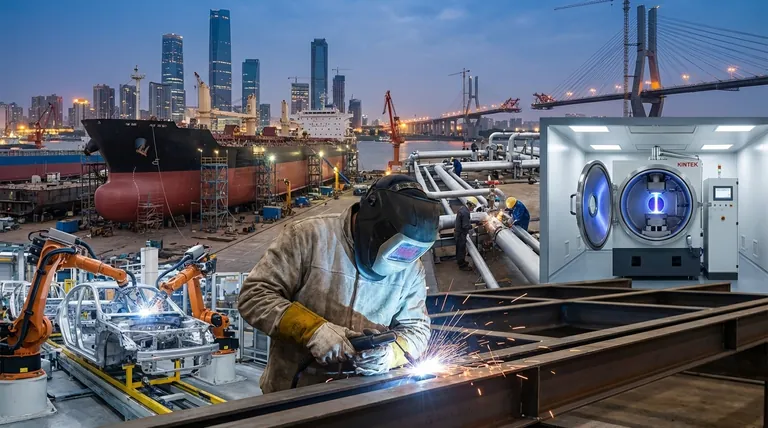
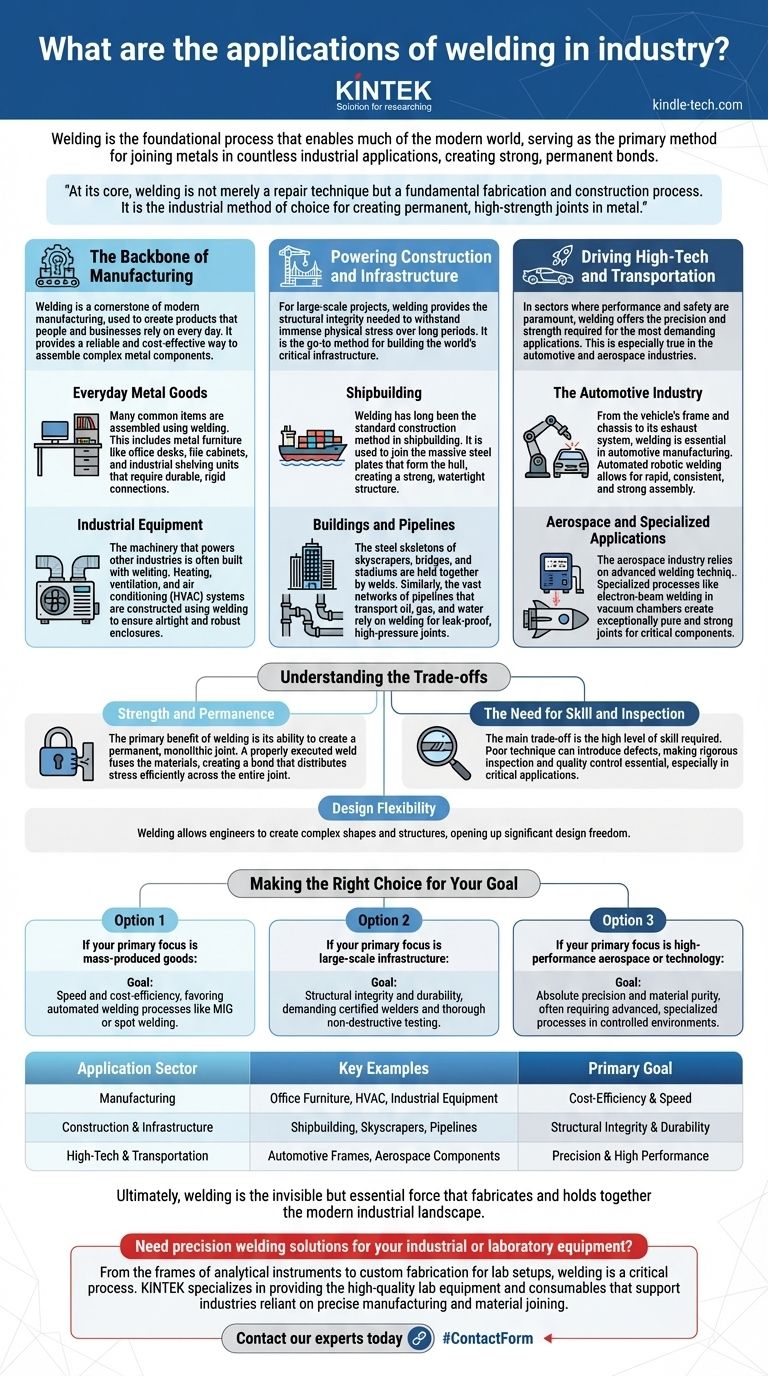
Welding is the foundational process that enables much of the modern world, serving as the primary method for joining metals in countless industrial applications. Its uses range from the mass production of everyday items like office furniture and HVAC units to the construction of massive structures like ships, pipelines, and buildings. Welding creates strong, permanent bonds that are often as strong or stronger than the base materials themselves.
