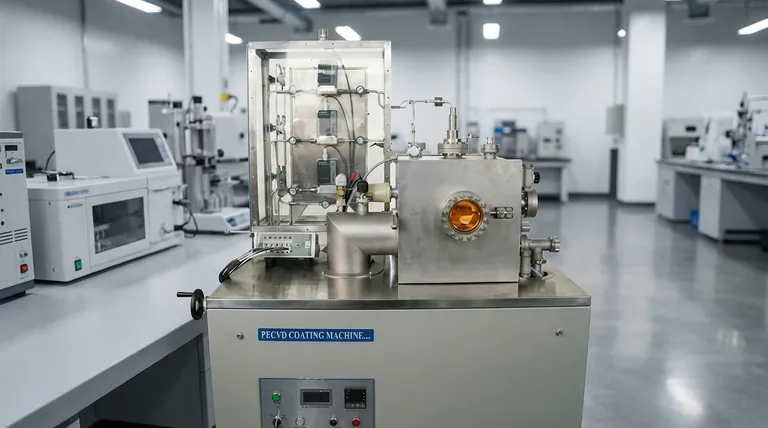
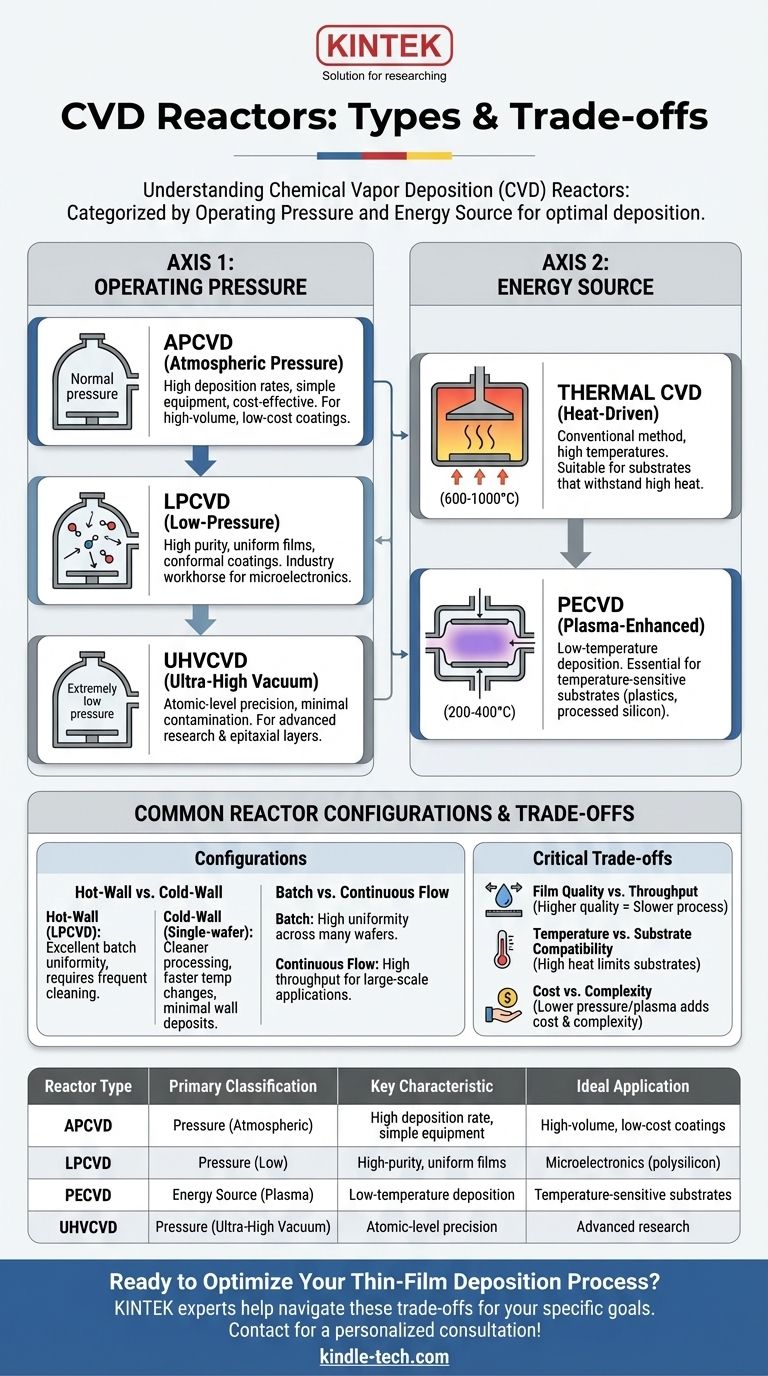
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) reactors are primarily categorized in two fundamental ways: by their internal operating pressure and by the energy source used to initiate the chemical reaction. Common pressure-based types include Atmospheric Pressure (APCVD) and Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD), while energy-based types are mainly Thermal CVD and Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD). These classifications define the reactor's capabilities and its ideal application.
The specific type of CVD reactor chosen is not an arbitrary detail; it is a critical engineering decision that dictates the trade-off between deposition speed, film quality, cost, and compatibility with the underlying material.

