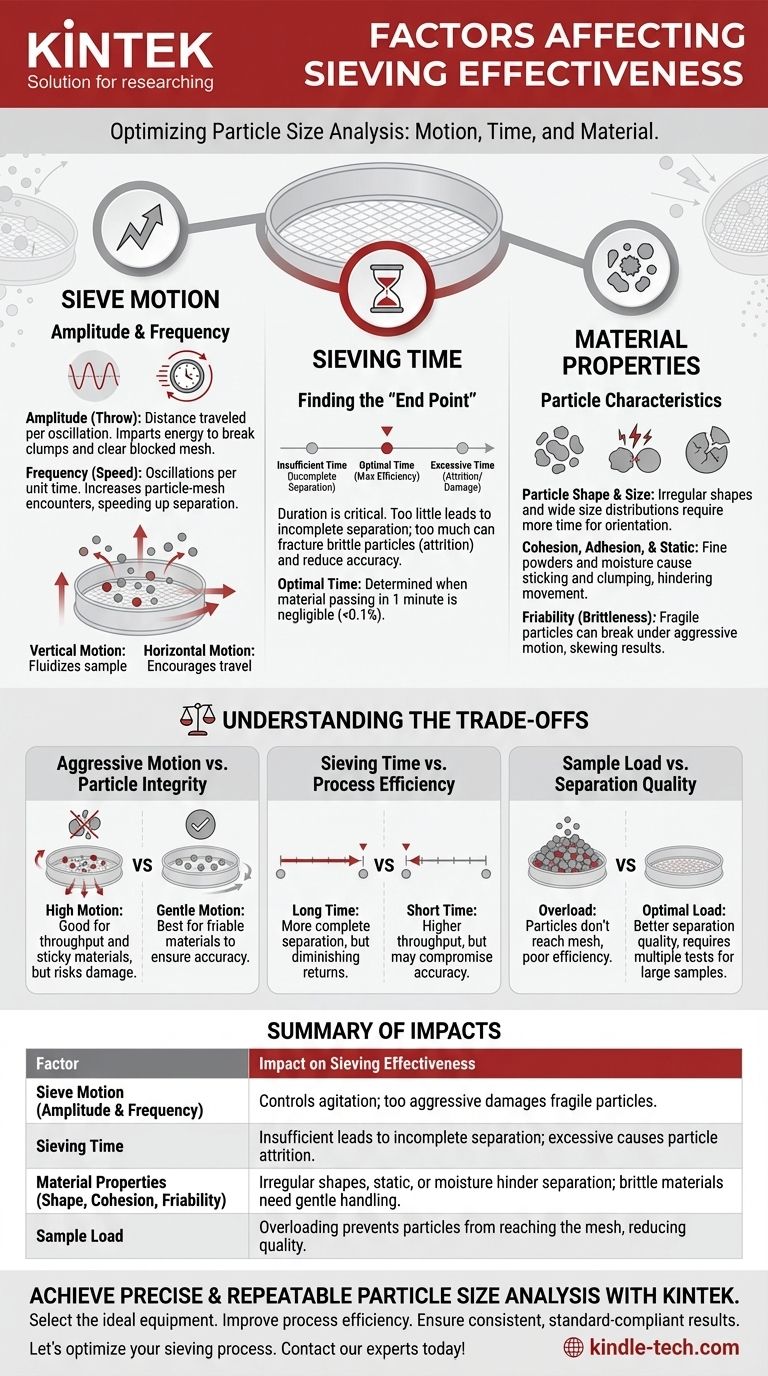
In short, the effectiveness of sieving is determined by the sieve's motion (its amplitude and speed), the total sieving time, and the physical characteristics of the material being separated. These factors work together to dictate the accuracy and efficiency of the particle size analysis.
The core challenge of effective sieving is finding the optimal balance between motion and time. The goal is to provide every particle with enough opportunities to pass through a sieve opening without causing particle damage or clogging the mesh.

The Fundamental Principle of Sieving
Creating Relative Motion
The entire process of sieving relies on one simple principle: creating relative motion between the particles of the sample and the surface of the sieve.
This motion can be vertical, horizontal, or a combination of both. Its purpose is to lift the particles off the mesh and give them a chance to reorient upon landing, presenting a different face to the openings. Without this constant movement, the material would simply sit on the mesh, preventing any meaningful separation.
How Motion Separates Particles
As the sieve moves, particles are agitated. Smaller particles work their way down through the larger ones to reach the mesh.
