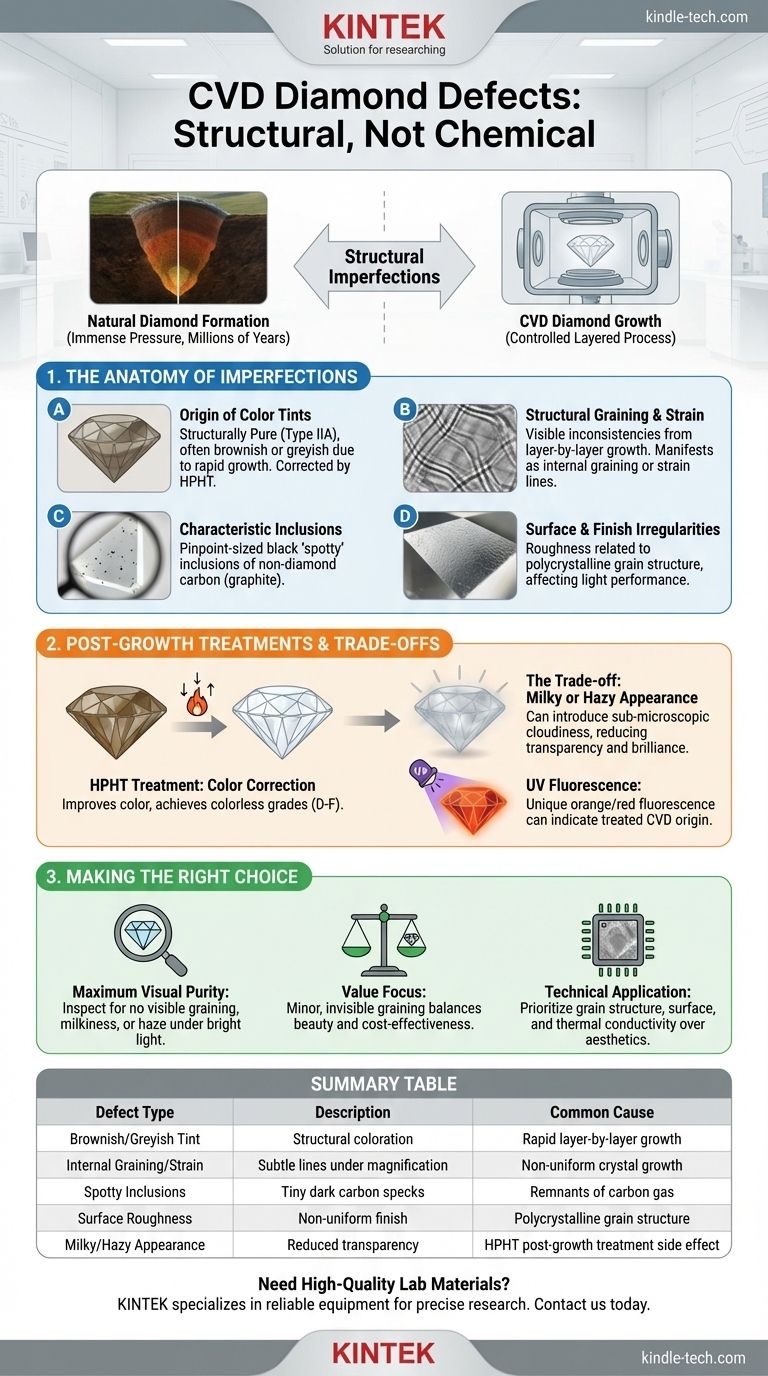
At their core, the defects in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) diamonds are not chemical impurities but structural imperfections rooted in their unique, layered growth process. The most common defects include brownish or greyish color tints, internal graining lines, and characteristic dark "spotty" inclusions. While post-growth treatments can improve color, they can sometimes introduce a secondary defect: a milky or hazy appearance.
CVD diamonds trade the chemical impurities of many natural diamonds for structural artifacts of their own. Understanding these specific defects—from graining to post-treatment haze—is the key to accurately assessing their quality and value.

The Anatomy of a CVD Diamond Defect
Unlike natural diamonds, which form under immense, uniform pressure over millions of years, CVD diamonds grow layer-by-layer in a controlled chamber. This additive process is the source of their most common and telling imperfections.
