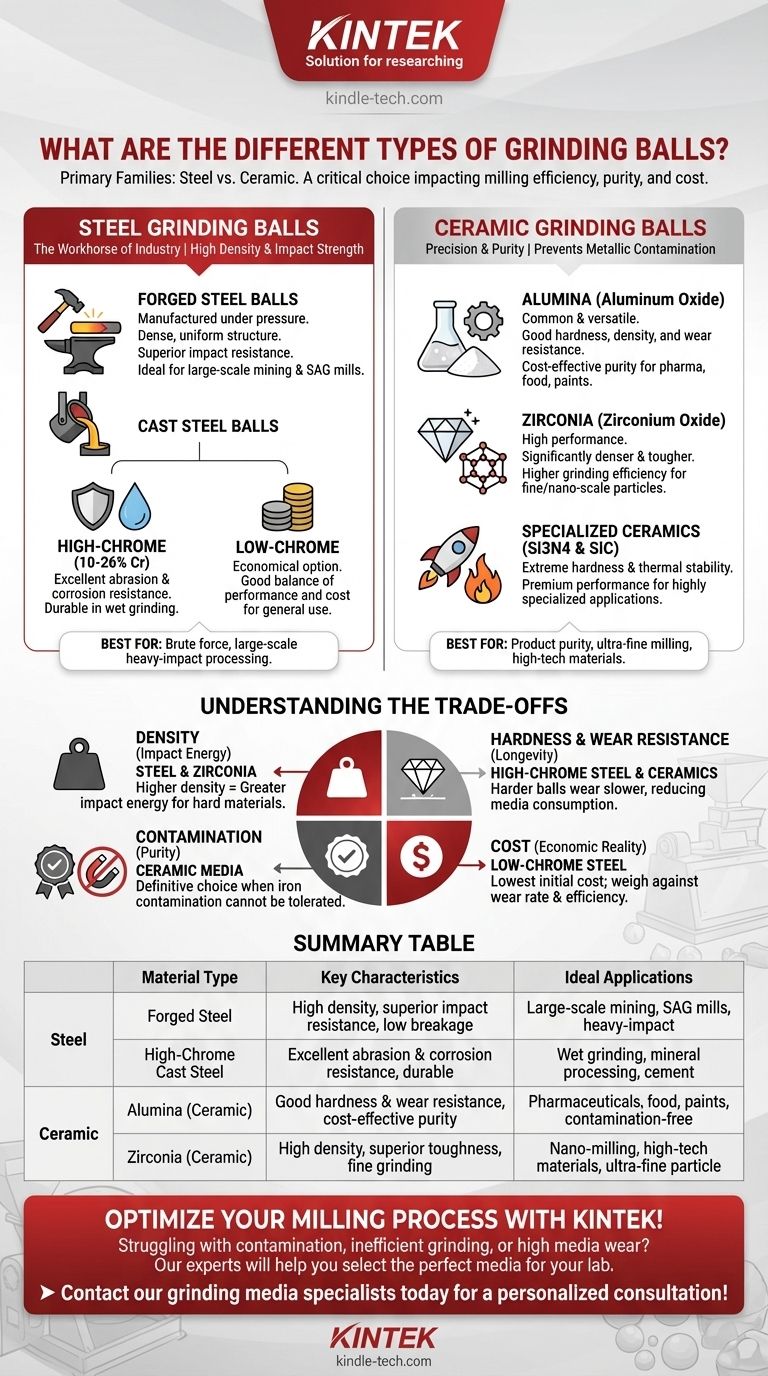
The primary types of grinding balls are broadly categorized by their material composition, most commonly falling into two main families: steel and ceramic. Steel balls, including forged and cast chrome variants, are the industry standard for large-scale, heavy-impact applications like mining. Ceramic balls, such as alumina and zirconia, are chosen for applications where preventing metallic contamination and achieving fine particle sizes are critical.
The selection of a grinding ball is a critical decision that directly impacts milling efficiency, product purity, and operational cost. The core trade-off lies between the brute force and cost-effectiveness of steel media versus the precision and purity offered by ceramic media.
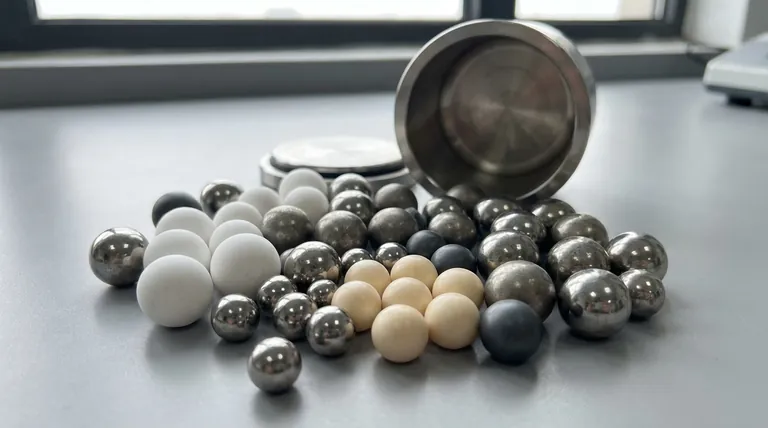

The Two Primary Families: Steel vs. Ceramic
The most fundamental distinction in grinding media is the material. This choice dictates nearly every performance characteristic, from impact strength to the potential for contaminating the material being milled.
