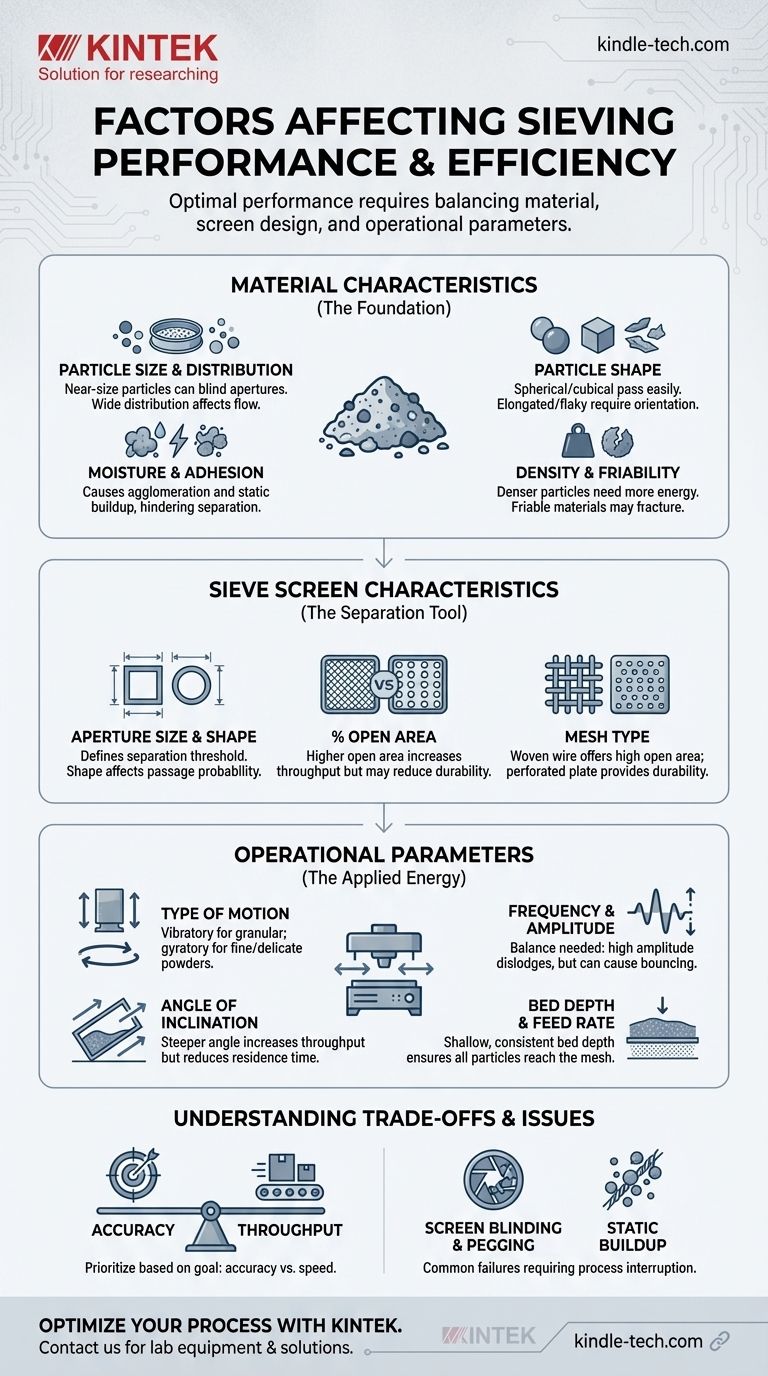
Achieving optimal sieving performance is a matter of controlling the interplay between three core elements: the physical properties of the material being separated, the design of the sieve screen itself, and the operational parameters of the sieving machine. The fundamental principle is to create relative motion between particles and the sieve, but efficiency hinges on how these factors are balanced to maximize the probability of correctly sized particles passing through the mesh apertures.
Sieving efficiency is not determined by a single setting, but by a dynamic system. True optimization comes from understanding how the material's nature, the screen's geometry, and the machine's energy input interact to either facilitate or impede particle separation.

Material Characteristics: The Foundation of Sieving
The properties of the material you are trying to separate are the most critical and often least controllable variables. They dictate the approach you must take for all other parameters.
Particle Size and Distribution
The range of particle sizes in your sample, known as its distribution, directly impacts performance. A sample with a high concentration of particles very close to the aperture size (near-size particles) is much more difficult to sieve efficiently.
These near-size particles tend to block or "blind" the apertures, reducing the available open area for other particles to pass through.
Particle Shape
The shape of the particles significantly affects their ability to pass through the sieve mesh. Spherical or cubical particles have a much higher probability of passing through an aperture than elongated, flat, or irregular particles.
Needle-like or flaky particles may only pass if oriented correctly, requiring more residence time on the screen to achieve proper separation.
