While often promoted as a green alternative, the primary disadvantages of biomass pellets relate to their impact on air quality, the potential for unsustainable sourcing that leads to deforestation, and the practical challenges of their supply chain and storage. Burning pellets, while cleaner than raw wood, still releases harmful particulate matter, and their production requires significant energy.
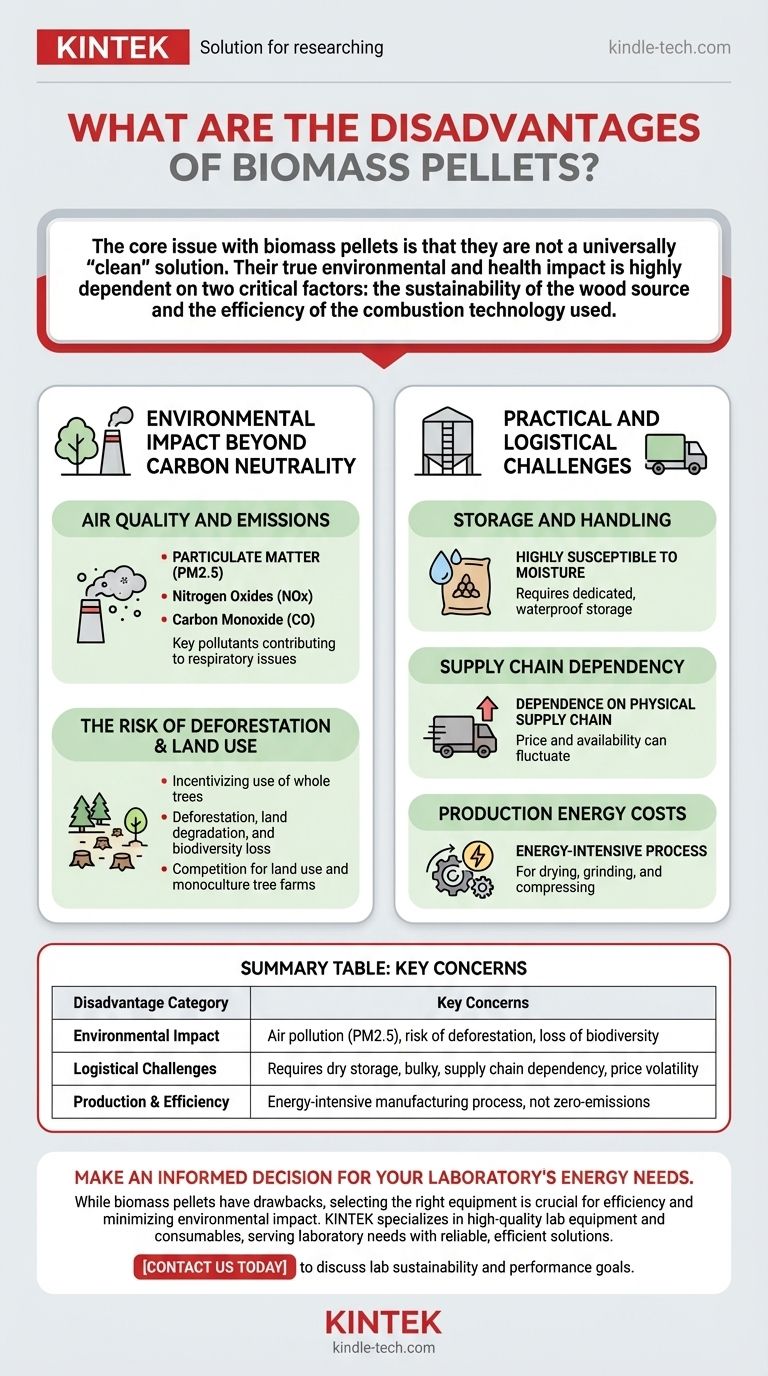
The core issue with biomass pellets is that they are not a universally "clean" solution. Their true environmental and health impact is highly dependent on two critical factors: the sustainability of the wood source and the efficiency of the combustion technology used.

