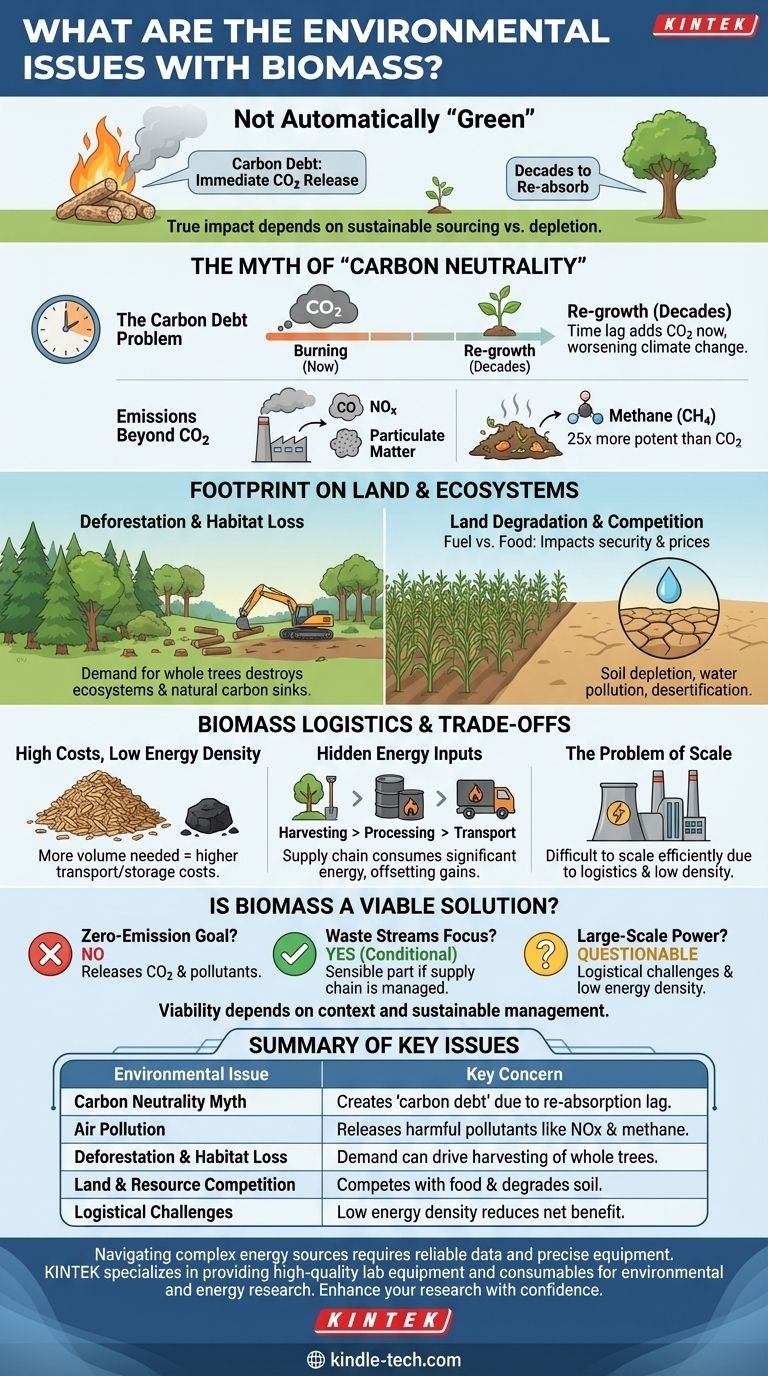
While often presented as a clean, renewable energy source, biomass carries significant environmental liabilities. The primary issues are its potential to drive deforestation, degrade land and ecosystems, and release harmful air pollutants, including greenhouse gases. The sustainability of biomass is not inherent; it is entirely dependent on how the raw material is sourced and managed.
The core environmental problem with biomass is that it is not automatically "green" or "carbon neutral." Its true impact hinges on whether the feedstock comes from sustainable waste streams or from practices that deplete forests and compete with food production, creating a long-term "carbon debt."
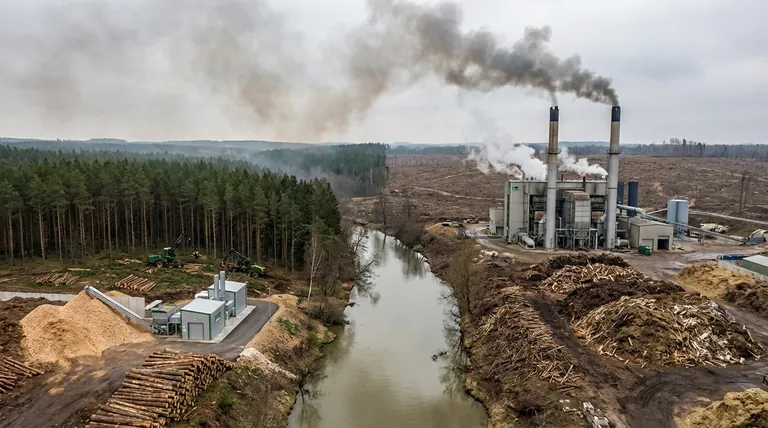

The Myth of "Carbon Neutrality"
The most common argument for biomass is that it's "carbon neutral"—the idea that the carbon dioxide released when biomass is burned is equal to the carbon absorbed by the plants as they grew. The reality is far more complex.
