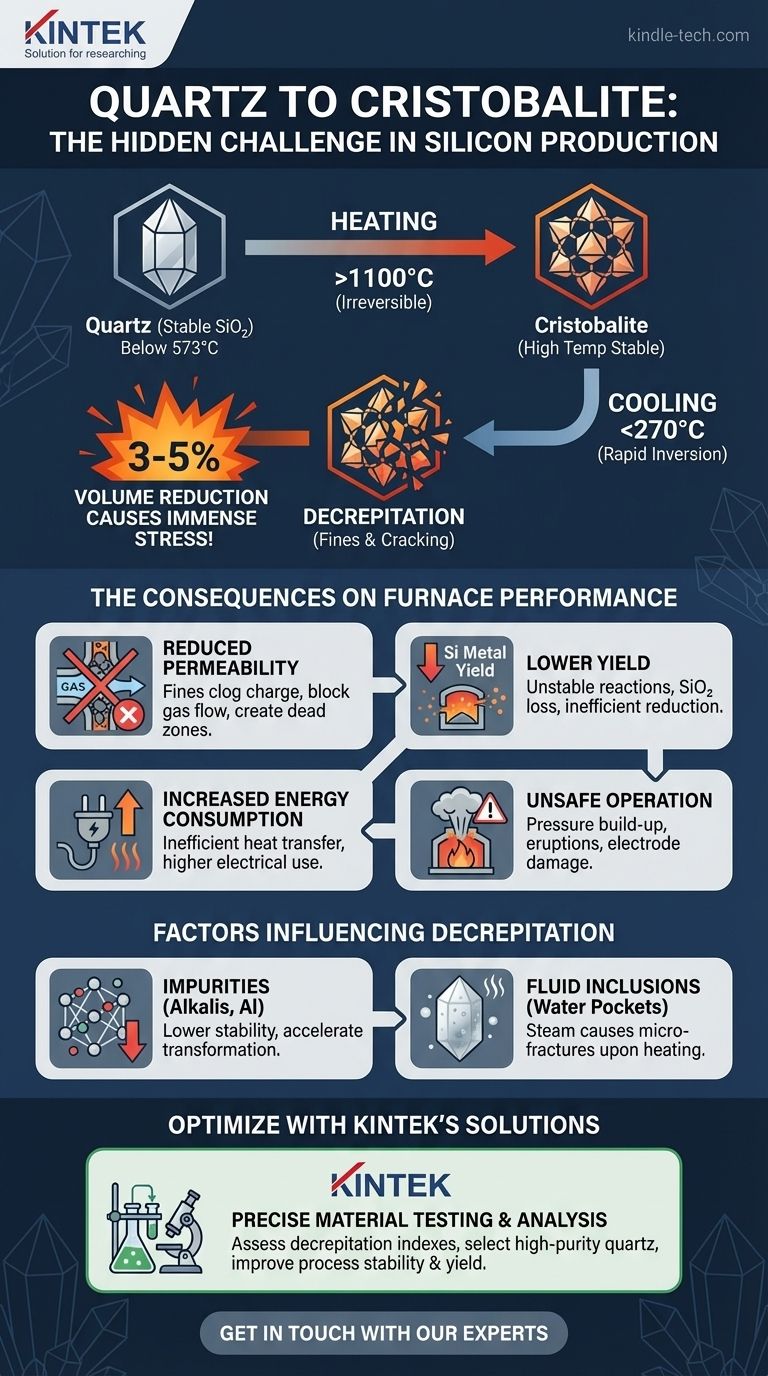
At its core, the heating of quartz in a silicon furnace initiates an irreversible phase transformation into cristobalite, a different crystalline form of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). This transformation, particularly the rapid volume change that occurs when cristobalite cools, is the primary driver of mechanical instability in the raw material, directly impacting furnace efficiency, safety, and overall silicon yield.
The central challenge in using quartz for silicon production is not the heating itself, but the consequences of the cooling cycle. The transformation to cristobalite introduces a structural "memory" that causes the material to fracture upon cooling, generating fine particles that disrupt the entire smelting process.

The Fundamental Transformation: Quartz to Cristobalite
Understanding the behavior of quartz begins with recognizing that it is not inert under the extreme heat of a silicon furnace. It undergoes a profound and permanent change in its crystal structure.
What is Quartz?
Quartz is the stable crystalline form of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) at ambient temperatures and pressures. It exists as α-quartz below 573°C and transitions reversibly to β-quartz above this temperature. This initial transition involves only a minor structural shift.
The Irreversible High-Temperature Change
As temperatures climb above approximately 1100°C in the furnace, the quartz structure begins to slowly and irreversibly rearrange into cristobalite, a polymorph of SiO₂ that is stable at very high temperatures. While another phase, tridymite, can also form, cristobalite is the more critical and common transformation product in this industrial context.
Why Cristobalite is the Key Player
Once formed, cristobalite does not revert back to quartz upon cooling. This means that quartz lumps that have been heated to high temperatures in the upper zones of the furnace are no longer quartz; they are now lumps of cristobalite. This new material has entirely different physical properties.
The Critical Problem: The Cristobalite Inversion
The most significant consequence of forming cristobalite arises not at peak temperature, but during periods of cooling within the furnace charge.
