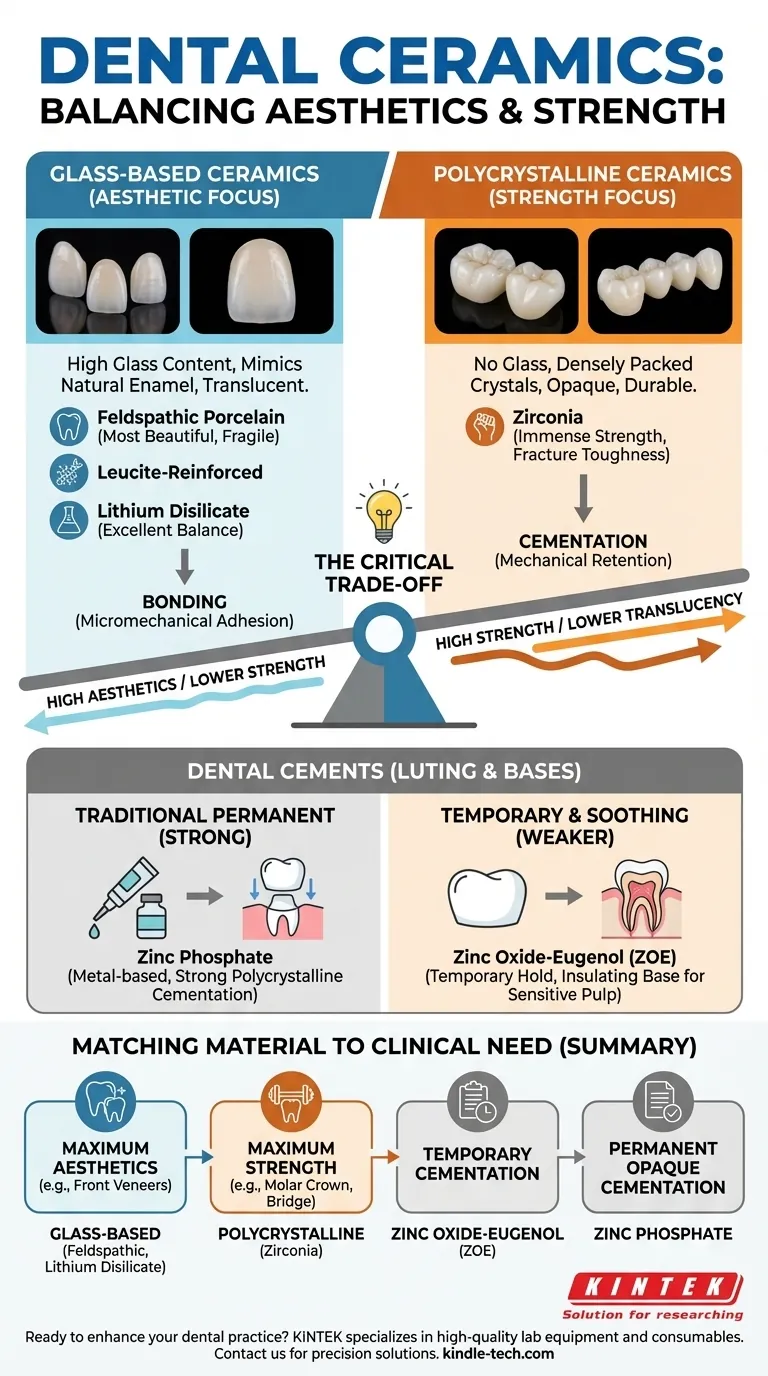
In dentistry, ceramics are broadly classified into two main families: glass-based systems prized for their aesthetics and polycrystalline systems valued for their immense strength. These materials are used for restorations like crowns and bridges, while distinct ceramic-based cements, such as zinc phosphate and zinc oxide-eugenol, are used to secure them.
The central decision in dental ceramics is managing the fundamental trade-off between esthetics and strength. Glass-based ceramics mimic the natural translucency of teeth, while polycrystalline ceramics provide the durability required for high-stress areas.
The Two Core Categories of Restorative Ceramics
The materials used to fabricate crowns, veneers, and bridges fall into two primary structural groups. The key difference lies in the amount of glass they contain, which directly dictates their appearance and mechanical properties.
