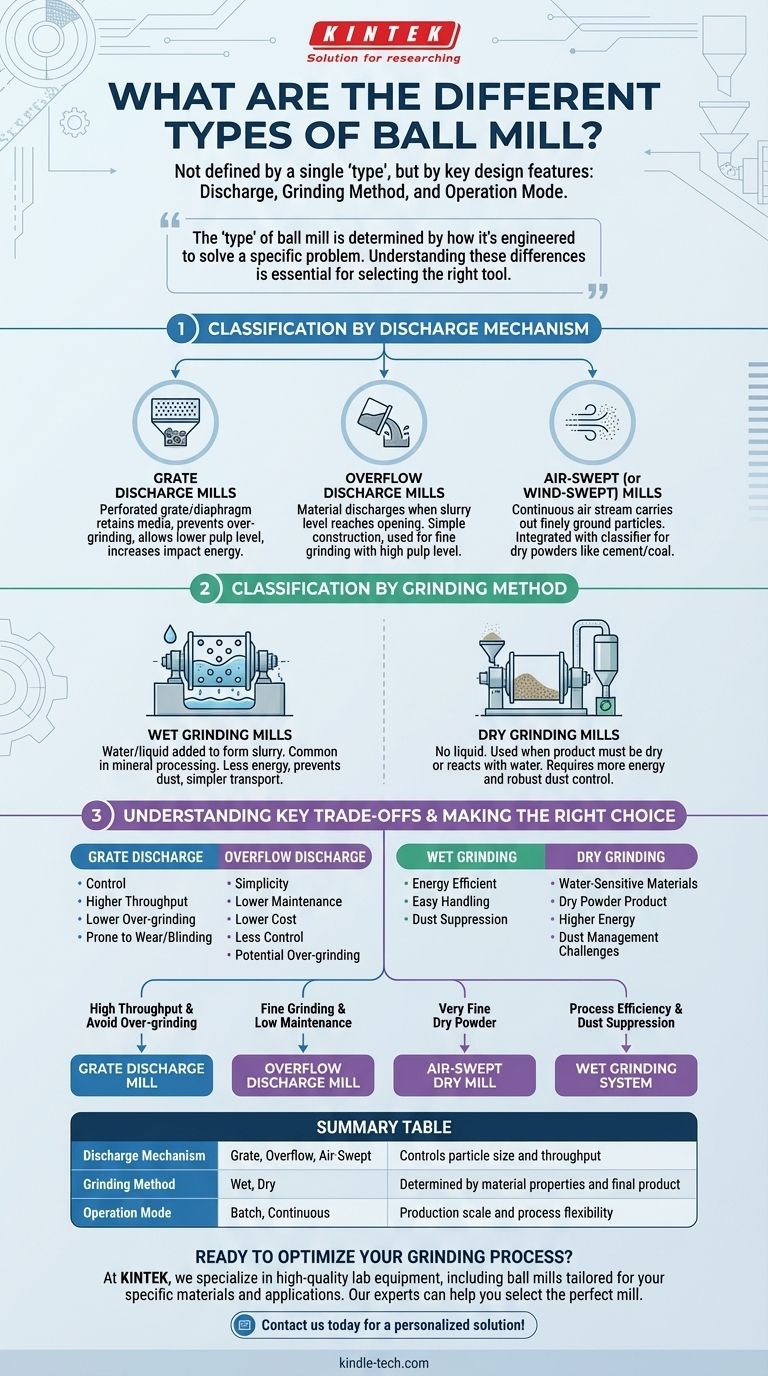
At its core, a ball mill is not defined by a single "type." Instead, ball mills are classified by a combination of key design features, primarily their material discharge mechanism, their grinding method (wet or dry), and their mode of operation (batch or continuous). These designs are engineered to solve specific material processing challenges.
The most critical takeaway is that the "type" of ball mill is determined by how it's engineered to solve a specific problem. Understanding the differences between overflow vs. grate discharge, or wet vs. dry grinding, is essential for selecting the right tool for your material and desired outcome.

