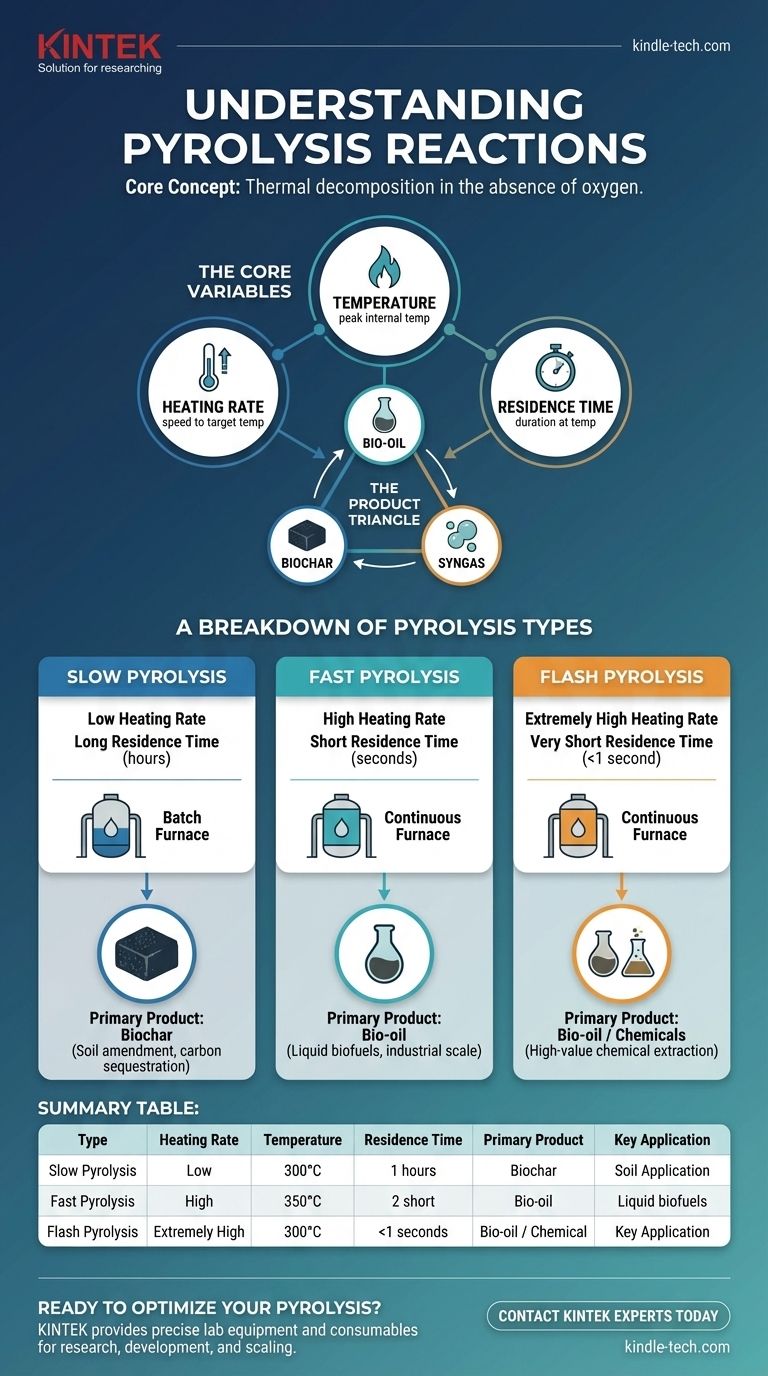
At its core, all pyrolysis is thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen. The primary types of pyrolysis are distinguished not by a fundamental change in chemistry, but by the speed and temperature at which this decomposition occurs. The main categories are slow, fast, and flash pyrolysis, with the key difference being the process conditions—heating rate, temperature, and residence time—which are manipulated to favor the production of either solids (biochar), liquids (bio-oil), or gases (syngas).
The choice between pyrolysis methods is a deliberate engineering decision. By controlling the reaction conditions, you are essentially choosing whether to prioritize the creation of solid biochar for agricultural use, liquid bio-oil for fuel, or valuable chemicals.

