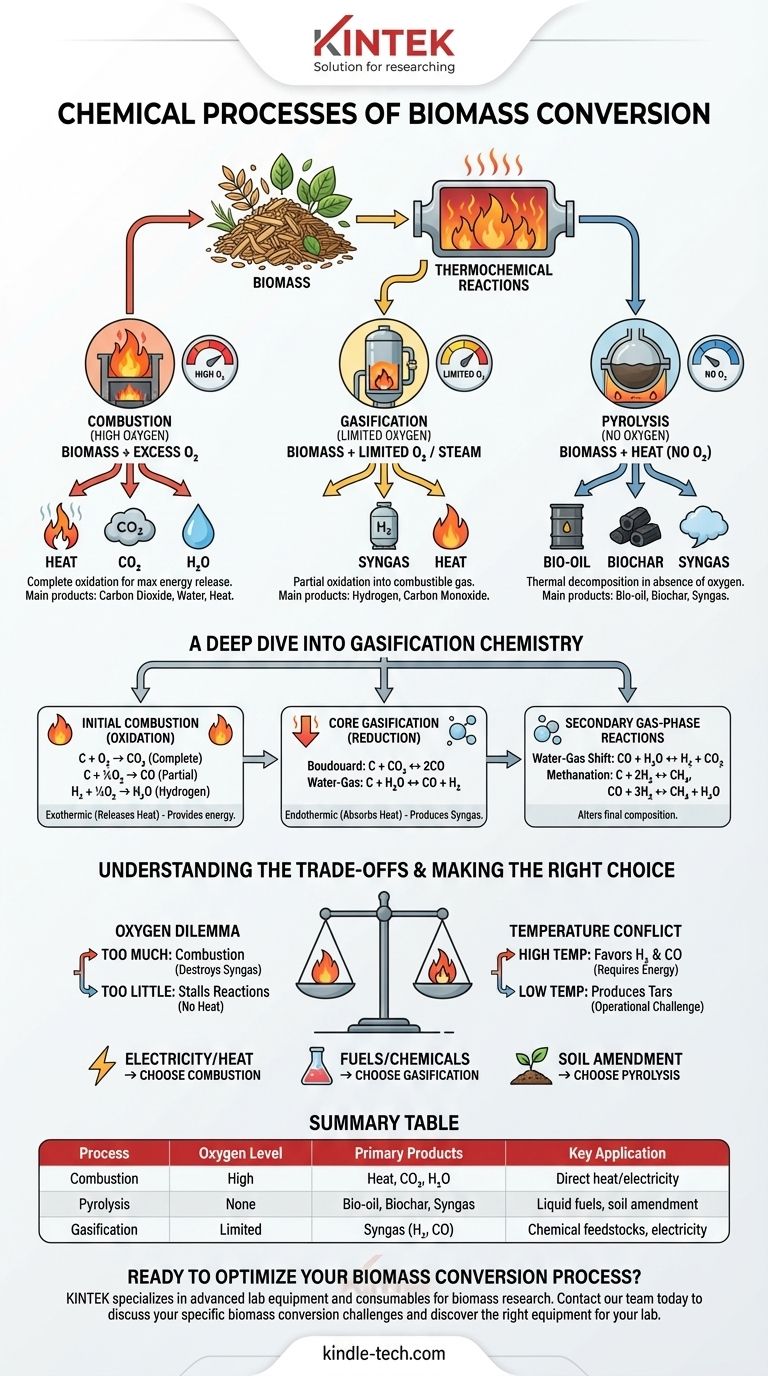
At its core, biomass conversion relies on a series of controlled thermochemical reactions to break down complex organic matter. Processes like gasification, pyrolysis, and combustion manipulate temperature and oxygen to transform biomass into valuable products like synthesis gas (syngas), bio-oil, or heat, driven by fundamental reactions involving carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
The central challenge of biomass conversion is not merely starting chemical reactions, but precisely controlling them. By managing factors like temperature and the amount of oxygen, we can steer the process to favor the creation of valuable fuels and chemicals over simple combustion into heat and carbon dioxide.
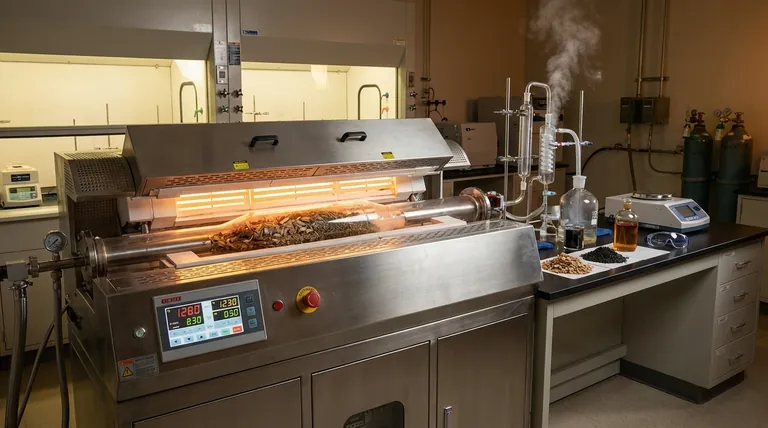

The Principal Thermochemical Pathways
To understand the chemistry, you must first understand the primary methods. The key difference between them is the amount of oxygen supplied to the process, which dictates the final products.