Environmental Impact Beyond Carbon Neutrality
The "carbon neutral" label can be misleading. It only refers to the cycle of carbon absorption by trees and its release during combustion. It does not account for other significant environmental effects.
Air Quality and Emissions
Burning any organic material releases pollutants. While modern pellet stoves are far more efficient than traditional wood fires, they are not emission-free.
The key emissions of concern are particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon monoxide (CO). These pollutants are known to contribute to respiratory problems and other health issues, particularly in areas with poor air circulation.
The Risk of Deforestation
The source of the wood is the most critical factor in a pellet's sustainability. When pellets are made from sawmill residue or sustainably managed forest waste, the impact is minimal.
However, rising demand can incentivize the use of whole trees from clear-cut forests. This practice leads directly to deforestation, land degradation, and a loss of biodiversity, negating any claimed carbon benefits.
Land Use and Competition
Large-scale biomass operations can lead to the creation of monoculture tree farms dedicated to pellet production. This can displace agriculture needed for food production and drastically reduce the natural biodiversity of an area.
Practical and Logistical Challenges
Beyond the environmental concerns, using biomass pellets comes with a set of practical drawbacks that must be considered.
Storage and Handling Requirements
Biomass pellets are highly susceptible to moisture. They must be stored in a completely dry, protected environment to prevent them from swelling and disintegrating, which renders them useless.
This requires dedicated, waterproof storage space, which can be a significant constraint. The pellets are also bulky and are typically delivered in large bags, demanding logistical planning.
Supply Chain Dependency
Unlike solar or geothermal energy, using pellets makes you dependent on a physical supply chain. You must have consistent access to a supplier.
The price and availability of pellets can fluctuate based on demand, transportation costs, and the availability of raw materials, introducing a level of unpredictability.
Production Energy Costs
The process of creating pellets is energy-intensive. It involves drying the raw biomass, grinding it into a fine powder, and then compressing it under extreme pressure. This entire manufacturing and transportation process consumes energy, which can offset some of the fuel's net environmental benefit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
An objective evaluation requires comparing pellets not just to an ideal standard, but to other real-world alternatives.
Pellets vs. Raw Wood
It is crucial to recognize that pellets are a significant improvement over burning raw, moist firewood. Their low moisture content and uniform density allow for a much cleaner, more consistent, and more efficient combustion process with far fewer emissions than a traditional log fire.
The Myth of "Zero Emissions"
No combustion-based energy source is free of emissions. The goal is to minimize them. The term "carbon neutral" should not be confused with "pollution-free." The direct impact on local air quality is a separate and important consideration from the global carbon cycle.
The Importance of Stove Technology
The appliance used to burn the pellets is just as important as the fuel itself. A modern, high-efficiency, EPA-certified pellet stove is designed to maximize heat output while minimizing particulate emissions. Using pellets in an old or inappropriate appliance will produce significantly more pollution.
Making an Informed Decision on Biomass Pellets
To determine if pellets are the right choice, you must weigh their drawbacks against your specific goals and context.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Your top priority must be to verify the source of the pellets, looking for certifications that guarantee they are made from waste or sustainably managed forests.
- If your primary focus is local air quality and health: Invest in the highest-quality, modern, EPA-certified pellet stove available and commit to its regular maintenance.
- If your primary focus is energy independence and convenience: You must realistically assess your access to a reliable supply chain and your capacity for proper, dry storage.
Ultimately, mitigating the disadvantages of biomass pellets depends on making conscious choices about both the fuel you source and the technology you use to burn it.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Concerns |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Air pollution (PM2.5), risk of deforestation, loss of biodiversity |
| Logistical Challenges | Requires dry storage, bulky, supply chain dependency, price volatility |
| Production & Efficiency | Energy-intensive manufacturing process, not zero-emissions |
Make an informed decision for your laboratory's energy needs.
While biomass pellets have drawbacks, selecting the right equipment is crucial for efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable, efficient solutions.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your lab's sustainability and performance goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds





