Despite its appeal, the process of converting plastic waste into fuel through pyrolysis is fraught with significant environmental, operational, and economic disadvantages. The high temperatures required and the chemical complexity of mixed plastic waste create challenges that are often overlooked, including the potential for harmful air emissions and the creation of other contaminated byproducts that require careful management.
The core challenge of plastic pyrolysis is that it is not a clean or simple solution. It is an energy-intensive industrial process that can trade one form of pollution (solid waste) for another (air emissions and hazardous byproducts) if not executed under stringent, costly controls.
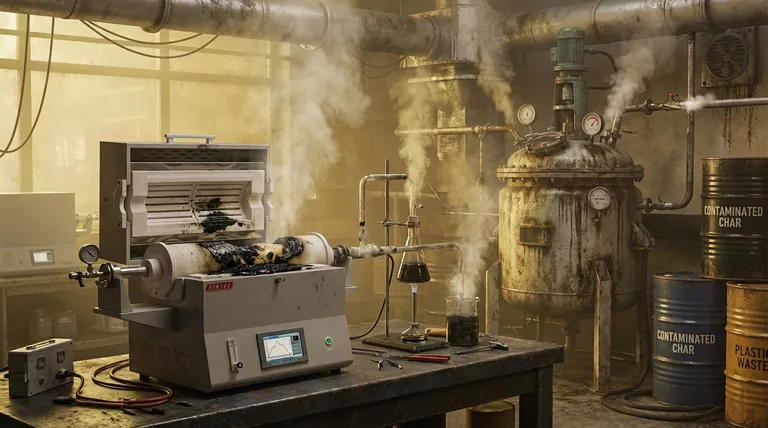
The Challenge of Harmful Byproducts and Emissions
The primary promise of pyrolysis is to break down complex plastics into simpler, useful substances. However, the reality of this chemical decomposition is messy and creates outputs that can be just as problematic as the original waste.
Air Quality Concerns
The process requires heating plastic to extremely high temperatures (200-900°C) in a low-oxygen environment. If the system is not perfectly designed, operated, and maintained, these conditions can lead to the release of harmful emissions into the atmosphere, negatively impacting air quality.
Any leaks or incomplete combustion can release a cocktail of pollutants, undermining the technology's claim as an "environmentally friendly" solution.
Creation of Contaminated Byproducts
Pyrolysis doesn't just create liquid fuel. It also produces a solid residue known as char and non-condensable gases. The composition of this char can be contaminated with heavy metals, additives, and other toxins present in the original plastic waste, making its disposal a new environmental challenge.
High Energy and Operational Demands
The theoretical simplicity of "heating plastic" belies a complex and resource-intensive industrial reality. The operational requirements for successful pyrolysis are a major disadvantage, impacting both its environmental footprint and economic viability.
Significant Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures necessary for pyrolysis demands a massive amount of energy. The energy balance of the entire operation can be unfavorable, meaning the energy required to run the plant can be substantial relative to the energy value of the fuel it produces.
This high energy input often relies on traditional power sources, contributing to a carbon footprint that can negate the benefits of recycling plastic.
The Need for Meticulous Pre-treatment
Plastic waste is not a uniform or clean feedstock. The references note the need to remove impurities and grind the material, but this step is a major operational burden. Food residue, dirt, and other non-plastic materials must be removed.
Furthermore, different types of plastic (like PVC, which contains chlorine) can corrode equipment and create highly toxic substances like dioxins during heating, requiring careful sorting before processing. This pre-treatment adds significant cost, labor, and complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Viewing pyrolysis as a perfect cure for plastic pollution is a common pitfall. Acknowledging its trade-offs is critical for any serious evaluation of the technology.
A Waste Management Process, Not a Magic Bullet
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a waste-processing technology. It can reduce the volume of plastic going to landfills, but it does not eliminate the core problem. It transforms a visible solid waste issue into less visible but potentially more harmful issues related to air quality and hazardous byproducts.
Questionable Economic Viability
The combination of high capital costs for the reactor, significant ongoing energy costs, and intensive labor for pre-treatment makes pyrolysis economically challenging. The resulting fuel oil often requires further refining to be usable, adding another layer of expense. This makes it difficult for pyrolysis-derived fuel to compete with conventional fossil fuels on price.
Evaluating Pyrolysis for Your Goal
To make an informed decision, you must align the technology's capabilities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: You must demand a full life-cycle analysis, including the energy source for the plant and a transparent plan for managing all byproducts and emissions.
- If your primary focus is economic investment: You must rigorously assess the cost and consistency of your plastic feedstock, as operational efficiency and profitability are highly sensitive to waste quality and pre-treatment demands.
Ultimately, a clear-eyed assessment reveals that pyrolysis is not a simple fix but a complex industrial process with serious limitations that must be carefully managed.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Harmful air emissions, creation of contaminated char byproduct |
| Operational Demands | High energy consumption, meticulous pre-treatment & sorting required |
| Economic Viability | High capital & operational costs, difficulty competing with conventional fuels |
Need a reliable solution for your laboratory's material processing or waste analysis? The challenges of complex processes like pyrolysis underscore the need for precise, dependable equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools you need for accurate testing, analysis, and research. Let us help you optimize your operations and achieve your sustainability goals with confidence. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What is the function of a tube furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing in a Controlled Atmosphere
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















