The primary disadvantage of flash pyrolysis lies in its demanding operational requirements and the associated risks if those conditions are not met. The very speed and efficiency that make the process attractive also make it highly sensitive to variations in feedstock and temperature, which can lead to inconsistent product quality and the potential for harmful environmental emissions.
While flash pyrolysis promises higher yields and faster processing, these advantages are fundamentally tied to significant technical complexity. The core disadvantages stem from the high cost and precision engineering required to prepare feedstock and control the reaction, coupled with the environmental risks of a poorly managed process.
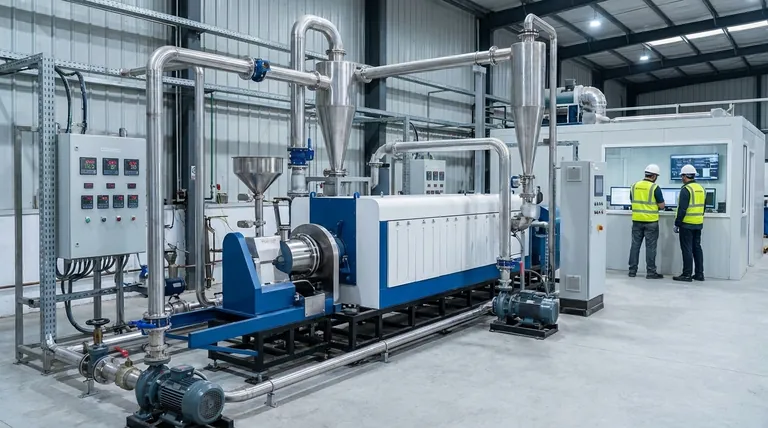

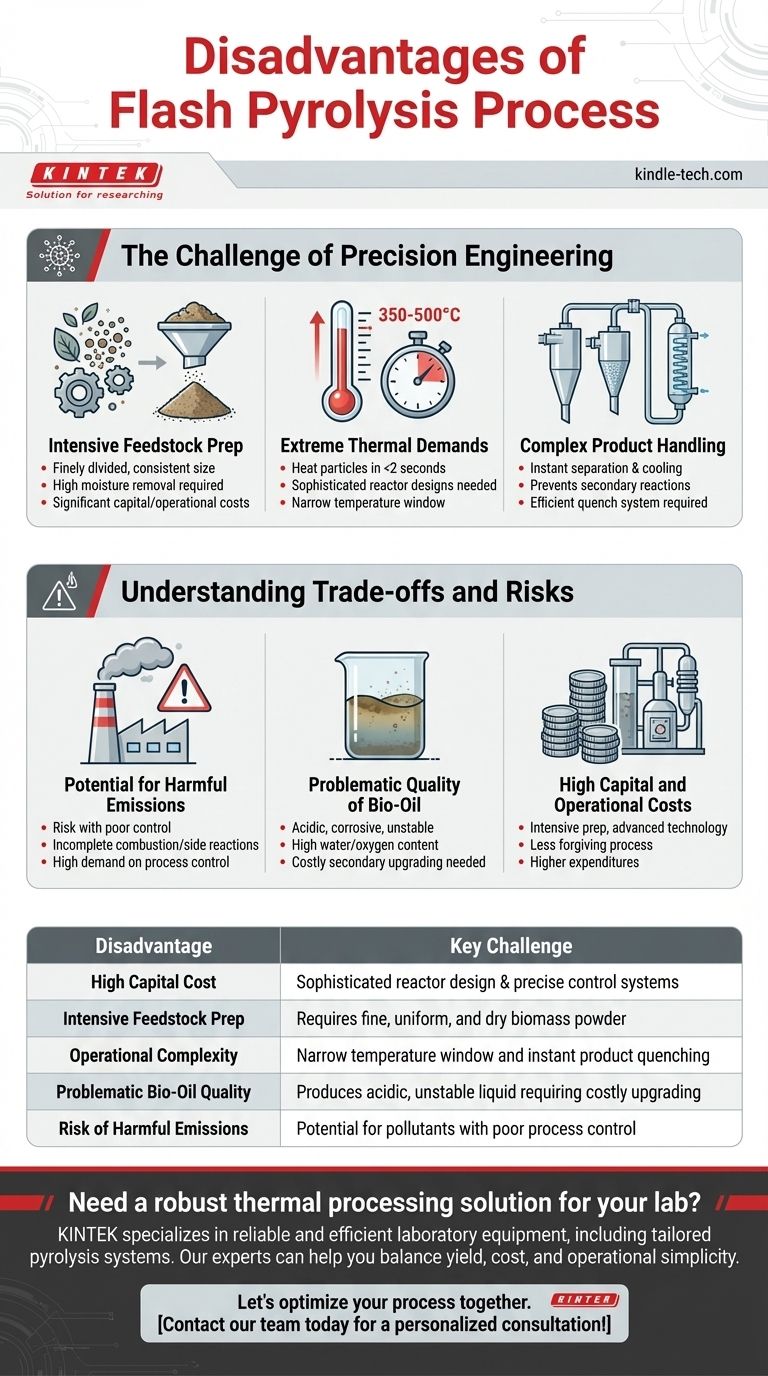
The Challenge of Precision Engineering
The term "flash" pyrolysis implies speed, but achieving this speed reliably requires overcoming significant engineering hurdles before and during the process. These requirements are the source of its primary drawbacks.
