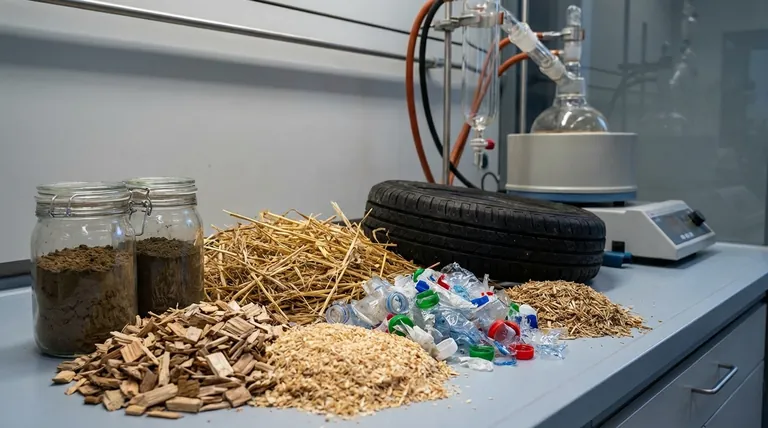
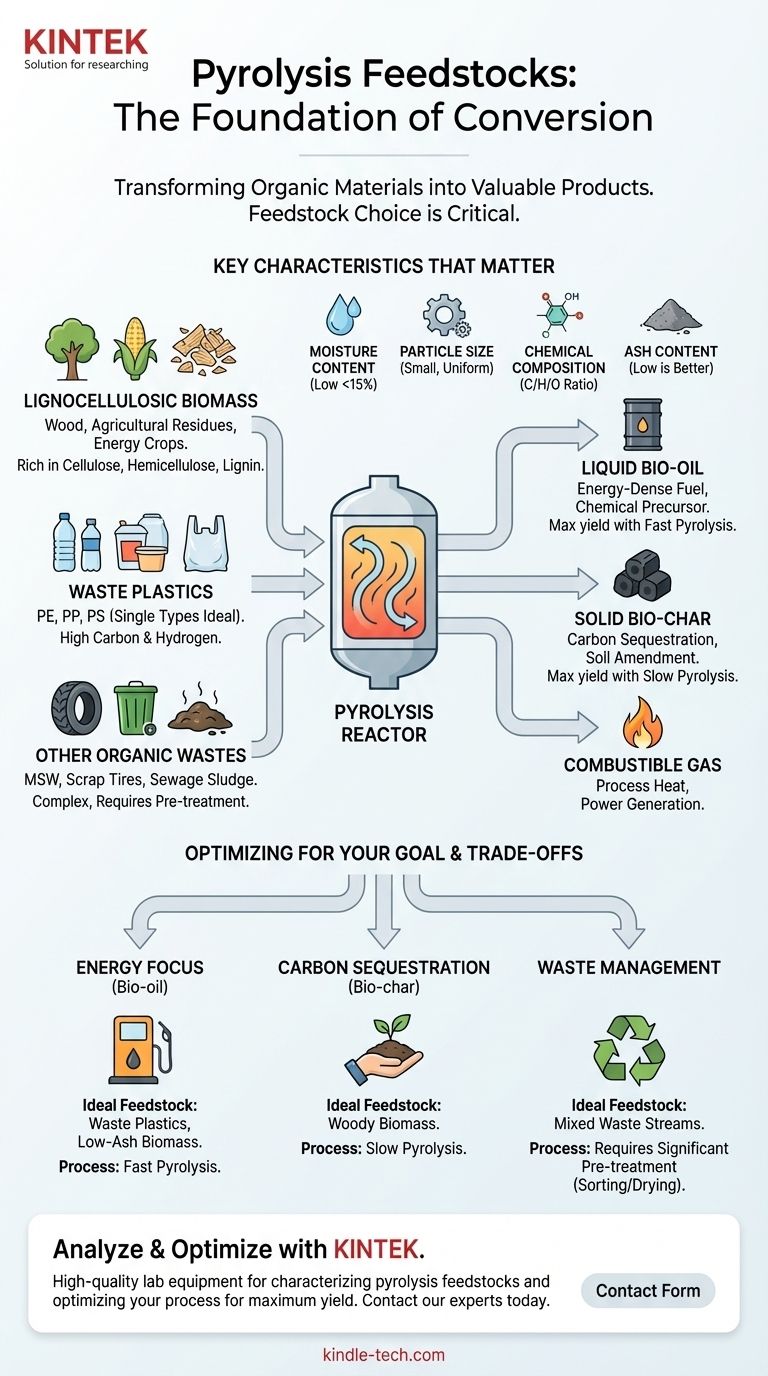
In short, pyrolysis can process a vast range of organic materials. The most common feedstocks fall into three main categories: lignocellulosic biomass (like wood and agricultural waste), waste plastics, and other organic wastes (such as tires and sewage sludge). The choice of feedstock is the single most critical factor that dictates the process conditions required and the final products you will obtain.
The central principle of pyrolysis is that while almost any organic material can be a feedstock, its specific physical and chemical characteristics—primarily moisture, particle size, and elemental composition—will determine the efficiency of the process and whether the primary output is liquid bio-oil, solid bio-char, or combustible gas.