Moisture Content and Adhesion
Excess moisture is a primary cause of poor sieving performance. It causes fine particles to agglomerate, or stick together, forming larger clumps that cannot pass through the mesh.
Similarly, static electricity can cause dry, fine powders to adhere to the sieve wires and frame, preventing effective separation.
Material Density and Friability
Heavier, denser particles respond differently to vibration than lighter ones and may require more energy to be properly stratified.
Friability, or the tendency of a material to break down into smaller pieces, is also a concern. Overly aggressive sieving action can fracture brittle particles, altering the particle size distribution and corrupting your results.
Sieve Screen Characteristics: The Separation Tool
The physical design of your sieve screen is the tool that performs the separation. Its specifications must be matched to both the material and your desired outcome.
Aperture Size and Shape
This is the most fundamental characteristic, defining the size threshold for separation. The accuracy of these openings is critical for quality control applications.
While square apertures are most common, other shapes exist for specific applications. The key is consistency across the entire screen surface.
Percentage of Open Area
This refers to the proportion of the screen surface that is holes versus wire or solid material. A higher percentage of open area allows for greater capacity and faster throughput.
However, a higher open area, often achieved with thinner wires, may come at the expense of screen durability and longevity.
Mesh Type (Woven vs. Perforated)
Woven wire mesh is the standard for most laboratory and industrial sieving, offering a high open area. Perforated plate sieves have round or square holes punched in a solid sheet, offering superior durability for abrasive materials but with a lower open area.
Operational Parameters: The Applied Energy
How you operate the sieving equipment determines the energy and motion applied to the material. This is where you have the most direct control to optimize the process.
Type of Motion
The reference to "vertical or horizontal motion" points to different sieving actions. Vibratory motion (vertical tapping and horizontal shaking) is common for granular materials. Gyratory motion (a circular motion in the horizontal plane) is gentler and often used for fine or delicate powders to prevent breakage.
Frequency and Amplitude
Frequency is the speed of the vibration, while amplitude is the intensity or distance of the movement. A balance is crucial.
High amplitude helps dislodge stuck particles but can cause fine material to bounce too high, reducing its chances of finding an aperture. Low amplitude might not provide enough energy to stratify the material bed.
Angle of Inclination
For continuous sieving processes, the angle of the screen deck affects how quickly material travels across it. A steeper angle increases throughput but reduces residence time, potentially lowering the accuracy of the separation.
Bed Depth and Feed Rate
The amount of material on the sieve at any one time is the bed depth. If it's too deep, particles at the top never get a chance to reach the screen surface.
Controlling the feed rate to maintain a shallow, consistent bed depth is one of the most effective ways to ensure every particle is challenged by the screen apertures, maximizing efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Issues
Perfect sieving is an ideal. In practice, you must manage a set of competing priorities and common problems.
Accuracy vs. Throughput
This is the most fundamental trade-off. Achieving very precise, accurate separation requires more time on the screen and a lower feed rate. Pushing for maximum throughput (tons per hour) almost always involves a sacrifice in separation efficiency.
Screen Blinding and Pegging
These are the two primary modes of screen failure. Blinding occurs when near-size particles get stuck in the apertures, blocking them. Pegging is when an oversized, irregular particle (like a sliver) becomes wedged in an opening.
Both phenomena drastically reduce the screen's open area and efficiency, requiring process interruption for cleaning.
Static Buildup
For fine, non-conductive powders, static electricity can be a significant problem. It causes particles to repel each other and cling to the screen wires, severely hindering performance. Grounding the equipment and controlling humidity can help mitigate this.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational strategy should be dictated by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing accuracy for quality control: Prioritize a lower feed rate, select the right motion type for your material, and conduct regular checks for screen blinding.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput for production: Optimize for a higher percentage of open area in your screen and fine-tune the screen's angle and vibration to move material across quickly while maintaining acceptable separation.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting poor separation: Begin by examining the material for excess moisture or static, then check for screen blinding, and finally, experiment with adjusting the machine's amplitude and frequency.
By systematically evaluating these factors, you can move from a brute-force approach to a controlled and highly efficient separation process.
Summary Table:
| Factor Category | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Material Characteristics | Particle size & shape, moisture content, adhesion, density, friability |
| Sieve Screen Design | Aperture size & shape, percentage of open area, mesh type (woven vs. perforated) |
| Operational Parameters | Type of motion, frequency & amplitude, angle of inclination, bed depth & feed rate |
Struggling with inconsistent sieving results or low throughput? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions tailored to your specific laboratory needs—whether for precise quality control or high-volume production. Let us help you select the right sieves and optimize your process for maximum accuracy and efficiency. Contact KINTEL today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide



















