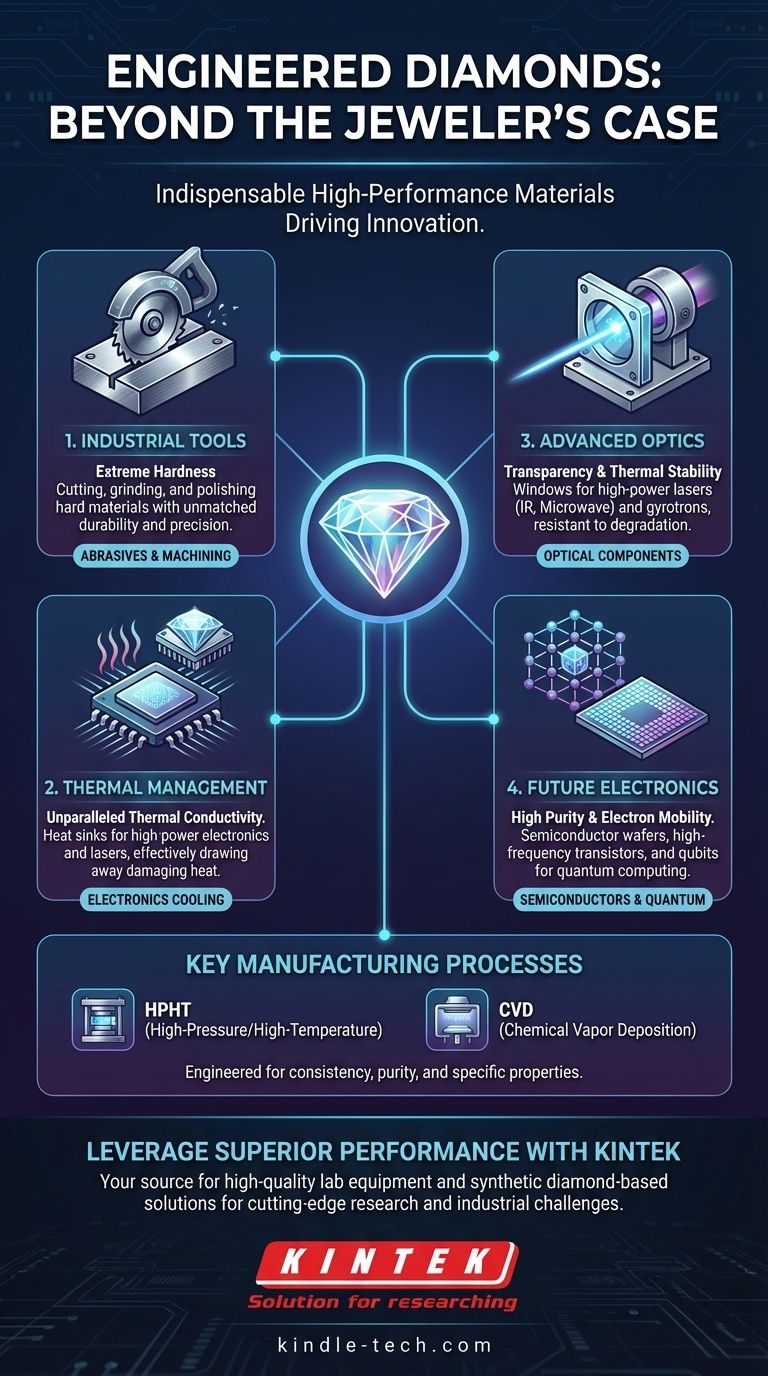
Beyond the jeweler's case, synthetic diamonds are indispensable engineered materials that drive innovation across a vast range of industries. Their primary applications include industrial machining and cutting tools, thermal management as heat sinks for advanced electronics, transparent windows for high-power lasers, and as a foundational material for next-generation semiconductors and quantum computers.
While often perceived as a gemstone alternative, the true significance of synthetic diamonds lies in their role as a high-performance material. By precisely controlling their creation, we produce diamonds with specific, superior properties—like exceptional thermal conductivity and purity—making them essential for technical applications where natural diamonds are often unsuitable or cost-prohibitive.

Why Synthetic Diamonds Are a Critical Technical Material
The utility of synthetic diamonds stems from our ability to engineer them for specific tasks, often creating a material that outperforms its natural equivalent.
Engineered for Superior Performance
Unlike most natural diamonds, which vary in quality, synthetic diamonds can be manufactured with consistently superior properties. These include extreme hardness, unparalleled thermal conductivity, and high electron mobility.
The creation process allows these properties to be tailored, optimizing the diamond for a specific function, whether it's for abrasion, heat dissipation, or electronic performance.
