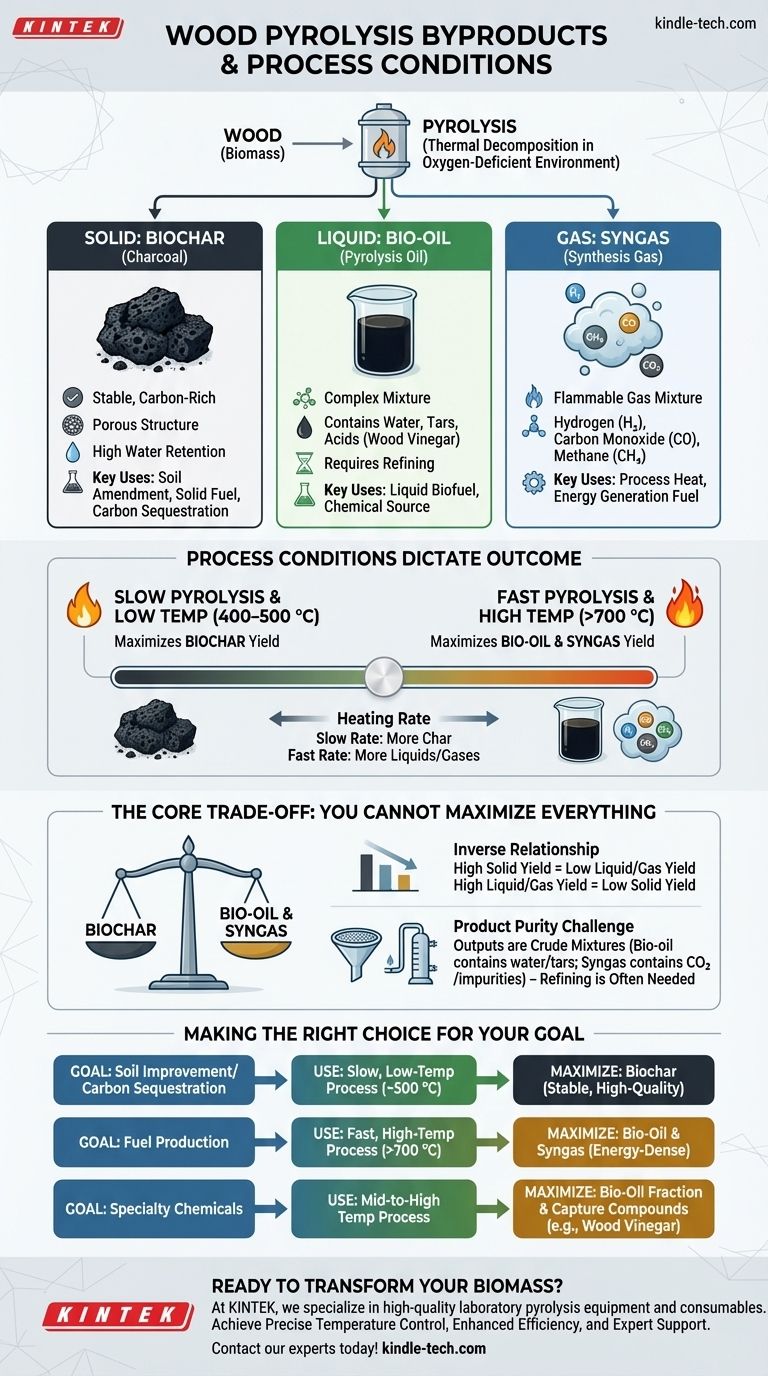
In short, the pyrolysis of wood yields three distinct types of byproducts. These are a solid residue known as biochar (or charcoal), a complex liquid called bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil), and a mixture of non-condensable gases referred to as syngas.
The fundamental principle to grasp is that you do not get these three products in fixed amounts. The specific conditions of the pyrolysis process, primarily temperature, directly control which of these byproducts you will produce in the highest quantity.

The Three States of Pyrolysis Products
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of material at high temperatures in an oxygen-deficient environment. Unlike combustion (burning), which produces ash, this process breaks down wood's complex structure into simpler, valuable components.
The Solid Product: Biochar
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after pyrolysis is complete. It is essentially a more refined form of charcoal.
This material is highly porous and resistant to decomposition. Its primary applications are as a high-quality soil amendment to improve water retention and soil health, or as a solid fuel.
The Liquid Product: Bio-Oil
As the wood heats, volatile compounds vaporize and are then cooled and condensed into a dark, dense liquid known as bio-oil.
