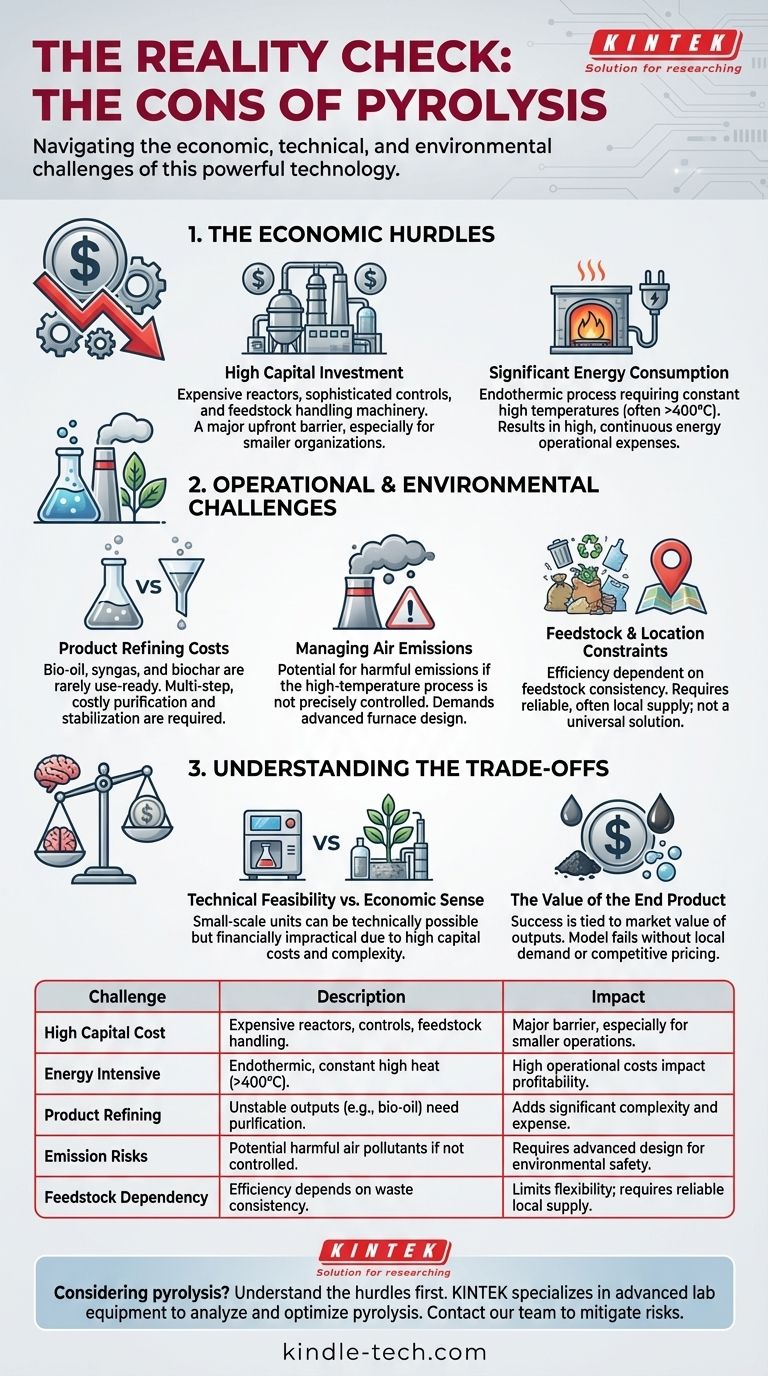
While a powerful technology for waste-to-value conversion, pyrolysis is not without significant challenges. The primary disadvantages are its high capital and energy costs, the necessity for complex and expensive downstream processing of its products, and the potential for harmful air emissions if the system is not designed and operated with precision.
The core challenge of pyrolysis lies not in its technical feasibility, but in its economic viability. The process involves high upfront investments and significant operational costs that can easily outweigh the value of the resulting products without careful engineering, scale, and market access.