The Two Primary Classification Methods
To understand CVD reactors, it's best to think of them along two independent axes: the pressure environment and the energy source. A single reactor is often described by both, such as a "Low-Pressure Thermal CVD" system.
Axis 1: Operating Pressure
The pressure inside the chamber dramatically affects how precursor gas molecules travel and react, directly influencing the quality and uniformity of the resulting film.
Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD) This process occurs in a chamber at normal atmospheric pressure. It is characterized by high deposition rates and simple equipment, making it inexpensive. However, the high pressure can lead to gas-phase reactions that create particles, resulting in lower-purity films.
Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) Operating at sub-atmospheric pressures significantly reduces unwanted gas-phase reactions and increases the "mean free path" of gas molecules. This allows for highly uniform and conformal coatings over complex topographies, making LPCVD an industry workhorse for high-quality films in microelectronics.
Ultra-High Vacuum CVD (UHVCVD) This is the extreme end of the pressure scale, operating at pressures below 10⁻⁶ Pa. The ultra-clean environment minimizes contamination and allows for precise, atomic-level control over film growth, which is critical for advanced research and epitaxial layers.
Axis 2: Energy Source
The energy source provides the activation energy needed to break down the precursor gases and deposit the film onto the substrate.
Thermal CVD This is the most conventional method, where the substrate (and sometimes the entire chamber) is heated to high temperatures, typically from 600°C to over 1000°C. The thermal energy alone is sufficient to drive the chemical reaction. Its main limitation is that the high temperatures can damage or alter sensitive substrates.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) PECVD uses an electric field to generate plasma, an ionized gas of highly reactive species. This plasma provides the energy to break down precursor gases, allowing deposition to occur at much lower temperatures (typically 200-400°C). This makes it essential for depositing films on temperature-sensitive materials like plastics or fully processed silicon wafers.
Common Reactor Configurations
Beyond the primary classifications, practical reactor designs also differ in how they manage heat and process substrates, which impacts uniformity and throughput.
Hot-Wall vs. Cold-Wall Reactors
A hot-wall reactor, common in LPCVD, is an externally heated furnace tube where the walls and substrates are at the same high temperature. This design offers excellent temperature uniformity for batch processing many wafers at once but suffers from film deposition on the chamber walls, requiring frequent cleaning.
A cold-wall reactor heats only the substrate, usually from below, while the chamber walls remain cool. This minimizes unwanted wall deposits and is common in single-wafer systems and research, allowing for faster temperature changes and cleaner processing.
Batch vs. Continuous Flow
Batch reactors, like a hot-wall LPCVD furnace, process a set number of substrates at a time. This is ideal for applications demanding high uniformity and quality across many wafers.
Continuous flow reactors, often used in APCVD, move substrates through the reaction zone on a conveyor belt. This enables very high throughput, making it suitable for large-scale industrial coating applications like solar panels or glass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a CVD reactor involves navigating a series of critical compromises. There is no single "best" type; there is only the best fit for a specific goal.
Film Quality vs. Throughput
Processes that yield the highest quality and purity, such as UHVCVD and LPCVD, are generally slower. Conversely, high-throughput systems like APCVD often operate at the expense of film purity and uniformity.
Temperature vs. Substrate Compatibility
Thermal CVD offers a straightforward process but is limited to substrates that can withstand high heat. PECVD breaks this thermal budget constraint, enabling a vast range of new applications, but it can introduce its own challenges like plasma-induced damage or hydrogen incorporation into the film.
Cost vs. Complexity
APCVD systems are relatively simple and inexpensive to build and operate. As you move to lower pressures (LPCVD and UHVCVD) or add plasma capabilities (PECVD), the required vacuum pumps, power supplies, and control systems dramatically increase the reactor's cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of reactor technology must be directly aligned with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost coatings: APCVD is the most effective solution due to its high deposition rates and simple setup.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, uniform films for microelectronics: LPCVD is the established industry standard for materials like polysilicon and silicon nitride.
- If your primary focus is depositing films on temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is the essential choice to avoid thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is atomic-level precision for advanced research: UHVCVD provides the ultimate control and purity required for creating next-generation materials and devices.
Ultimately, selecting the right CVD reactor is about precisely matching the process capabilities to the specific requirements of your material and application.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Primary Classification | Key Characteristic | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| APCVD | Pressure (Atmospheric) | High deposition rate, simple equipment | High-volume, low-cost coatings (e.g., glass) |
| LPCVD | Pressure (Low) | High-purity, uniform films | Microelectronics (e.g., polysilicon) |
| PECVD | Energy Source (Plasma) | Low-temperature deposition | Temperature-sensitive substrates (e.g., plastics) |
| UHVCVD | Pressure (Ultra-High Vacuum) | Atomic-level precision, minimal contamination | Advanced research & epitaxial layers |
Ready to Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition Process?
Choosing the right CVD reactor is critical for achieving your desired film quality, throughput, and substrate compatibility. The experts at KINTEK are here to help you navigate these critical trade-offs. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including CVD systems, to meet the precise needs of your research or production goals.
Let us help you select the perfect system to enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Contact our technical specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained



