At its core, welding is not merely a repair technique but a fundamental fabrication and construction process. It is the industrial method of choice for creating permanent, high-strength joints in metal, making it indispensable across nearly every sector of the economy.

The Backbone of Manufacturing
Welding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, used to create products that people and businesses rely on every day. It provides a reliable and cost-effective way to assemble complex metal components.
Everyday Metal Goods
Many common items are assembled using welding. This includes metal furniture like office desks, file cabinets, and industrial shelving units that require durable, rigid connections.
Industrial Equipment
The machinery that powers other industries is often built with welding. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, for instance, are constructed using welding to ensure airtight and robust enclosures.
Powering Construction and Infrastructure
For large-scale projects, welding provides the structural integrity needed to withstand immense physical stress over long periods. It is the go-to method for building the world's critical infrastructure.
Shipbuilding
Welding has long been the standard construction method in shipbuilding. It is used to join the massive steel plates that form the hull, creating a strong, watertight structure capable of navigating the seas.
Buildings and Pipelines
The steel skeletons of skyscrapers, bridges, and stadiums are held together by welds. Similarly, the vast networks of pipelines that transport oil, gas, and water rely on welding to create leak-proof, high-pressure joints.
Driving High-Tech and Transportation
In sectors where performance and safety are paramount, welding offers the precision and strength required for the most demanding applications. This is especially true in the automotive and aerospace industries.
The Automotive Industry
From the vehicle's frame and chassis to its exhaust system, welding is essential in automotive manufacturing. Automated robotic welding allows for the rapid, consistent, and strong assembly of car bodies.
Aerospace and Specialized Applications
The aerospace industry relies on advanced welding techniques for building aircraft and spacecraft. Specialized processes like electron-beam welding, which has been used since the 1950s, are performed in vacuum chambers to create exceptionally pure and strong joints for critical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, choosing to weld involves specific considerations. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Strength and Permanence
The primary benefit of welding is its ability to create a permanent, monolithic joint. A properly executed weld fuses the materials, creating a bond that distributes stress efficiently across the entire joint.
Design Flexibility
Welding allows engineers to create complex shapes and structures that would be difficult or impossible to cast or machine from a single piece of material. This opens up significant design freedom.
The Need for Skill and Inspection
The main trade-off is the high level of skill required to produce a quality weld. Poor technique can introduce defects and weaknesses, making rigorous inspection and quality control essential, especially in critical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific welding process and standards applied depend entirely on the final application and its performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is mass-produced goods: The goal is typically speed and cost-efficiency, favoring automated welding processes like MIG or spot welding.
- If your primary focus is large-scale infrastructure: The priority is structural integrity and durability, demanding certified welders and thorough non-destructive testing methods.
- If your primary focus is high-performance aerospace or technology: The emphasis is on absolute precision and material purity, often requiring advanced, specialized processes in controlled environments.
Ultimately, welding is the invisible but essential force that fabricates and holds together the modern industrial landscape.
Summary Table:
| Application Sector | Key Examples | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Office Furniture, HVAC, Industrial Equipment | Cost-Efficiency & Speed |
| Construction & Infrastructure | Shipbuilding, Skyscrapers, Pipelines | Structural Integrity & Durability |
| High-Tech & Transportation | Automotive Frames, Aerospace Components | Precision & High Performance |
Need precision welding solutions for your industrial or laboratory equipment?
From the frames of analytical instruments to custom fabrication for lab setups, welding is a critical process. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support industries reliant on precise manufacturing and material joining.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific needs for durability, performance, and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of coating deposition? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Engineering
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods


















