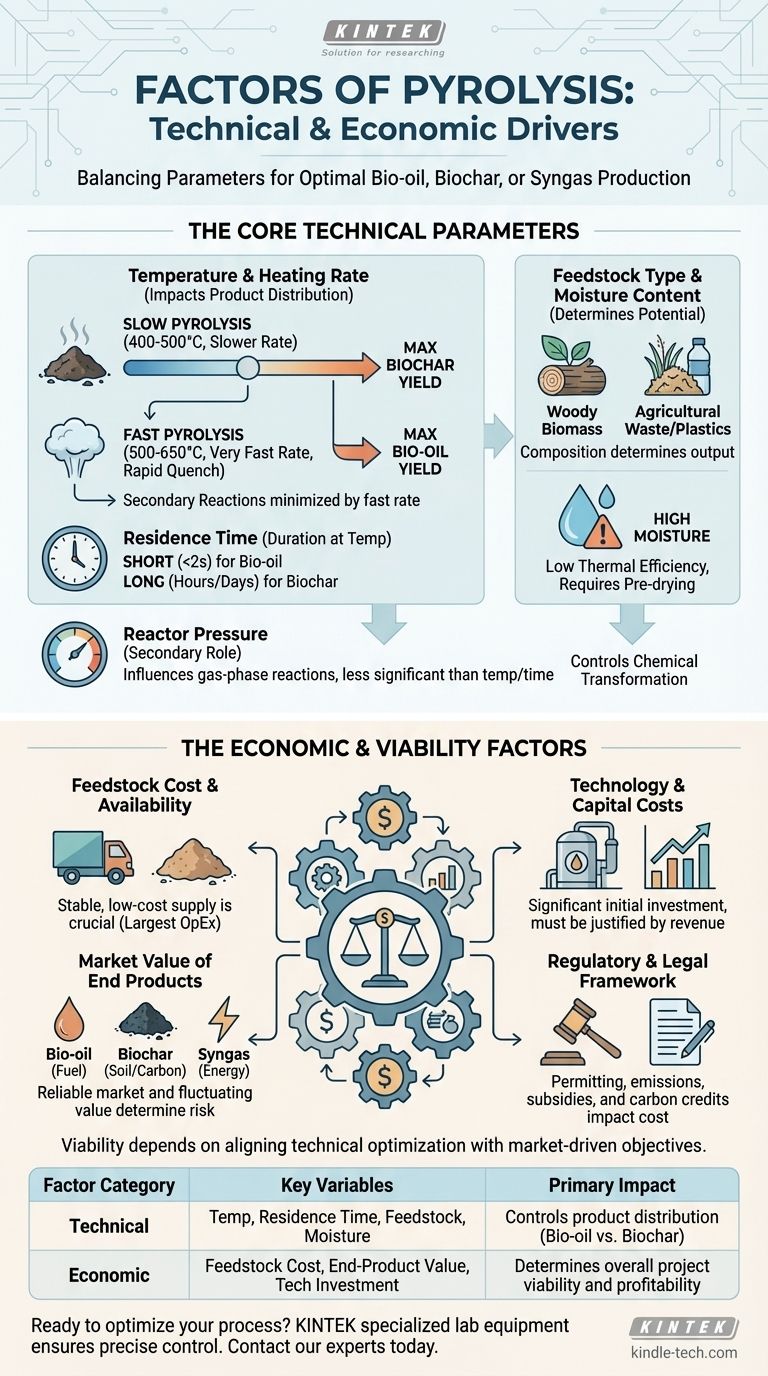
In short, the factors of pyrolysis fall into two distinct categories: the technical parameters that govern the chemical reaction and the economic conditions that determine a project's overall viability. The key technical factors include temperature, residence time, feedstock type, and moisture content, while the economic factors are driven by the cost of feedstock, the value of the end products, and the initial technology investment.
The central challenge of pyrolysis is not merely managing a thermal process, but strategically balancing these technical and economic levers. The "optimal" conditions are entirely dependent on your end goal, whether that is maximizing liquid fuel, solid biochar, or overall project profitability.

The Core Technical Parameters
To control the outcome of pyrolysis, you must first understand the primary technical inputs that dictate the chemical transformation of the feedstock.
Temperature and Heating Rate
Temperature is the most critical factor in pyrolysis. It directly influences the product distribution (the ratio of gas, liquid, and solid outputs).