Classification by Discharge Mechanism
The method a mill uses to discharge the ground material is one of its most fundamental design distinctions. This determines the mill's efficiency, particle size control, and suitability for different materials.
Grate Discharge Mills
Grate discharge mills have a perforated grate or diaphragm at the discharge end. This acts like a screen, retaining the grinding media and coarser material inside the mill for further grinding.
Only material fine enough to pass through the grate openings can exit. This design prevents over-grinding of particles and allows for a lower pulp level, which increases the impact energy of the grinding media.
Overflow Discharge Mills
Overflow mills are simpler in construction. Material is discharged when the slurry (pulp) level inside the mill reaches the height of the discharge opening, causing it to overflow.
This design is typically used for fine grinding applications where a high pulp level is desirable. It is common in secondary grinding circuits.
Air-Swept (or Wind-Swept) Mills
These are specialized dry grinding mills. A continuous stream of air is passed through the mill, picking up the finely ground particles and carrying them out.
This method is often integrated with a classifier system to separate particles by size, returning oversized material to the mill for further grinding. It is ideal for producing very fine, dry powders like cement or coal.
Classification by Grinding Method
Whether water is used in the process dramatically changes the mill's operation, energy consumption, and downstream processing requirements.
Wet Grinding Mills
In wet grinding, water or another liquid is added with the feed material to form a slurry. This is the most common method in the mineral processing industry.
Wet grinding consumes less energy, prevents dust issues, and simplifies the transportation of the ground product as a slurry. Overflow and grate discharge mills are both commonly used for wet grinding.
Dry Grinding Mills
Dry grinding is performed without the addition of any liquid. This is necessary when the final product must be dry or when the material reacts with water.
This method typically requires more energy and necessitates robust dust control systems. Air-swept mills are exclusively used for dry grinding applications.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing a ball mill design is a matter of balancing competing priorities like throughput, energy efficiency, and final particle size.
Grate Discharge vs. Overflow Discharge
The primary trade-off is between control and simplicity. Grate discharge offers better control over particle residence time, reducing over-grinding and increasing throughput. However, the grates can be prone to blinding or wear.
Overflow discharge mills are mechanically simpler and have lower maintenance costs, but they offer less control over product size, which can lead to over-grinding of softer particles.
Wet Grinding vs. Dry Grinding
The decision here is dictated by the material and the final product requirements. Wet grinding is more energy-efficient and creates a product that is easy to pump and handle.
Dry grinding is essential if the material is water-sensitive (like cement) or if the final application requires a dry powder. However, it comes with higher energy costs and the significant operational challenge of dust management.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection should be guided by your end goal. Match the mill's features to your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and avoiding over-grinding of coarse material: A grate discharge mill is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is fine grinding in a simple, low-maintenance circuit: An overflow discharge mill is often the most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is producing a very fine, dry powder for products like cement: An air-swept dry grinding mill is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and dust suppression in mineral processing: A wet grinding system is almost always preferred.
Ultimately, understanding these core design principles empowers you to select not just a ball mill, but the correct comminution system for your specific objective.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Types | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Discharge Mechanism | Grate Discharge, Overflow Discharge, Air-Swept | Controls particle size and throughput efficiency |
| Grinding Method | Wet Grinding, Dry Grinding | Determined by material properties and final product requirements |
| Operation Mode | Batch, Continuous | Suited for different production scales and process flexibility |
Ready to optimize your grinding process? The right ball mill is critical for achieving your desired particle size, throughput, and efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including ball mills tailored for your specific materials and applications. Our experts can help you select the perfect mill to enhance your productivity and results. Contact us today to discuss your needs and get a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a planetary ball mill? Unlock the Right Grinding Technology for Your Lab
- What are the parameters of a planetary ball mill? Master Speed, Time, and Media for Perfect Grinding
- What is the principle of planetary ball mill? Achieve Rapid, High-Energy Grinding for Your Materials
- What is the function of a planetary ball mill for c-LLZO precursors? Master Solid Electrolyte Prep
- What are the effects of ball milling? A Deep Dive into Mechanical Alloying and Material Transformation



