The Core Variables That Define Pyrolysis
To understand the difference between the types, you must first understand the three process levers that control the outcome. The balance of these variables dictates the final product distribution.
Heating Rate
This is the speed at which the biomass is brought up to the target pyrolysis temperature. Rates can range from very slow (degrees per minute) to extremely rapid (thousands of degrees per second).
Temperature
This is the peak temperature the material reaches inside the reactor. Different compounds break down at different temperatures, influencing the final chemical makeup of the products.
Residence Time
This refers to the amount of time the raw material (and the vapors it releases) is held at the reaction temperature. This can range from several hours to less than a second.
The Product Triangle: Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas
All pyrolysis reactions produce a mix of the same three core products, but in different proportions.
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid, similar to charcoal.
- Bio-oil: A complex liquid mixture of oxygenated organic compounds. It is a renewable fuel source.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases, primarily carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
A Breakdown of Pyrolysis Types
Each pyrolysis type represents a different set of operating conditions designed to maximize the yield of a specific product.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Solid Biochar
Slow pyrolysis uses a low heating rate and a very long residence time, often lasting several hours.
This process is designed to give the biomass sufficient time to fully carbonize, breaking down volatile components and leaving behind a solid, carbon-rich structure. It is the ideal method for maximizing the production of biochar.
Fast Pyrolysis: Optimizing Liquid Bio-oil
Fast pyrolysis, the most common industrial method, uses a very high heating rate and a short residence time of just a few seconds.
The goal is to rapidly heat the biomass to a vapor before it can break down into char and gas. These vapors are then quickly cooled and condensed into bio-oil. A typical yield is around 60% bio-oil, 20% biochar, and 20% syngas.
Flash Pyrolysis: Pushing the Limits for Liquids and Chemicals
Flash pyrolysis is an even more extreme version of fast pyrolysis, featuring an extremely high heating rate and a residence time of less than one second.
This process further minimizes the opportunity for secondary reactions that form char and gas. It is used to achieve the highest possible yields of bio-oil and specific high-value chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Equipment
The theoretical process conditions must be met by physical equipment, and this introduces practical trade-offs.
The Link Between Process and Reactor
The type of reactor used directly enables the pyrolysis process.
- Slow Pyrolysis is often done in simple batch furnaces or rotary kilns that can hold material for long periods.
- Fast and Flash Pyrolysis require more complex continuous furnaces designed for rapid material feed, intense heat transfer, and quick removal of vapors.
Complexity vs. Yield
There is a direct relationship between process complexity and product value.
Slow pyrolysis is mechanically simpler to achieve but produces biochar, a relatively lower-value bulk product. In contrast, fast and flash pyrolysis require more sophisticated engineering to manage heat and material flow but yield higher-value liquid fuels and chemicals.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
The right type of pyrolysis is entirely dependent on your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the most direct and simplest path to producing stable biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels at an industrial scale: Fast pyrolysis offers the best-established balance for maximizing bio-oil yields.
- If your primary focus is extracting high-value platform chemicals: Flash pyrolysis provides the extreme conditions needed to maximize liquid yields and capture specific chemical compounds.
Ultimately, understanding these reaction types allows you to select the precise thermal conditions to transform biomass into your desired end product.
Summary Table:
| Type of Pyrolysis | Heating Rate | Temperature | Residence Time | Primary Product | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | Low | Moderate | Long (hours) | Biochar | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Fast Pyrolysis | High | Moderate | Short (seconds) | Bio-oil | Liquid biofuels, industrial scale |
| Flash Pyrolysis | Extremely High | Moderate | Very Short (<1 second) | Bio-oil / Chemicals | High-value chemical extraction |
Ready to select the right pyrolysis process for your biomass conversion goals?
The choice between slow, fast, and flash pyrolysis is critical for maximizing your yield of biochar, bio-oil, or syngas. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to research, develop, and scale these processes efficiently.
We help our customers in the laboratory and bioenergy sectors achieve optimal results. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your pyrolysis research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