High vs. Low-Temperature Cristobalite
Similar to quartz, cristobalite has two forms: a high-temperature β-cristobalite (stable above ~270°C) and a low-temperature α-cristobalite. The transition between these two forms is rapid and reversible.
The Source of Instability: Sudden Volume Change
When β-cristobalite cools below approximately 270°C, it inverts instantaneously to α-cristobalite. This inversion is accompanied by a sudden and significant volume reduction of 3-5%. This rapid contraction generates immense internal stress within the material.
The Consequence: Decrepitation
The internal stress caused by the α-β cristobalite inversion is often too great for the material to withstand. The result is decrepitation—the violent cracking, fracturing, and breakdown of the quartz lumps into smaller pieces and fine particles. Think of it as the material shattering itself from the inside out.
How Decrepitation Impacts Silicon Production
The generation of fine particles is not a minor issue; it fundamentally degrades the performance and stability of the submerged arc furnace used for silicon production.
Effect on Furnace Permeability
A silicon furnace relies on good permeability, allowing hot CO gas generated in the hearth to flow upwards, preheating and reacting with the descending charge. Fine particles from decrepitation clog the spaces between larger lumps, dramatically reducing this permeability.
This leads to poor gas distribution, creating "channels" where gas flow is too high and "dead zones" where it is too low.
Impact on Reactivity and Yield
Fines have two negative effects on yield. First, the intense gas flow in channels can blow fine SiO₂ particles straight out of the furnace, representing a direct loss of raw material.
Second, the unpredictable charge movement and gas flow disrupt the stable reaction zones, leading to inefficient reduction of SiO₂ to silicon metal and lowering the overall process yield.
Increased Energy Consumption
Poor gas distribution means inefficient heat transfer. More energy is required to maintain the necessary temperatures throughout the furnace, increasing electrical consumption and operational costs.
Unstable and Unsafe Operation
Blocked gas flow can cause pressure to build up in pockets within the furnace charge. The sudden release of this trapped gas can cause "eruptions" or "blows," leading to highly unstable furnace operation, potential damage to electrodes, and significant safety hazards for personnel.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Not All Quartz is Equal
The tendency of a specific quartz source to decrepitate is a critical quality parameter. This is heavily influenced by the material's purity and internal structure.
The Role of Impurities
Impurities within the quartz crystal lattice, particularly alkalis (like potassium and sodium) and aluminum, act as fluxes. They lower the energy barrier for the transformation to cristobalite, causing it to happen faster and at lower temperatures, which increases the degree of decrepitation.
The Impact of Fluid Inclusions
"Milky" or opaque quartz is filled with microscopic fluid inclusions, which are tiny pockets of trapped water. When heated, this water turns to high-pressure steam, creating micro-fractures from within. This weakens the structure and severely worsens the effects of decrepitation. High-purity, transparent quartz generally performs better.
Evaluating Thermal Stability
Because of these factors, the "thermal stability" or "decrepitation index" of quartz is a key metric for raw material selection. This is often determined by lab tests that heat a sample of the quartz to simulate furnace conditions and measure the amount of fine material produced.
Optimizing Your Process with Quartz Selection
A deep understanding of quartz transformation allows you to move from reactive problem-solving to proactive process control by managing your primary raw material.
- If your primary focus is maximizing furnace stability and yield: Prioritize sourcing high-purity quartz with a proven low decrepitation index and minimal fluid inclusion content.
- If your primary focus is managing a variable raw material supply: Implement routine decrepitation testing to classify your quartz lots and blend them strategically to maintain a consistent and predictable charge behavior.
- If your primary focus is reducing energy costs: Ensure good charge permeability by minimizing the use of quartz prone to decrepitation, as this directly improves gas distribution and heat transfer efficiency.
Mastering the behavior of your SiO₂ source is the foundation for a stable, efficient, and profitable silicon production operation.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Change | Primary Effect on Si Production |
|---|---|---|
| Heating (>1100°C) | Irreversible transformation of quartz to cristobalite. | Sets the stage for material instability upon cooling. |
| Cooling (<270°C) | Rapid α-β cristobalite inversion with 3-5% volume reduction. | Causes decrepitation (violent fracturing), generating fine particles. |
| Furnace Operation | Fines clog charge, reducing permeability and disrupting gas flow. | Lowers yield, increases energy consumption, and creates unsafe conditions. |
Achieve stable and efficient silicon production by mastering your raw material behavior. The transformation of quartz under heat is a critical factor in furnace performance. KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab equipment and consumables for precise material testing and analysis. Our solutions help you accurately assess quartz decrepitation indexes and optimize your raw material selection for maximum yield and operational safety. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in silicon production R&D and quality control.
Get in touch with our experts to optimize your process
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What improvements does a precision magnetic stirring system provide to indium electrowinning? Boost Efficiency Now
- What temperature does sintering occur? Master the Thermal Profile for Your Material
- Does sintering increase porosity? How to Control Porosity for Stronger Materials
- How do you test the purity of precious metals? From Acid Tests to Lab Analysis
- What is the application of reactive sputtering? Synthesize High-Performance Compound Films
- Why is biomass better than coal? A Sustainable, Low-Carbon Energy Alternative
- What is the double sintering method? Achieve Maximum Density with Controlled Microstructure
- What are the disadvantages of using metal? Understanding Corrosion, Weight, and Cost Challenges



