The Economic Hurdles of Pyrolysis
For many, the most significant barriers to adopting pyrolysis are financial. The process demands substantial investment at multiple stages, making profitability a careful balancing act.
High Capital Investment
The equipment required for a pyrolysis plant is expensive. This includes the high-temperature reactor, sophisticated control systems, and the machinery needed to handle feedstock and manage the output products. These high upfront capital costs can be a major deterrent, especially for smaller organizations.
Significant Energy Consumption
Pyrolysis is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a constant input of energy to maintain very high temperatures (often above 400°C) in an oxygen-free environment. This results in high, continuous energy consumption, which is a major operational expense that directly impacts the cost-effectiveness of the entire operation.
The Hidden Costs of Product Refining
The outputs of pyrolysis—bio-oil, syngas, and biochar—are rarely ready for immediate use. Bio-oil, for instance, is often acidic, unstable, and requires significant refining before it can be used as a transportation fuel. This multi-step separation and purification process adds another layer of complexity and expense.
Operational and Environmental Challenges
Beyond the financial aspects, pyrolysis presents technical and environmental hurdles that must be managed to ensure a safe and beneficial outcome.
Managing Air Emissions
The high-temperature decomposition of organic matter can produce harmful emissions if the process is not perfectly controlled. Proper furnace design, meticulous operation, and consistent maintenance are essential to minimize air quality impacts and ensure the process is genuinely environmentally friendly.
Feedstock and Location Constraints
Pyrolysis is not a universal solution for all types of organic waste. The efficiency and output of the process are highly dependent on the composition and consistency of the feedstock. This means a facility may not be suitable for certain waste streams and requires a reliable, often local, supply to be economical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A critical part of evaluating pyrolysis is understanding its inherent compromises, particularly concerning its scale.
Technical Feasibility vs. Economic Sense
While pyrolysis units can be built at a relatively small scale for remote locations, they often struggle with cost-effectiveness. The high capital cost is much harder to recoup with lower throughput, and the operational complexity remains. A system may be technically possible but financially impractical.
The Value of the End Product
The economic success of a pyrolysis project is directly tied to the market value of its outputs. If there is no local demand for biochar as a soil amendment or if the cost to refine bio-oil is higher than the price of conventional fuel, the entire model can fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if pyrolysis is the correct path, you must align the technology's characteristics with your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is large-scale waste management with established end-product markets: Pyrolysis can be a viable, albeit capital-intensive, solution when integrated into a broader industrial ecosystem.
- If your primary focus is small-scale or remote energy production: You must rigorously model the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and product refining, against the true value of the energy or materials produced.
- If your primary focus is maximizing environmental benefit: Acknowledge that a low-emission, highly efficient process requires significant upfront investment in advanced design, control systems, and operational oversight.
A successful pyrolysis project hinges on a clear-eyed assessment of its economic realities, not just its technical potential.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| High Capital Cost | Expensive reactors, control systems, and feedstock handling equipment. | Major barrier to entry, especially for smaller operations. |
| Energy Intensive | Endothermic process requires constant high heat (often >400°C). | High operational costs that impact profitability. |
| Product Refining | Outputs like bio-oil are unstable and require costly purification. | Adds significant complexity and expense to the value chain. |
| Emission Risks | Potential for harmful air pollutants if not meticulously controlled. | Requires advanced design and strict operation for environmental safety. |
| Feedstock Dependency | Efficiency and output quality depend heavily on waste stream consistency. | Limits flexibility and requires a reliable, local feedstock supply. |
Considering pyrolysis for your waste management or energy goals? Understanding the economic and technical hurdles is the first step to success. At KINTEK, we specialize in the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables needed to analyze, test, and optimize pyrolysis processes. Whether you're researching feedstock viability, characterizing bio-oil, or scaling up your operation, our precise tools provide the data-driven insights essential for making informed decisions and mitigating risks. Let our expertise support your project—contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is the basic construction and temperature control mechanism of a laboratory tube furnace? Master Precision Heating for Your Lab
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation



