The Key Manufacturing Processes
Two methods dominate commercial production: High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
HPHT mimics the natural diamond-forming process by subjecting carbon to immense pressure and heat. CVD, in contrast, "grows" diamond layer by layer from a carbon-containing gas, allowing for the creation of large, high-purity diamond wafers.
Other niche methods exist, such as detonation synthesis for creating nanodiamonds, but HPHT and CVD are the industrial workhorses.
Purity and Predictability
Natural diamonds almost always contain impurities and structural flaws, such as inclusions of foreign minerals. These imperfections can hinder performance in sensitive applications.
Synthetic diamonds can be produced with near-perfect purity, providing the reliability and consistency required for high-tech uses in optics, electronics, and scientific research.
Key Application Domains Explained
The engineered properties of synthetic diamonds have made them the material of choice in several critical fields, with an estimated 98% of all industrial-grade diamond demand being met by synthetics.
Industrial Abrasives and Cutting Tools
This is the largest application by volume. The exceptional hardness of synthetic diamonds makes them ideal for tools used in cutting, grinding, and polishing extremely hard materials. They provide durability and precision that other materials cannot match.
Thermal Management in Electronics
Diamonds are the best known thermal conductor. This property is leveraged by using synthetic diamonds as heat sinks to draw damaging heat away from sensitive components like high-power lasers and advanced microprocessors.
Advanced Optical Components
Synthetic diamonds possess a unique combination of thermal stability, strength, and transparency to specific wavelengths like infrared and microwaves. This makes them the perfect material for protective optical windows in high-power CO2 lasers and gyrotrons, where other materials would quickly degrade or fail.
The Future of Electronics and Computing
The high purity and excellent electronic properties of CVD diamond are paving the way for new technologies. It is used as a substrate for semiconductor wafers, enabling the creation of high-power switches and high-frequency transistors.
Furthermore, specific defects intentionally created in the diamond's crystal lattice can function as qubits, the fundamental building blocks of quantum computers.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
While physically identical to natural diamonds, it's crucial to understand the context of their use and the variations between them.
Not a Monolith: Properties Depend on the Process
The final properties of a synthetic diamond—and thus its ideal application—are determined by its manufacturing method. For instance, large, ultra-pure sheets grown via CVD are ideal for optical and electronic applications, while HPHT is often used to produce grits for abrasives.
Gemstones vs. Industrial Material
While lab-grown diamonds are an increasingly popular and ethical choice in jewelry, this market is distinct from their industrial use. In technical fields, the choice is not about aesthetics but about leveraging a unique set of physical properties that often cannot be found in nature.
Identification and Terminology
Synthetic diamonds can be identified by gemological labs through specific characteristics, such as patterns of fluorescence or the absence of natural inclusions. The term "synthetic" can be misleading; "engineered" or "lab-grown" more accurately describes a material that is chemically and structurally a real diamond, simply created by human technology.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective determines which aspect of synthetic diamonds is most relevant to your work.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing or machining: Synthetic diamond abrasives and cutting tools offer unparalleled durability and precision for working with hard materials.
- If your primary focus is thermal engineering: The exceptional thermal conductivity of engineered diamonds makes them the superior choice for high-performance heat sinks in demanding electronic systems.
- If your primary focus is optics or high-energy physics: CVD diamond provides a unique combination of transparency, thermal stability, and durability for high-power optical windows and detectors.
- If your primary focus is next-generation computing: High-purity synthetic diamonds are the foundational material for emerging semiconductor and quantum applications.
Ultimately, synthetic diamonds represent a triumph of materials science, providing an engineered solution that is more consistent, cost-effective, and often superior to its natural counterpart for the world's most demanding technical challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application Domain | Key Property Utilized | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Tools | Extreme Hardness | Cutting, grinding, and polishing tools |
| Thermal Management | Unparalleled Thermal Conductivity | Heat sinks for high-power electronics and lasers |
| Optical Components | Transparency & Thermal Stability | Windows for high-power lasers and gyrotrons |
| Electronics & Computing | High Purity & Electron Mobility | Semiconductor wafers and quantum computing qubits |
Ready to leverage the superior performance of engineered diamonds in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including synthetic diamond-based tools and components for cutting-edge research and industrial applications. Whether you need durable abrasives for material processing, efficient heat sinks for thermal management, or specialized optics for your experiments, our solutions are engineered for precision and reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how synthetic diamonds can solve your most demanding technical challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance
- What is the historical background of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process? From Nuclear Roots to Industry Standard
- What is HIP in material processing? Achieve Near-Perfect Density for Critical Components
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance
- Is hot isostatic pressing a heat treatment? A Guide to Its Unique Thermomechanical Process



