Combustion (High Oxygen)
Combustion is the complete oxidation of biomass in the presence of excess oxygen.
Its primary purpose is to release the maximum amount of energy as heat. This heat can then be used to produce steam for electricity generation or for direct heating applications. The main products are carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
Pyrolysis (No Oxygen)
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass in the complete absence of oxygen.
Instead of burning, the biomass breaks down into three main products: a liquid known as bio-oil, a solid residue called biochar, and a gaseous mixture known as syngas.
Gasification (Limited Oxygen)
Gasification is a partial oxidation process that uses a limited, controlled amount of oxygen or steam.
It is designed to convert solid biomass primarily into a combustible gas mixture called syngas, which is rich in hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO). This syngas is a versatile intermediate that can be burned to generate electricity or used as a chemical feedstock.
A Deep Dive into Gasification Chemistry
Gasification chemistry is a multi-stage process where initial combustion provides the energy for subsequent reactions that produce the desired syngas. The reactions listed below often occur simultaneously in different zones of a gasifier.
Step 1: Initial Combustion (Oxidation)
The process begins by introducing a small amount of oxygen, which initiates combustion reactions. These are exothermic (they release heat), providing the high temperatures needed for the rest of the process.
C + O₂ → CO₂(Complete Combustion)C + ½O₂ → CO(Partial Combustion)H₂ + ½O₂ → H₂O(Hydrogen Combustion)
Step 2: Core Gasification (Reduction)
In the high-temperature, oxygen-poor environment created by the initial combustion, the hot CO₂ and steam (H₂O) react with the remaining carbon (char). These are the critical endothermic (they absorb heat) reactions that produce syngas.
- Boudouard Reaction:
C + CO₂ ↔ 2CO - Water-Gas Reaction:
C + H₂O ↔ CO + H₂
These two reactions are the heart of converting solid carbon into valuable gaseous fuel.
Step 3: Secondary Gas-Phase Reactions
Once the initial syngas is formed, further reactions occur in the gas phase that alter its final composition. Controlling these helps optimize the gas for its intended use.
-
Water-Gas Shift Reaction:
CO + H₂O ↔ H₂ + CO₂This reaction is crucial for adjusting the hydrogen-to-carbon monoxide ratio in the final syngas. -
Methanation Reactions:
C + 2H₂ ↔ CH₄CO + 3H₂ ↔ CH₄ + H₂OThese reactions produce methane (CH₄), which increases the heating value of the gas but may be undesirable if pure H₂ or CO is the goal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Successfully managing a biomass conversion process is a balancing act. The ideal conditions depend entirely on your desired end product.
The Oxygen Dilemma
The amount of oxygen is the most critical control parameter. Too much oxygen leads to complete combustion, releasing energy as heat but destroying the valuable syngas. Too little oxygen will fail to produce enough heat, stalling the endothermic gasification reactions.
The Temperature Conflict
Higher temperatures (above 800°C) favor the production of hydrogen and carbon monoxide via the Boudouard and Water-Gas reactions. However, maintaining these high temperatures requires more energy input or consumes more of the feedstock for combustion.
The Role of Moisture and Tar
Biomass is not pure carbon. Its moisture content directly feeds the Water-Gas and Water-Gas Shift reactions, influencing the H₂/CO ratio. Incomplete conversion, especially at lower temperatures, can also produce complex hydrocarbons known as tars, which can clog equipment and are a significant operational challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal chemical pathway depends entirely on what you want to achieve.
- If your primary focus is generating heat or electricity directly: Complete combustion is the most straightforward path, maximizing immediate energy release.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid fuels or chemical feedstocks: Gasification is superior, as it produces a versatile syngas intermediate that can be catalytically converted into fuels (via Fischer-Tropsch) or chemicals like methanol.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for soil amendment: Pyrolysis is the target process, as it maximizes the solid char residue while co-producing bio-oil and gas.
By understanding these fundamental chemical pathways, you can effectively control the transformation of raw biomass into valuable energy and products.
Summary Table:
| Process | Oxygen Level | Primary Products | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combustion | High | Heat, CO₂, H₂O | Direct heat/electricity |
| Pyrolysis | None | Bio-oil, Biochar, Syngas | Liquid fuels, soil amendment |
| Gasification | Limited | Syngas (H₂, CO) | Chemical feedstocks, electricity |
Ready to Optimize Your Biomass Conversion Process?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for biomass research and development. Whether you're developing catalysts, analyzing bio-oil, or scaling up gasification reactions, our precise tools help you control critical parameters like temperature and atmosphere. Let our experts support your journey from raw biomass to valuable energy products.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific biomass conversion challenges and discover the right equipment for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision



