The Origin of Color Tints
While CVD diamonds are classified as Type IIA—meaning they are chemically pure and lack nitrogen—they often exhibit a brownish or greyish tint after their initial growth.
This coloration is a structural phenomenon related to the rapid crystal formation process. To correct this, most gem-quality CVD diamonds undergo a secondary High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT) treatment to improve their color.
Structural Imperfections: Graining and Strain
The layer-by-layer growth can create visible inconsistencies within the crystal lattice. These manifest as internal graining or strain lines.
These lines are often subtle and may not be visible without magnification, but they are a distinct structural marker of the CVD growth method. They represent boundaries where the crystal growth was not perfectly uniform.
Characteristic Inclusions
Inclusions in CVD diamonds are different from the mineral crystals often trapped inside natural diamonds. They are typically tiny, dark, "spotty" inclusions of graphite or another form of non-diamond carbon.
These can appear as pinpoint-sized black dots and are remnants from the carbon-rich gas used during the diamond's formation.
Surface and Finish Irregularities
The surface of a CVD diamond can exhibit a certain roughness and non-uniform composition directly related to its polycrystalline grain structure.
While polishing removes most of this for gemstone use, the underlying structure can affect the final finish and light performance compared to a single, uniform crystal.
Understanding Post-Growth Treatments and Their Side Effects
Most CVD diamonds on the market have been enhanced to improve their appearance. This treatment is a standard part of the production process, but it comes with its own set of trade-offs that you must be aware of.
The Role of HPHT Treatment
HPHT treatment is a corrective process. By applying immense pressure and heat, labs can effectively "bleach" the brown or grey tints out of a CVD diamond, dramatically improving its color grade.
This treatment is what allows CVD diamonds to achieve colorless (D-F) and near-colorless (G-J) grades.
The Trade-off: Potential for Haze
The primary risk of HPHT treatment is the introduction of a milky or hazy appearance. This sub-microscopic cloudiness can reduce the diamond's transparency and brilliance, making it look slightly dull or oily, especially in certain lighting conditions.
This effect is a crucial quality factor to assess, as it is not always noted on a standard grading report but significantly impacts the stone's beauty.
UV Fluorescence as an Indicator
CVD diamonds can exhibit unique fluorescence under ultraviolet (UV) light, which can be an indicator of their origin and treatment.
While not a defect in itself, a strong or unusual color of fluorescence (such as orange or red) can sometimes be a clue that the diamond is a treated CVD stone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating a CVD diamond isn't about finding a "perfect" stone, but understanding which characteristics matter for your specific needs. A grading report is a start, but a visual inspection is critical.
- If your primary focus is maximum visual purity: Look for stones with no visible graining under magnification and carefully inspect for any signs of milkiness or haze, particularly in bright, direct light.
- If your primary focus is value: A CVD diamond with minor structural graining that is not visible to the naked eye can represent an excellent balance of beauty and cost-effectiveness.
- If you are considering a technical application: Characteristics like grain structure, surface roughness, and thermal conductivity become the critical performance factors, far outweighing aesthetic color or clarity.
By understanding the specific nature of CVD defects, you can make a truly informed decision based on knowledge, not just marketing.
Summary Table:
| Defect Type | Description | Common Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Brownish/Greyish Tint | Structural coloration from rapid growth. | Layer-by-layer CVD process. |
| Internal Graining/Strain | Subtle lines visible under magnification. | Non-uniform crystal growth. |
| Spotty Inclusions | Tiny dark specks of non-diamond carbon. | Remnants from the carbon gas source. |
| Surface Roughness | Non-uniform finish. | Polycrystalline grain structure. |
| Milky/Hazy Appearance | Reduced transparency and brilliance. | Side effect of HPHT post-growth treatment. |
Need High-Quality Lab Materials for Your Research?
Understanding material properties, like the defects in CVD diamonds, is crucial for successful experiments. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables to support your research and development.
We help you achieve precise and reproducible results.
Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can benefit your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
People Also Ask
- What are the challenges of lab-grown diamonds? Navigating Value, Perception & Technical Limits
- Which lab grown diamond process is best? Focus on Quality, Not the Method
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- How does microwave plasma work? Unlock Precision Material Synthesis for Advanced Manufacturing
- How do lab-grown diamonds compare to natural diamonds? Uncover the Truth About Origin, Price, and Value











