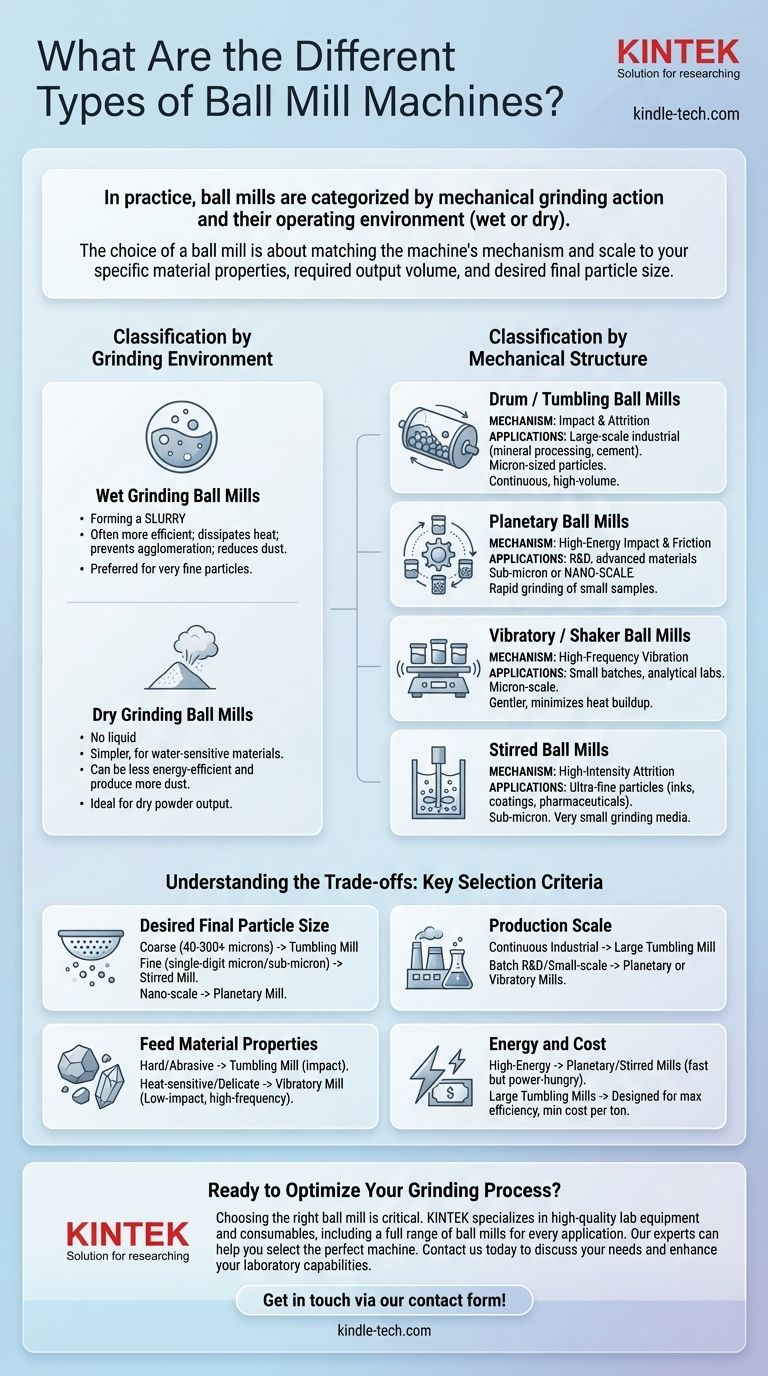
In practice, ball mills are primarily categorized by their mechanical grinding action and their operating environment (wet or dry). The main structural types include tumbling (or drum) mills, high-energy planetary mills, vibratory mills, and stirred mills, each designed to apply force in a distinct way to achieve a specific particle size reduction goal.
The choice of a ball mill is not about finding the "best" type, but about matching the machine's mechanism and scale to your specific material properties, required output volume, and desired final particle size.

Classification by Grinding Environment
The first major distinction is whether the grinding process occurs in a liquid slurry or in a dry state. This choice fundamentally impacts efficiency, contamination, and the final product's characteristics.
Wet Grinding Ball Mills
Wet grinding involves mixing the material with a liquid, typically water, to form a slurry. This method is often more efficient than dry grinding.
The liquid medium helps dissipate heat, prevents material from agglomerating or sticking to the mill walls, and reduces airborne dust. It is the preferred method for producing very fine particles and is essential when subsequent processing steps are also wet.
Dry Grinding Ball Mills
Dry grinding is performed without any liquid. This approach is simpler and necessary for materials that are sensitive to or react with water.
While it can be less energy-efficient and produce more dust, dry grinding is ideal when the final product must be a dry powder. These mills often incorporate systems for air classification to separate particles as they reach the target size.
Classification by Mechanical Structure
The physical design of the mill dictates how energy is transferred to the grinding media and, consequently, to the material being processed. This is the most critical factor influencing grinding speed and final particle size.