This is not a single substance but a complex mixture. It contains water, tars, and acidic compounds like wood vinegar. While it can be refined into a liquid biofuel, its complexity and corrosive nature mean it often requires significant upgrading before use.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
Syngas, short for "synthesis gas," is the collection of gases that do not condense back into a liquid when cooled.
This gas mixture is flammable and primarily composed of hydrogen (H2), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH4), and carbon dioxide (CO2). It is often captured and used as a fuel source to provide the heat for the pyrolysis reactor itself, creating a self-sustaining system.
How Process Conditions Dictate the Outcome
You can steer the pyrolysis reaction to favor one type of product over the others. The outcome is not random; it is a direct result of the process parameters you set.
The Critical Role of Temperature
Temperature is the single most important factor determining the final product yields.
Slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures, typically 400–500 °C, maximizes the production of biochar. The slower process allows more carbon to remain in a fixed, solid structure.
Fast pyrolysis at higher temperatures, often above 700 °C, favors the production of bio-oil and syngas. The intense, rapid heat "cracks" the wood's structure into smaller volatile molecules that become liquids and gases.
The Influence of Heating Rate
The speed at which the wood is heated also plays a crucial role. A slow heating rate gives the wood time to gradually carbonize, maximizing char.
Conversely, a very fast heating rate vaporizes the organic material quickly, pushing the yields toward liquids and gases before they can form into a stable char structure.
Understanding the Core Trade-off
Pyrolysis is not a magic bullet that produces maximum yields of everything simultaneously. Acknowledging the inherent trade-offs is critical for any practical application.
You Cannot Maximize Everything
There is an inverse relationship between product yields. A process optimized for high biochar output will inherently produce less bio-oil and syngas.
Conversely, maximizing liquid fuel production will leave you with a minimal amount of solid biochar. Your primary goal must dictate your process conditions.
The Challenge of Product Purity
The raw outputs of pyrolysis are often crude mixtures. Bio-oil contains significant amounts of water, acids, and tars that must be separated or refined for use as a high-grade fuel.
Similarly, syngas contains CO2 and other impurities that may need to be "scrubbed" depending on its intended application, such as in advanced chemical synthesis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy for pyrolysis should be guided by your end objective. There is no single "best" way; there is only the best way for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is soil improvement or carbon sequestration: Use a slow, lower-temperature process (around 500 °C) to maximize the yield of stable, high-quality biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing fuel: Use a fast, higher-temperature process (above 700 °C) to maximize the output of energy-dense bio-oil and flammable syngas.
- If your primary focus is generating specialty chemicals: Use a mid-to-high temperature process and invest in downstream equipment to capture and separate valuable compounds like wood vinegar from the bio-oil fraction.
By understanding how process variables control the output, you can transform wood from a simple material into a predictable source of valuable products.
Summary Table:
| Byproduct | Description | Key Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | Carbon-rich, porous solid residue. | Soil amendment, solid fuel, carbon sequestration. |
| Bio-Oil (Liquid) | Complex, dense liquid from condensed vapors. | Liquid biofuel (after refining), source of chemicals. |
| Syngas (Gas) | Flammable gas mixture (H₂, CO, CH₄). | Process heat, fuel for energy generation. |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable products?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality laboratory pyrolysis equipment and consumables. Whether your goal is to maximize biochar for soil research, produce bio-oil for fuel analysis, or generate syngas for energy studies, our solutions are designed for precision, control, and reliability.
We help you achieve:
- Precise Temperature Control: Optimize your process to target the specific byproduct yields you need.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Reliable equipment built for consistent performance in demanding lab environments.
- Expert Support: Get the right setup for your unique application, from R&D to quality control.
Let's build the right pyrolysis solution for your laboratory. Contact our experts today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of pyrolysis? Converting Waste into Valuable Fuels and Chemicals
- What is the capacity of a rotary furnace? Choose Between Batch or Continuous Processing
- What is the difference between refining and calcination? A Guide to Material Processing Stages
- What is pyrolysis of biomass to produce hydrogen? A Guide to Carbon-Negative Green Hydrogen
- In which furnace is calcination and roasting done? A Guide to Selecting the Right Thermal Processing Equipment
- What are the methods of producing bio-oil? The Definitive Guide to Pyrolysis and Alternative Biofuel Processes
- What are the factors affecting biomass pyrolysis? Master Temperature, Feedstock & Economics for Optimal Output
- Is pyrolysis the same as waste to energy? Unlocking Chemical Recycling vs. Energy Recovery



