Steel: The Workhorse of Industry
Steel grinding balls are the default choice for most large-scale industrial grinding, particularly in mineral processing and cement production. Their high density and impact strength make them exceptionally effective for breaking down large, tough materials.
Ceramics: Precision and Purity
Ceramic media are used when the final product's purity is paramount. Applications in pharmaceuticals, high-tech materials, food products, and paints cannot tolerate the iron contamination that comes from steel balls. They are also essential for achieving very fine, or even nano-scale, particle sizes.
A Deeper Look at Steel Grinding Balls
Within the steel family, the manufacturing process and alloy composition create significant performance differences.
Forged Steel Balls
Forged steel balls are manufactured by heating steel billets and shaping them under extreme pressure. This process creates a very dense, uniform internal structure, resulting in superior impact resistance and a very low breakage rate, making them ideal for high-impact SAG and ball mills.
High-Chrome Cast Steel Balls
As the name implies, these balls are cast from molten steel with a high chromium content (typically 10-26%). The chromium forms extremely hard chromium carbide compounds within the steel matrix, providing excellent abrasion and corrosion resistance. This makes them highly durable, especially in wet grinding environments.
Low-Chrome Cast Steel Balls
This is a more economical option where the intense wear resistance of high-chrome is not required. Low-chrome cast balls offer a good balance of performance and cost for less demanding applications, though they will wear faster than their high-chrome counterparts.
Exploring the Spectrum of Ceramic Media
Ceramic grinding media offer a wide range of properties based on their specific chemical composition.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide)
Alumina is one of the most common and versatile ceramic media. It offers good hardness, density, and excellent wear resistance at a reasonable cost. It is a reliable choice for a wide array of applications where metal contamination is a concern.
Zirconia (Zirconium Oxide)
Zirconia balls are a step up in performance. They are significantly denser and tougher than alumina, allowing for much higher grinding efficiency and the ability to mill materials to finer particle sizes. This high density translates to greater impact energy in the mill.
Specialized Ceramics: Silicon Nitride & Carbide
Materials like silicon nitride and silicon carbide represent the high-performance end of the spectrum. They offer extreme hardness and thermal stability but come at a premium price. They are reserved for highly specialized applications where other media fail to perform.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right media involves balancing four critical factors. Each material type presents a different profile of strengths and weaknesses.
Density: The Driver of Impact Energy
Higher density means more mass in the same volume, leading to greater kinetic energy upon impact. This is why dense zirconia and steel balls are so effective at milling hard materials and reducing particle size quickly.
Hardness & Wear Resistance: The Key to Longevity
A harder grinding ball will wear down more slowly, reducing media consumption costs and maintaining a consistent charge in the mill. High-chrome steel and most ceramics excel in this area.
Contamination: The Purity Factor
This is often the deciding factor. If your process cannot tolerate iron contamination, steel media is not an option. Ceramic media is the definitive choice for ensuring product purity.
Cost: The Economic Reality
The initial purchase price of grinding media varies dramatically. Low-chrome steel is the most affordable, while specialized ceramics like silicon nitride are the most expensive. This cost must be weighed against media wear rate and grinding efficiency to determine the true operational cost.
How to Select the Right Grinding Media
Your choice should be dictated by your specific process goals and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is large-scale ore processing: Forged or high-chrome cast steel balls provide the necessary impact strength and wear resistance at an effective cost.
- If your primary focus is preventing metal contamination: Alumina or zirconia ceramic balls are the only viable options to ensure product purity.
- If your primary focus is achieving ultra-fine particle sizes (nanomilling): High-density zirconia balls deliver the high impact energy required for efficient fine grinding.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance and budget: High-purity alumina offers excellent value for contamination-sensitive applications, while low-chrome steel works well for general-purpose grinding.
Ultimately, the optimal grinding media is the one that aligns perfectly with your material, process, and purity requirements.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Characteristics | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Forged Steel | High density, superior impact resistance, low breakage | Large-scale mining, SAG mills, heavy-impact grinding |
| High-Chrome Cast Steel | Excellent abrasion & corrosion resistance, durable | Wet grinding, mineral processing, cement production |
| Alumina (Ceramic) | Good hardness & wear resistance, cost-effective purity | Pharmaceuticals, food, paints, general contamination-free milling |
| Zirconia (Ceramic) | High density, superior toughness, fine grinding efficiency | Nano-milling, high-tech materials, ultra-fine particle size reduction |
Optimize your milling process with the right grinding media from KINTEK!
Struggling with contamination, inefficient grinding, or high media wear? Our experts will help you select the perfect steel or ceramic grinding balls to maximize your lab's efficiency, ensure product purity, and reduce operational costs.
➤ Contact our grinding media specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of the grinding process in LiCoO2/LSPS mixtures? Optimize Solid-State Battery Conductivity
- What is the average speed of a ball mill? Optimize Grinding with Critical Speed Calculations
- What is the purpose of ball milling? A Versatile Tool for Material Synthesis and Modification
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials
- What affects ball mill efficiency? Optimize Grinding Speed, Media, and Material for Peak Performance



