A slower heating rate at lower temperatures (around 400-500°C) allows for secondary reactions, maximizing the yield of solid biochar. This is known as slow pyrolysis.
Conversely, a very fast heating rate at moderate temperatures (around 500-650°C) with rapid quenching minimizes secondary reactions, maximizing the yield of liquid bio-oil. This is known as fast pyrolysis.
Feedstock Type and Moisture Content
The composition of your input material, or feedstock, fundamentally determines the potential outputs. A woody biomass rich in cellulose and lignin will produce different results than agricultural waste or plastics.
Equally important is the moisture content. Water in the feedstock must be evaporated before pyrolysis can begin, which consumes a significant amount of energy. High moisture content lowers the overall thermal efficiency of the process, making pre-drying a critical step for many operations.
Residence Time
Residence time is the duration the feedstock spends at the reaction temperature inside the pyrolysis reactor.
It works in tandem with temperature. Fast pyrolysis uses a very short residence time (often less than 2 seconds) to quickly vaporize the material and condense it into bio-oil. Slow pyrolysis uses a much longer residence time (hours or even days) to ensure the complete carbonization of the material into biochar.
Reactor Pressure
While temperature and residence time are the dominant factors, pressure also plays a role. Most pyrolysis systems operate at or near atmospheric pressure.
Increasing pressure can influence the composition of the secondary gas-phase reactions, but for most biomass applications, its impact is less significant than the other variables.
The Economic and Viability Factors
A technically perfect pyrolysis process is useless if it is not economically sustainable. These factors determine if a project can succeed in the real world.
Feedstock Cost and Availability
For most pyrolysis operations, the cost of acquiring and transporting feedstock is the largest ongoing operational expense. A successful project requires a stable, consistent, and low-cost supply of suitable material.
Technology and Capital Costs
The initial investment in the pyrolysis reactor and associated equipment (shredders, dryers, storage tanks) is significant. The cost of the technology must be justified by the potential revenue from the end products.
Market Value of End Products
This is the revenue side of the equation and is often the most critical factor for viability. You must have a reliable market for the bio-oil, biochar, or syngas you produce. The value of these products can fluctuate, introducing market risk.
The Regulatory and Legal Framework
Permitting, emissions regulations, and waste disposal laws can create significant hurdles and costs. Conversely, government incentives, carbon credits, or renewable energy subsidies can dramatically improve a project's financial outlook.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing pyrolysis is a game of balancing competing priorities. Improving one aspect often comes at the expense of another.
Bio-oil vs. Biochar: The Primary Conflict
You cannot simultaneously maximize the yield of both bio-oil and biochar. The conditions that favor one are detrimental to the other. A clear decision must be made about which product is the primary target based on market demand and value.
Efficiency vs. Cost
Pre-drying wet feedstock improves the thermal efficiency of the reactor, but it also requires additional equipment and energy, increasing both capital and operational costs. The added expense of drying must be offset by the value gained from improved efficiency.
Matching Your Process to Your Goal
Your approach to pyrolysis should be dictated by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for agriculture or carbon sequestration: Use slow pyrolysis with lower temperatures and longer residence times to maximize the solid char yield.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid bio-oil as a fuel source: Use fast pyrolysis with very high heating rates and short residence times.
- If your primary focus is on-site energy generation: Optimize the process to produce a mix of combustible syngas and bio-oil that can be used to power the facility itself.
- If your primary focus is economic viability: Begin by securing a low-cost feedstock and confirming a stable market for your chosen end-product before you invest in technology.
Ultimately, successful pyrolysis implementation hinges on aligning these technical and economic factors with a clear, market-driven objective.
Summary Table:
| Factor Category | Key Variables | Primary Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Technical | Temperature, Residence Time, Feedstock Type, Moisture Content | Controls product distribution (bio-oil vs. biochar) |
| Economic | Feedstock Cost, End-Product Value, Technology Investment | Determines overall project viability and profitability |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process? The right laboratory equipment is critical for precise control over temperature, residence time, and feedstock preparation. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab reactors, furnaces, and preparatory equipment to help you accurately test and scale your pyrolysis parameters. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve your specific goals for bio-oil, biochar, or syngas production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- How do I choose a tube furnace? A Guide to Matching Your Process Needs



















