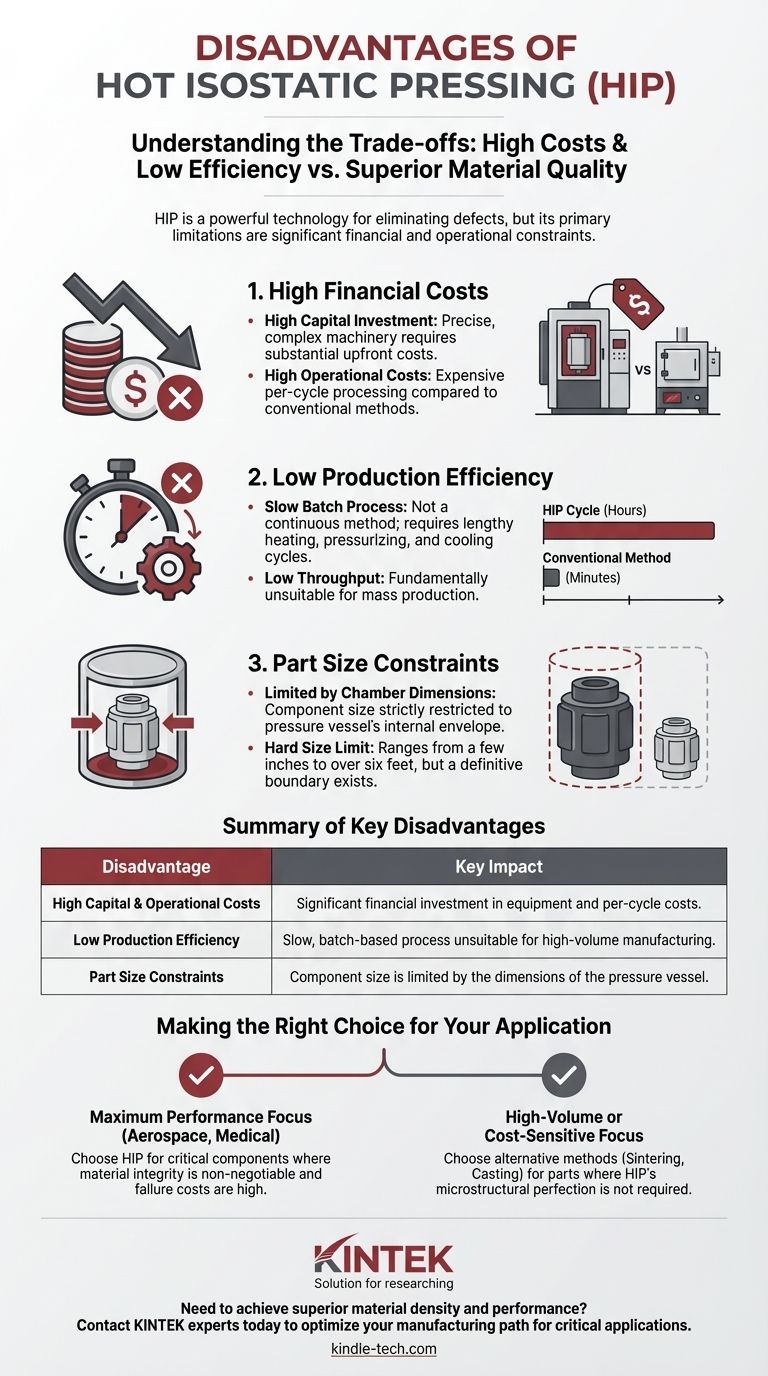
While a powerful technology for eliminating defects, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is primarily limited by its significant financial and operational costs. The process is characterized by low production efficiency and high capital investment, making it unsuitable for high-volume or cost-sensitive applications where alternative methods are sufficient.
The primary disadvantages of Hot Isostatic Pressing are not technical failures but economic and logistical realities. You are trading higher production costs and slower cycle times for unparalleled improvements in material density, uniformity, and mechanical performance.

Why Choose HIP in the First Place?
To understand the disadvantages of HIP, it's crucial to first recognize the unique problems it solves. Manufacturers invest in this technology to achieve material properties that are often unattainable through other means.
Eliminating Internal Porosity
HIP subjects components to both elevated temperature and high, uniform pressure from all sides. This combination effectively collapses and welds shut internal voids, pores, and defects within a material.
This is critical for additively manufactured (3D printed) parts, which often suffer from porosity and poor layer adhesion that can compromise structural integrity.
Creating Uniform Microstructures
The isostatic pressure ensures that density is increased uniformly throughout the entire part, regardless of its shape. This prevents the anisotropy (direction-dependent properties) that can occur with unidirectional pressing methods.
The result is a homogenous material with predictable and consistent mechanical properties, such as improved ductility and fatigue resistance.
Consolidating Manufacturing Steps
In some workflows, HIP can combine heat treatment, quenching, and aging processes into a single cycle. This consolidation can reduce the total number of manufacturing steps, offsetting some of its inherent slowness.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Core Disadvantages
The decision to use HIP hinges on whether its benefits justify its significant drawbacks. These disadvantages are almost entirely related to cost and production logistics.
High Production and Equipment Costs
The machinery required for HIP is precise, complex, and must safely handle extreme pressures and temperatures. This results in a very high initial capital investment.
Furthermore, the operational cost per cycle is substantial, making the price per part much higher compared to conventional sintering or casting methods.
Low Production Efficiency
HIP is a batch process, not a continuous one. Loading the chamber, running the heating and pressurization cycle, and cooling can take many hours.
This slow cycle time leads to low throughput, making it fundamentally unsuitable for mass production. It is a method for quality, not quantity.
Constraints on Part Size
The size of the component that can be processed is strictly limited by the internal dimensions of the HIP system's cylindrical pressure chamber.
While systems exist in various sizes, from a few inches to over six feet in diameter, there is always a hard limit on the part's envelope.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing whether to use Hot Isostatic Pressing requires a clear understanding of your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and reliability: HIP is the superior choice when the cost of component failure is extremely high and material integrity is non-negotiable, as in aerospace or medical implants.
- If your primary focus is high-volume or cost-sensitive production: Alternative methods like conventional sintering, casting, or forging are far more economically viable for parts that do not require HIP's level of microstructural perfection.
Ultimately, viewing Hot Isostatic Pressing as a specialized finishing step for critical components, rather than a general manufacturing method, is the key to leveraging its power effectively.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Capital & Operational Costs | Significant financial investment in equipment and per-cycle costs. |
| Low Production Efficiency | Slow, batch-based process unsuitable for high-volume manufacturing. |
| Part Size Constraints | Component size is limited by the dimensions of the pressure vessel. |
Need to achieve superior material density and performance for your critical components?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for materials testing and processing. If you're developing components for aerospace, medical implants, or other high-performance applications, our expertise can help you determine the most efficient and effective manufacturing path.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material challenges and how our solutions can help you optimize for quality and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance
- What is the HIP material process? Achieve Near-Perfect Density and Reliability
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process



