Drum / Tumbling Ball Mills
This is the classic and most common type used in large-scale industrial applications, such as mineral processing and cement production. A horizontal cylinder rotates, causing grinding media (steel balls or ceramic pebbles) to tumble and cascade.
Grinding occurs through two primary mechanisms: impact (balls falling from the top of the rotation) and attrition (balls rubbing against each other and the material). They are workhorses designed for continuous, high-volume production of micron-sized particles.
Planetary Ball Mills
Planetary mills are high-energy laboratory machines used for rapid grinding of small samples down to the sub-micron or even nano-scale. The grinding jars are mounted on a rotating "sun wheel" and simultaneously rotate on their own axes, but in the opposite direction.
This combined motion creates extremely high centrifugal forces, resulting in powerful impacts and friction. The high energy input allows for much faster and finer grinding than a conventional tumbling mill, making it ideal for R&D and advanced materials synthesis.
Vibratory / Shaker Ball Mills
In a vibratory mill, the grinding chamber is not rotated but is instead subjected to high-frequency vibration. This agitation keeps the grinding media in constant motion, creating numerous low-energy impacts.
This method is highly effective for smaller batches and is gentler than planetary milling, which helps to minimize heat buildup and potential changes to the material's crystal structure. They are often used for sample preparation in analytical labs.
Stirred Ball Mills
Stirred mills, also known as attritor mills, are designed for producing ultra-fine particles efficiently. Unlike tumbling mills where energy is limited by gravity, these mills use a central agitator shaft with arms or discs to stir the grinding media at high speed.
This decouples the energy input from the mill's rotation speed, allowing for the use of very small grinding media (down to fractions of a millimeter). The result is a high-density field of attrition that is exceptionally effective for creating fine slurries for inks, coatings, and pharmaceuticals.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Key Selection Criteria
Choosing the right mill involves balancing performance against operational constraints. There is no single best solution; there are only optimal choices for specific goals.
Desired Final Particle Size
This is the most important factor. For coarse grinding (e.g., 40-300 microns), a tumbling ball mill is standard. For fine grinding into the single-digit micron or sub-micron range, a stirred mill is more efficient. For nano-scale particles in a lab setting, a planetary mill is required.
Production Scale
For continuous, 24/7 industrial production measured in tons per hour, large tumbling ball mills are the only viable option. For batch-based R&D, sample prep, or small-scale specialty production, planetary or vibratory mills are far more practical.
Feed Material Properties
Very hard and abrasive materials often require the high-impact energy of steel media in a tumbling mill. Heat-sensitive or delicate crystalline materials benefit from the lower-impact, high-frequency action of a vibratory mill.
Energy and Cost
High-energy mills like planetary and stirred types are extremely fast but consume significant power relative to their small volume. Large tumbling mills are designed for maximum energy efficiency over long, continuous runs, minimizing the cost per ton of processed material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your equipment by defining your primary objective first.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial output (e.g., mining or cement): Your default choice is a continuous, wet or dry tumbling ball mill.
- If your primary focus is rapid R&D and achieving nano-particle sizes: A planetary ball mill is the essential tool for your laboratory.
- If your primary focus is producing ultra-fine material in a wet slurry: A stirred media mill provides the best efficiency and particle size control.
- If your primary focus is small-batch lab preparation with minimal contamination or heat: A vibratory shaker mill is an excellent and cost-effective choice.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct energy transfer mechanism of each mill type empowers you to select the precise tool for your material processing task.
Summary Table:
| Mill Type | Primary Mechanism | Ideal Particle Size | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumbling / Drum Mill | Impact & Attrition | 40-300+ microns | Large-scale industrial production (e.g., mining, cement) |
| Planetary Ball Mill | High-Energy Impact | Sub-micron to Nano-scale | R&D, advanced materials synthesis |
| Vibratory / Shaker Mill | High-Frequency Vibration | Micron-scale | Small-batch lab prep, heat-sensitive materials |
| Stirred / Attritor Mill | High-Intensity Attrition | Ultra-fine (sub-micron) | Wet grinding for inks, coatings, pharmaceuticals |
Ready to Optimize Your Grinding Process?
Choosing the right ball mill is critical for achieving your target particle size and maximizing efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of ball mills for every application. Our experts can help you select the perfect machine for your specific material and production goals.
Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your research forward. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
- Hybrid High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
People Also Ask
- What is the specific function of high-energy ball milling in sodium-ion battery synthesis? Master Crystal Purity
- What is the core function of a high-energy vibratory ball mill? Unlock Advanced Mechanochemical Synthesis
- What is the role of a high-energy vibratory ball mill in YSZ-SiC preparation? Achieve Perfect Core-Shell Structures
- How many types of ball mills are there? Choose the Right Mill for Your Lab or Industry
- What is the role of a high-energy ball mill in Ti-based amorphous composite preparation? Master Mechanical Alloying



