The combination of the particle's energy and its orientation determines if it passes through. A particle smaller than the mesh opening will pass through if it approaches the opening correctly. A larger particle will be retained.
Key Factors You Can Control
Sieve Motion: Amplitude and Frequency
Amplitude (or throw) is the distance the sieve travels during its oscillation. A larger amplitude imparts more energy, which is effective for breaking up clumped particles and clearing blocked mesh openings (blinding).
Frequency (or speed) is how many oscillations occur per unit of time. Higher frequency increases the number of chances each particle has to encounter an opening, speeding up the separation process. The ideal motion is often a combination of a vertical throw to fluidize the sample and a horizontal motion to encourage particle travel across the mesh.
Sieving Time: Finding the "End Point"
The duration of the sieving process is critical for accuracy. Insufficient time will result in an incomplete separation, with many fine particles remaining in the coarser fraction.
Conversely, excessive sieving time leads to diminishing returns and can even damage brittle particles (a process called attrition), which skews the results by creating more fines. The optimal time is often determined experimentally by sieving until the amount of material passing through the sieve in a one-minute interval is negligible (e.g., less than 0.1% of the sample mass).
The Influence of Material Properties
Particle Shape and Size Distribution
Ideally, particles would be perfect spheres, which pass through openings with ease. In reality, particles can be elongated, flat, or irregular. These shapes require more time and specific motion to orient themselves correctly to pass through the mesh. A sample with a wide range of particle sizes will also behave differently than one with a very narrow distribution.
Cohesion, Adhesion, and Static Charge
Fine powders are often susceptible to cohesion (sticking to each other) and adhesion (sticking to the sieve frame and mesh), especially if moisture is present.
Electrostatic charges can also cause particles to clump together or cling to the sieve. Both effects prevent particles from moving freely and passing through the mesh, leading to inaccurate results.
Friability (Particle Brittleness)
Friable materials are those that are easily broken or crumbled. If the sieving motion is too aggressive (high amplitude or speed), these particles can be fractured. This artificially increases the amount of fine material and produces a particle size distribution that is not representative of the original sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Aggressive Motion vs. Particle Integrity
A fast, high-amplitude motion is excellent for separating dense or sticky materials and achieving high throughput. However, this same motion can destroy friable particles, compromising the accuracy of the analysis. The gentlest motion that still achieves separation is often the best.
Sieving Time vs. Process Efficiency
Longer sieving produces a more complete separation, but only up to a point. Every additional minute yields less and less separated material. For quality control or production environments, you must balance the need for accuracy against the need for timely results.
Sample Load vs. Separation Quality
Overloading a sieve is a common mistake. If the layer of material is too thick, particles in the upper layers never get a chance to reach the mesh. This results in poor separation efficiency. It is better to use a smaller sample or divide a large sample into multiple tests.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your process, you must first define your primary objective. Different goals require different approaches to balancing these factors.
- If your primary focus is analytical accuracy: Follow an established standard (like ISO or ASTM) or experimentally determine the sieving end-point to ensure separation is complete without causing particle attrition.
- If your primary focus is high throughput: Use a more aggressive motion for the shortest time that meets your quality specifications, but validate that this process does not fracture your material.
- If your primary focus is sieving difficult materials (fine, sticky, or fragile): Use a lower sample volume and experiment with intermittent motion or specialized shakers that combine vertical and horizontal movements to gently de-agglomerate the particles.
Understanding how these factors interact transforms sieving from a simple mechanical task into a controlled and repeatable analytical method.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Sieving Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Sieve Motion (Amplitude & Frequency) | Controls particle agitation and orientation; too aggressive can damage fragile particles. |
| Sieving Time | Insufficient time leads to incomplete separation; excessive time can cause particle attrition. |
| Material Properties (Shape, Cohesion, Friability) | Irregular shapes, static, or moisture hinder separation; brittle materials require gentle handling. |
| Sample Load | Overloading prevents particles from reaching the mesh, reducing separation quality. |
Achieve precise and repeatable particle size analysis with KINTEK.
Whether your goal is high-throughput quality control or delicate analytical accuracy, the right lab equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-quality sieves and shakers designed to provide the optimal motion and gentle handling your materials require.
We help you:
- Select the ideal equipment for your specific material properties and separation goals.
- Improve process efficiency and data reliability in your laboratory.
- Ensure consistent, standard-compliant results for materials ranging from dense granules to fine, cohesive powders.
Let's optimize your sieving process. Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
People Also Ask
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification



