Intensive Feedstock Preparation
The process requires feedstock to be finely divided and consistent in size. In practice, this means biomass or other materials must be dried to a low moisture content and then ground into a small, uniform powder.
This pre-processing step adds significant capital and operational costs to the overall system. It requires dedicated equipment for drying and milling, consumes energy, and adds another point of potential failure in the process chain.
Extreme Thermal Demands
Flash pyrolysis operates by heating particles to 350-500°C in less than two seconds. Achieving this rapid heat transfer is technically challenging and demands sophisticated and expensive reactor designs, such as fluidized bed or ablative reactors.
Simple furnaces are inadequate. The system must be engineered to prevent both overheating, which reduces liquid yield, and under-heating, which results in incomplete conversion. This narrow operational window requires precise temperature control.
Complex Product Handling
The rapid decomposition produces a complex mixture of hot gases, aerosols (bio-oil), and solid char. These products must be separated and cooled almost instantaneously to prevent secondary reactions that degrade the valuable liquid bio-oil.
This necessitates an efficient system of cyclones and condensers (a quench system) that can handle high throughputs and high temperatures, further adding to the system's complexity and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The benefits of flash pyrolysis are clear, but they come with operational and environmental trade-offs that must be carefully managed. Failure to do so can negate the advantages of the process.
Potential for Harmful Emissions
As with any high-temperature thermal process, there is a risk of producing harmful emissions if it is not perfectly controlled. The reference to "proper design, operation, and maintenance" highlights that this is a non-trivial operational burden.
If the process parameters drift, incomplete combustion or undesired side reactions can generate pollutants that negatively impact air quality. This places a high demand on process control systems and skilled operators.
The Problematic Quality of Bio-Oil
While the raw liquid product (bio-oil) can be a better feedstock for upgrading than products from slower pyrolysis, it is not a finished fuel. It is typically acidic, corrosive, unstable, and contains a high amount of water and oxygen.
This means bio-oil cannot be used directly in most conventional engines or refineries. It requires significant, often costly, secondary processing (upgrading) to become a stable, usable biofuel, which must be factored into the economic model.
High Capital and Operational Costs
Ultimately, the need for intensive feedstock preparation, sophisticated reactor technology, precise process control, and product upgrading translates into high capital and operational expenditures. The process is far less forgiving and more expensive to build and run than slower, simpler thermal conversion methods.
Making an Informed Decision for Your Project
Choosing the right thermal process depends entirely on your specific goals, resources, and tolerance for operational complexity.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid yield for high-value chemical production: Flash pyrolysis is a strong candidate, but you must be prepared for significant investment in reactor technology and product upgrading.
- If your primary focus is robust, low-cost waste volume reduction: A slower, less complex pyrolysis or gasification process may be more economically viable and operationally forgiving.
- If your primary focus is generating electricity from biomass with minimal pre-processing: A direct combustion or a more robust gasification system is likely a better-suited technology.
Understanding these inherent complexities is the first step toward successfully harnessing the power of this advanced thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Challenge |
|---|---|
| High Capital Cost | Sophisticated reactor design & precise control systems |
| Intensive Feedstock Prep | Requires fine, uniform, and dry biomass powder |
| Operational Complexity | Narrow temperature window and instant product quenching |
| Problematic Bio-Oil Quality | Produces acidic, unstable liquid requiring costly upgrading |
| Risk of Harmful Emissions | Potential for pollutants with poor process control |
Need a robust thermal processing solution for your lab?
While flash pyrolysis has its place, its high complexity and cost may not suit every project. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable and efficient laboratory equipment, including pyrolysis systems tailored to your specific research and production goals. Our experts can help you select the right technology to balance yield, cost, and operational simplicity.
Let's optimize your process together. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















