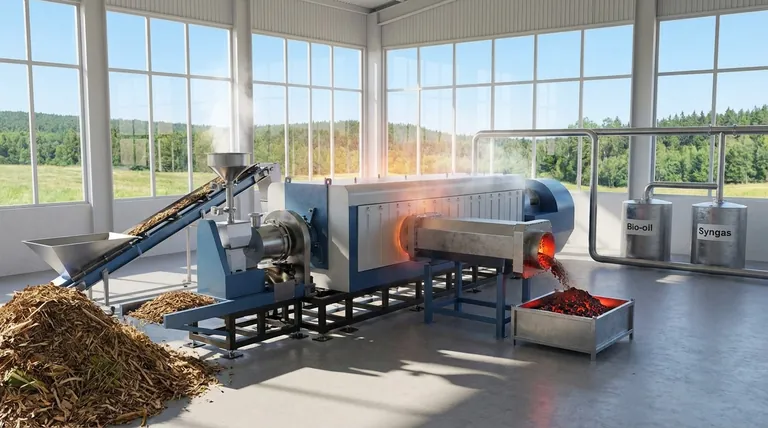
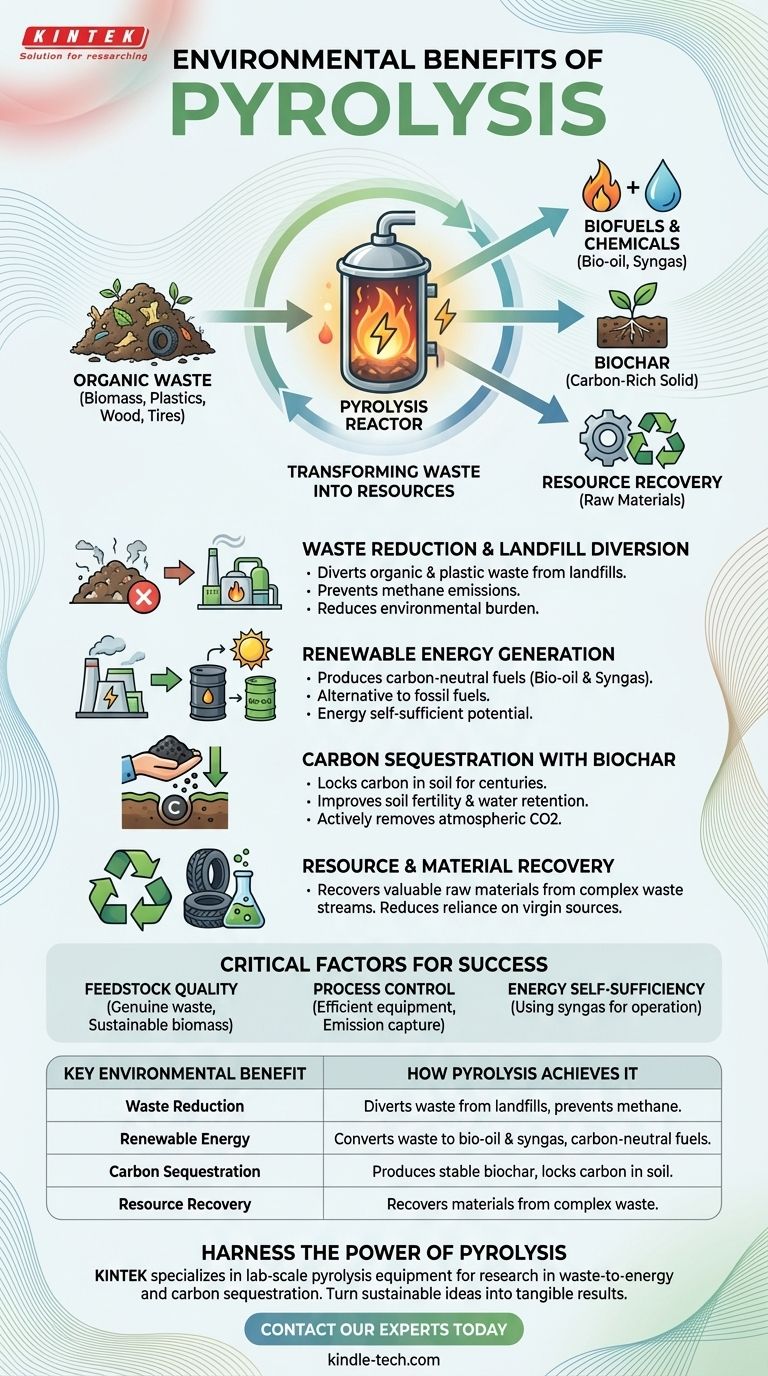
From an environmental standpoint, pyrolysis is a transformative technology. It converts organic waste materials—such as agricultural residues, wood waste, and even plastics—into valuable resources like biofuels, chemicals, and a carbon-rich solid called biochar. This process simultaneously reduces landfill waste, creates alternatives to fossil fuels, and can actively remove carbon from the atmosphere.