The Carbon Debt Problem
Burning wood or other organic matter releases its stored carbon into the atmosphere immediately. However, it takes decades, if not centuries, for a new forest to grow and re-absorb that same amount of carbon.
This time lag creates a carbon debt, where a large amount of CO2 is added to the atmosphere now, worsening climate change in the short and medium term.
Emissions Beyond CO2
The combustion process is rarely perfect. Burning biomass, especially from inconsistent sources, releases other harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter, which contribute to air pollution and public health issues.
Furthermore, if biomass is left to decay improperly in storage or if it's sourced from organic waste, it can release methane, a greenhouse gas over 25 times more potent than CO2 over a 100-year period.
The Footprint on Land and Ecosystems
Unlike wind or solar, biomass requires a constant physical input, which places immense pressure on land and natural habitats.
Deforestation and Habitat Loss
When demand for biomass outpaces the supply from genuine waste (like sawdust or crop residue), it can create a market for whole trees. This can directly lead to deforestation and the degradation of vital ecosystems.
Harvesting forests for fuel destroys habitats, reduces biodiversity, and impairs the ability of these ecosystems to act as natural carbon sinks.
Land Degradation and Competition
Growing specific crops for energy (energy crops) requires vast areas of land. This creates a direct competition between using land for fuel vs. food, which can impact food security and prices.
Intensive farming of energy crops can also lead to soil depletion, water pollution from fertilizers, and even desertification, making the land unsuitable for future agricultural use.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Reality of Biomass Logistics
The practical challenges of using biomass often undermine its environmental goals. It is a bulky, low-energy fuel that comes with significant hidden costs.
High Costs and Low Energy Density
Biomass has a low energy density compared to fossil fuels. You need to burn a much larger volume of wood pellets, for example, to produce the same amount of energy as a smaller volume of coal or natural gas.
This inefficiency translates directly into higher costs for transportation and storage. Specialized, costly facilities are required to keep the biomass dry and prevent it from decaying.
The Hidden Energy Inputs
The entire biomass supply chain consumes energy. The processes of harvesting, collecting, drying, pelletizing, and transporting the fuel often rely on fossil fuels.
This means that a significant amount of energy is expended just to get the biomass to the power plant, reducing the net energy gain and offsetting some of the intended carbon savings.
The Problem of Scale
Due to its low energy density and complex logistics, biomass is difficult to scale for large, centralized power grids. It is often economically and environmentally inefficient for producing energy on a massive scale compared to other renewable or even conventional sources.
Is Biomass a Viable Environmental Solution?
Biomass is not a simple good-or-bad energy source; its viability depends entirely on the context and your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is a truly zero-emission energy source: Biomass is not the right choice, as its combustion inevitably releases CO2 and other air pollutants.
- If your primary focus is to reduce reliance on fossil fuels using waste streams: Biomass from verified agricultural, forestry, or municipal waste can be a sensible part of a diverse energy portfolio, provided the supply chain is carefully managed.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, centralized power generation: The logistical challenges and low energy density make biomass an economically and environmentally questionable primary fuel source.
Ultimately, the environmental value of biomass is determined not by the fuel itself, but by the discipline and sustainability of the system that produces it.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Issue | Key Concern |
|---|---|
| Carbon Neutrality Myth | Creates a 'carbon debt' due to the time lag in re-absorption of CO2. |
| Air Pollution | Releases harmful pollutants like particulate matter, NOx, and methane. |
| Deforestation & Habitat Loss | Demand can drive the harvesting of whole trees, destroying ecosystems. |
| Land & Resource Competition | Intensive energy crops compete with food production and degrade soil. |
| Logistical Challenges | Low energy density and high transport costs reduce net environmental benefit. |
Navigating complex energy sources requires reliable data and precise equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for environmental and energy research. Whether you're analyzing biomass composition, monitoring emissions, or developing sustainable alternatives, our tools deliver the accuracy you need. Enhance your research with confidence—contact our experts today to find the right solution for your laboratory's challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage of sputtering? Achieve Superior, High-Purity Thin Films from Any Material
- What is the most effective extraction method? Choose the Right CO2 Process for Your Product Goal
- What is the role of a magnetic stirrer in the preparation of nano-filler reinforced epoxy coatings? Maximize Dispersion
- Why is vacuum used in evaporator? Unlock Efficient, Low-Temperature Evaporation
- What are the methods of thin film manufacturing? A Guide to Chemical vs. Physical Deposition
- Why are industrial homogenizers required for composite photosensitive resins? Ensure Uniform Particle Dispersion
- Why is industrial ultrasonic cleaning equipment necessary for UNS S32750 preparation? Ensure Plasma Nitriding Success
- How long does pyrolysis take? From Seconds to Days for Bio-Oil or Biochar



















