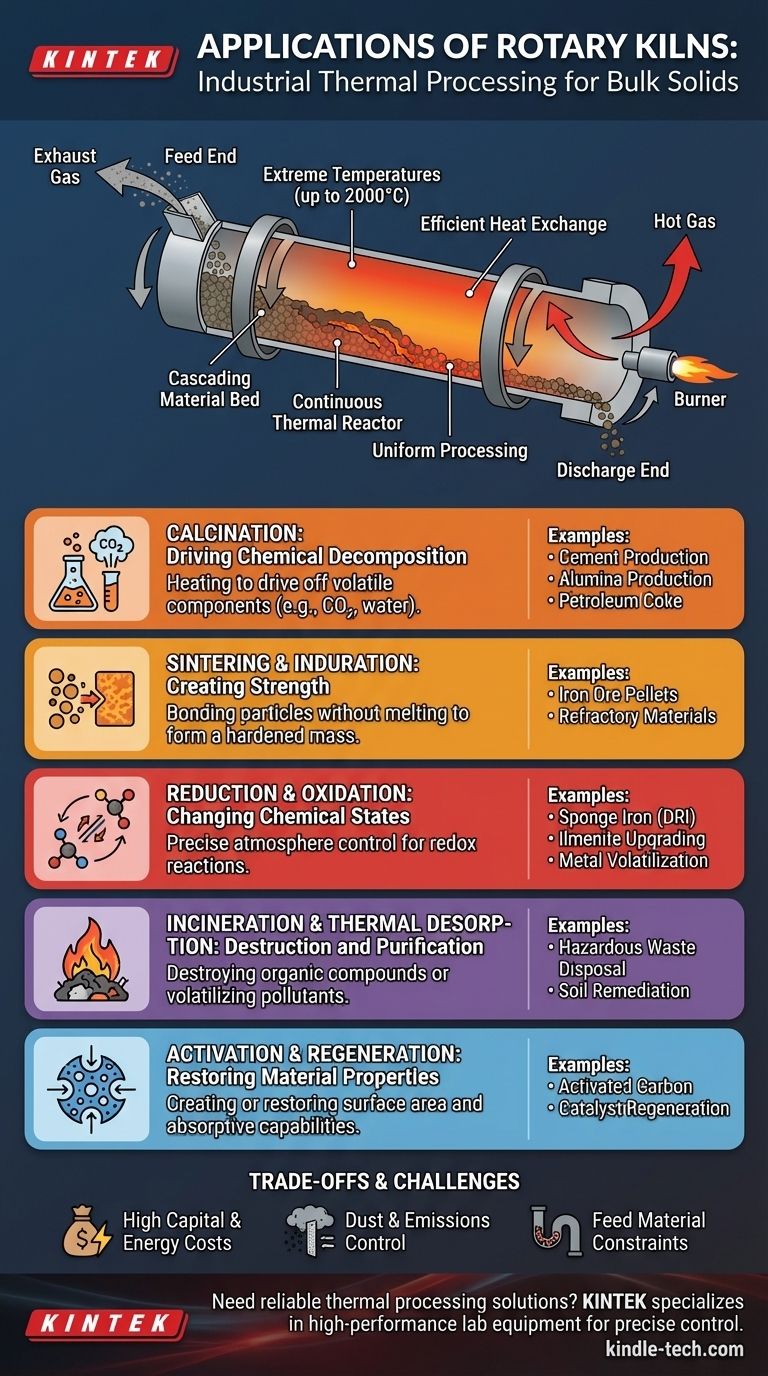
The Core Function: A Continuous Thermal Reactor
A rotary kiln is much more than a simple oven. It is a dynamic system designed for precise, continuous material processing.
Heat Exchange and Material Transport
The kiln is a long, cylindrical shell lined with refractory material, mounted at a slight incline. As the kiln rotates, the solid material inside is lifted and tumbles down, slowly progressing from the feed end to the discharge end.
Hot gas, produced by a burner, flows through the kiln, typically in the opposite direction of the solids (counter-current flow). This design creates an incredibly efficient heat exchanger, transferring energy from the gas to the material.
A High-Temperature Environment
Rotary kilns are engineered to create and sustain extreme temperatures, often reaching up to 1450°C (2640°F) and in some special cases, as high as 2000°C (3630°F). This capability is essential for initiating energy-intensive chemical reactions.