Glass-Based Ceramics: The Aesthetic Choice
These materials have a high glass content, which allows light to pass through them in a way that closely mimics natural tooth enamel. This makes them the ideal choice for highly visible areas.
The most common types include feldspathic porcelain, leucite-reinforced ceramics, and lithium disilicate. Lithium disilicate, in particular, offers an excellent balance of aesthetics and moderate strength, making it extremely popular for single crowns and veneers.
Polycrystalline Ceramics: The Strength-Focused Choice
These ceramics contain no glass and are composed of densely packed crystals. This structure prevents cracks from propagating and results in exceptional strength and fracture toughness.
The dominant material in this category is zirconia. Due to its opacity and immense strength, it is the material of choice for posterior crowns on molars, long-span bridges, and situations where durability is the absolute priority.
Understanding Dental Cements
While restorative ceramics rebuild the tooth structure, dental cements act as the luting agent to hold the restoration in place. Some of these are older, reliable systems with ceramic components.
Traditional Cement Systems
The reference materials correctly identify two major traditional cements: zinc phosphate and zinc oxide-eugenol (ZOE).
Zinc phosphate is a workhorse material used for the permanent cementation of metal-based or strong polycrystalline restorations. ZOE is a much weaker cement, often used for temporary restorations or as a calming, insulating base over sensitive tooth pulp.
The Role of Cements as Bases
Both zinc phosphate and ZOE can be used as insulating bases. When a cavity is deep, a layer of one of these cements can be placed to protect the tooth's nerve tissue from thermal shock (hot and cold) conducted through the final restoration.
The Critical Trade-Off: Strength vs. Esthetics
Choosing the right ceramic is never about finding one "best" material, but rather the best material for a specific clinical situation. This almost always involves balancing visual requirements with functional demands.
The Esthetic Spectrum
There is an inverse relationship between strength and translucency. Feldspathic porcelain is the most beautiful but also the most fragile. Lithium disilicate improves strength while retaining excellent aesthetics. Zirconia is the strongest but is also the most opaque, though modern variations have significantly improved its appearance.
Bonding vs. Cementation
The material's composition also dictates how it is secured to the tooth. Glass-based ceramics can be micro-mechanically bonded to tooth structure for a very strong and seamless seal. Polycrystalline ceramics like zirconia cannot be etched in the same way and traditionally rely more on mechanical retention and specialized primers for adhesion.
Matching the Ceramic to the Clinical Need
Selecting the appropriate material requires a clear understanding of the goal for the restoration and its position in the mouth.
- If your primary focus is maximum esthetics (e.g., front-tooth veneers): A glass-based ceramic like feldspathic porcelain or lithium disilicate is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength (e.g., a molar crown or a multi-tooth bridge): Zirconia is the most reliable and fracture-resistant option.
- If you need temporary cementation: Zinc oxide-eugenol (ZOE) provides a secure but easily removable hold.
- If you need permanent cementation for a strong, opaque restoration: Zinc phosphate remains a simple and effective traditional option.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct properties of each ceramic family empowers clinicians to restore both function and beauty with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Materials | Primary Use | Key Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glass-Based Ceramics | Feldspathic Porcelain, Leucite-Reinforced, Lithium Disilicate | Crowns, Veneers (Anterior) | High Aesthetics, Translucency |
| Polycrystalline Ceramics | Zirconia | Crowns, Bridges (Posterior) | High Strength, Durability |
| Dental Cements | Zinc Phosphate, Zinc Oxide-Eugenol (ZOE) | Luting, Temporary Restorations | Secure Retention, Insulation |
Ready to enhance your dental practice with the right ceramic solutions? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for dental laboratories. Whether you're fabricating aesthetic glass-ceramic veneers or durable zirconia bridges, our products support precision and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can meet your specific laboratory needs and help you deliver superior patient outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- What are 4 disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the Critical Limitations of This Joining Method
- What affects melting point chemistry? A Guide to Molecular Forces and Lattice Energy
- Why is Boron Nitride used in RRDE? Enhance Precision with Superior Insulating and Protective Material
- What is the function of a BN inner liner in a graphite mold during Flash Sintering? Master Precise Current Control