The core environmental benefit of pyrolysis is its ability to reframe "waste" as a resource. It creates a circular system where discarded materials are transformed into energy and stable carbon, tackling landfill overflow, fossil fuel dependency, and greenhouse gas emissions in a single process.

A Two-Pronged Approach: Waste Reduction and Resource Creation
Pyrolysis addresses environmental challenges by fundamentally changing how we manage organic materials at the end of their life cycle.
Diverting Waste from Landfills
Most organic waste sent to landfills decomposes and releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Pyrolysis offers a direct alternative by processing these materials, including agricultural residues, wood processing waste, and municipal solid waste, in a controlled environment.
This diversion dramatically reduces the environmental burden of landfills and prevents harmful emissions associated with traditional waste disposal.
Generating Renewable Energy
The process yields two primary energy products: bio-oil and syngas. These can be used directly for heat and power generation or further refined into advanced biofuels and chemicals.
This creates a carbon-neutral energy pathway. The carbon released during combustion is equivalent to the carbon absorbed by the biomass during its growth, unlike fossil fuels which release ancient, trapped carbon into the atmosphere.
Creating High-Value Biochar
The solid byproduct, biochar, is a stable, charcoal-like substance rich in carbon. When added to soil, it improves fertility and water retention.
More importantly, it serves as a method of carbon sequestration. The carbon locked within the biochar remains stable in the soil for hundreds or even thousands of years, effectively removing it from the atmospheric carbon cycle.
Recovering Materials from Waste
Pyrolysis can also be used to break down complex waste streams like used tires and plastics. This allows for the recovery of valuable raw materials and chemicals, reducing the environmental impact and energy consumption associated with producing these materials from virgin sources.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the environmental benefits of pyrolysis are not automatic. The net impact depends entirely on how the process is managed.
The Critical Role of Feedstock
The single most important factor is the source of the organic material, or feedstock. The benefits are only realized when using genuine waste materials or biomass from sustainably managed sources.
If pyrolysis drives deforestation or the use of purpose-grown crops that compete with food production, its environmental advantages are completely negated.
The Need for Process Control
A poorly designed or operated pyrolysis system can release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. The technology's clean performance characteristics depend on modern, efficient equipment that ensures complete conversion and captures any potential emissions.
Energy Self-Sufficiency
Modern pyrolysis plants are often designed to be energy self-sufficient, using a portion of the syngas they produce to power the entire operation. This greatly improves the overall energy balance and reduces reliance on external energy inputs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of pyrolysis can be tailored to address specific environmental objectives.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis offers a powerful method to dramatically reduce landfill volume while recovering value from organic and plastic waste streams.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: This technology converts low-value, bulky biomass into energy-dense liquid and gas fuels, providing a decentralized and reliable alternative to fossil fuels.
- If your primary focus is climate change mitigation: The production of biochar for carbon sequestration makes pyrolysis a potentially carbon-negative technology, actively removing CO2 from the atmosphere.
Ultimately, when sourced and managed responsibly, pyrolysis is a critical engineering tool for building a more circular and sustainable economy.
Summary Table:
| Key Environmental Benefit | How Pyrolysis Achieves It |
|---|---|
| Waste Reduction | Diverts organic & plastic waste from landfills, preventing methane emissions. |
| Renewable Energy | Converts waste into bio-oil & syngas, creating carbon-neutral fuels. |
| Carbon Sequestration | Produces stable biochar that locks carbon in soil for centuries. |
| Resource Recovery | Recovers valuable materials from complex waste streams like tires and plastics. |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis for your sustainability goals?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab-scale pyrolysis equipment and consumables, empowering researchers and developers to innovate in waste-to-energy and carbon sequestration technologies. Whether you're focused on renewable energy, advanced waste management, or climate change mitigation, our solutions help you turn sustainable ideas into tangible results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's critical role in building a circular economy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