Uniform Processing
The constant tumbling action, known as "cascading," ensures that the material bed is well-mixed. This promotes a uniform temperature distribution throughout the solids, guaranteeing that every particle undergoes the same degree of thermal treatment.
Key Applications by Process Type
While the list of materials processed in kilns is long, the applications can be understood by grouping them into a few fundamental thermal processes.
Calcination: Driving Chemical Decomposition
Calcination is the process of heating a solid to a high temperature to drive off a volatile component, such as carbon dioxide or water. This is arguably the most common use for a rotary kiln.
Examples include:
- Cement Production: Heating limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce lime (calcium oxide).
- Alumina Production: Calcining bauxite to remove water.
- Petroleum Coke: Removing residual volatile hydrocarbons.
Sintering and Induration: Creating Strength
Sintering involves heating granular material until the edges of the particles begin to fuse, bonding them into a single, hardened mass without melting the entire substance.
Examples include:
- Iron Ore Pellets: Hardening pellets before they are fed into a blast furnace.
- Refractory Materials: Sintering magnesite and dolomite to create durable, heat-resistant bricks.
Reduction and Oxidation: Changing Chemical States
Kilns allow for precise control over the furnace atmosphere, making them ideal for redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions.
Examples include:
- Sponge Iron: Reducing iron ore using coal to produce direct-reduced iron (DRI).
- Ilmenite Upgrading: Oxidizing ilmenite ore as a step in producing titanium dioxide.
- Volatilization: Removing metals like zinc, lead, and copper by converting them to volatile chlorides.
Incineration and Thermal Desorption: Destruction and Purification
The extreme temperatures inside a kiln are perfect for destroying organic compounds or volatilizing them for removal.
Examples include:
- Waste Disposal: Incinerating hazardous industrial waste, sewage sludge, or scrap tires.
- Soil Remediation: Heating contaminated soil to drive off and capture pollutants (thermal desorption).
Activation and Regeneration: Restoring Material Properties
Heat can be used to create or restore the porous structure of certain materials, enhancing their surface area and absorptive capabilities.
Examples include:
- Activated Carbon: Producing or reactivating carbon used in filtration systems.
- Catalyst Regeneration: Burning off coke and contaminants to restore the activity of industrial catalysts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary kiln is not a universal solution. Its design comes with specific limitations and challenges.
High Capital and Energy Costs
Rotary kilns are massive, complex pieces of machinery that represent a significant capital investment. Furthermore, maintaining temperatures above 1400°C consumes vast amounts of fuel, making energy a primary operational cost.
Dust and Emissions Control
Processing granular solids with high-velocity gas flow inevitably creates significant dust. All rotary kiln systems require extensive backend gas handling and cleaning equipment, such as cyclones and baghouses, to capture this particulate matter and control air emissions.
Feed Material Constraints
The process is optimized for granular, free-flowing solids. Materials that are too fine can be swept out of the kiln with the exhaust gas (entrainment), while materials that are sticky or form large lumps can disrupt flow and heat transfer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a rotary kiln depends entirely on the specific transformation you need to achieve at scale.
- If your primary focus is commodity production (e.g., cement, lime): The kiln's continuous, high-throughput capability is its greatest advantage.
- If your primary focus is metals extraction or refining: The kiln's ability to control the furnace atmosphere and achieve high temperatures is critical for driving specific reduction or oxidation reactions.
- If your primary focus is waste treatment: The kiln's destructive heat and robust nature make it ideal for reliably breaking down hazardous materials.
- If your primary focus is producing specialty materials (e.g., pigments, activated carbon): The kiln's uniform mixing and precise temperature control ensure a consistent, high-quality final product.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is the definitive solution when you need to induce a precise physical or chemical transformation in bulk solids on an industrial scale.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Calcination | Cement production, Alumina production, Petroleum coke |
| Sintering/Induration | Iron ore pellets, Refractory materials |
| Reduction/Oxidation | Sponge iron (DRI), Ilmenite upgrading, Metal volatilization |
| Incineration/Thermal Desorption | Hazardous waste disposal, Soil remediation |
| Activation/Regeneration | Activated carbon, Catalyst regeneration |
Need a reliable thermal processing solution for your laboratory or industrial needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Whether you're developing new materials, processing ores, or treating waste streams, our expertise can help you achieve precise temperature control and uniform results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your thermal processing efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding



