The Universe of Pyrolysis Feedstocks
Pyrolysis is a flexible technology defined by its ability to convert complex organic matter into simpler, more valuable substances. The potential feedstocks are diverse, but they are not interchangeable.
Lignocellulosic Biomass
This is the most traditional and widely studied category of feedstock. It includes any material derived from plants.
These materials are primarily composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. The ratio of these components influences the final product distribution.
Common examples include:
- Woody Biomass: Wood chips, sawdust, and forestry residues.
- Agricultural Residues: Corn stover, wheat straw, rice husks, and sugarcane bagasse.
- Energy Crops: Purpose-grown crops like switchgrass and miscanthus.
Waste Plastics
Using waste plastics as a feedstock is a rapidly growing field known as chemical recycling. This process aims to convert plastics back into a liquid hydrocarbon oil, which can be used to produce new plastics or fuels.
Ideal feedstocks are "clean" streams of single plastic types, such as:
- Polyethylene (PE): Used in plastic bags, films, and bottles.
- Polypropylene (PP): Found in containers, packaging, and automotive parts.
- Polystyrene (PS): Used for disposable cups and foam packaging.
Mixed plastic waste is more challenging due to varying compositions and the presence of contaminants.
Other Organic Wastes
Pyrolysis also serves as a powerful waste management tool for various other challenging organic streams.
These include:
- Municipal Solid Waste (MSW): The organic fraction of household garbage.
- Scrap Tires: A major source of high-quality liquid oil and a solid carbon black (char).
- Sewage Sludge: A wet, complex waste that requires significant drying but can be converted into energy and a nutrient-rich char.
Key Feedstock Characteristics That Matter
Simply having an organic material is not enough. Several key properties determine its suitability for pyrolysis and heavily influence the design and operation of the system.
Moisture Content
Water must be evaporated before the organic material can thermally decompose. High moisture content is a major energy drain on the system, significantly reducing its overall efficiency. Most pyrolysis processes require feedstocks to be dried to below 10-15% moisture.
Particle Size
Heat transfer is fundamental to pyrolysis. Smaller, uniform particles heat up more rapidly and evenly, which is essential for fast pyrolysis where the goal is to maximize liquid bio-oil yield. Large, non-uniform pieces lead to inefficient processing and a lower-quality product.
Chemical Composition
The elemental makeup of the feedstock directly correlates to the output.
- High Carbon & Hydrogen (e.g., Plastics, Tires): These feedstocks produce a higher yield of energy-dense liquid oil.
- High Oxygen (e.g., Biomass): This results in more water, CO, CO2, and oxygenated compounds in the bio-oil, which can make it acidic and less stable.
Ash and Inorganic Content
Ash is the inorganic, non-combustible portion of the feedstock (e.g., dirt, minerals, metals). It does not pyrolyze and ends up concentrated in the solid bio-char. High ash content can lower the quality of the char and may introduce catalytic or corrosive elements into the reactor, causing operational issues.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Feedstock vs. Output
The feedstock you choose and the process you use are directly linked to the product you want to create. There is no "one size fits all" solution.
For Maximum Liquid Bio-oil
If your goal is a liquid fuel or chemical precursor, you need a feedstock and process that favor this outcome. Clean, dry feedstocks like waste plastics (PE, PP) or low-ash biomass are ideal. These are typically processed using fast pyrolysis, which involves rapid heating to moderate temperatures (around 500°C) with a very short vapor residence time.
For Maximum Bio-char
If your primary product is bio-char for carbon sequestration or soil amendment, your strategy changes completely. Woody biomass is the preferred feedstock due to its high lignin content, which creates a stable char. The process used is slow pyrolysis, involving slow heating to a lower temperature over several hours.
The Challenge of Contaminants
Real-world feedstocks are rarely pure. Contaminants can have a severe impact on the process and products.
- Chlorine, often from PVC in mixed plastic waste, forms highly corrosive hydrochloric acid (HCl) gas, which can destroy equipment.
- Sulfur, present in tires and some biomass, can form hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and other undesirable sulfur compounds.
- Heavy metals, found in sewage sludge or treated wood, become concentrated in the char and oil, requiring careful management.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a feedstock is the first and most important step in designing a pyrolysis project. Your decision should be driven by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is energy production (bio-oil): Choose clean, dry feedstocks like waste plastics or low-ash biomass and plan for a fast pyrolysis process.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration (biochar): Use lignocellulosic biomass, particularly wood, in a slow pyrolysis system to produce stable, high-quality char.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Be prepared to invest in significant pre-treatment (sorting, shredding, drying) to handle inconsistent feedstocks like MSW or sludge.
Ultimately, a successful pyrolysis operation begins with a deep understanding and characterization of your input material.
Summary Table:
| Feedstock Category | Key Examples | Primary Product Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Lignocellulosic Biomass | Wood chips, agricultural residues | Bio-char, Bio-oil |
| Waste Plastics | Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP) | Liquid Hydrocarbon Oil |
| Other Organic Wastes | Scrap tires, sewage sludge | Energy, Waste Management |
Ready to select the ideal feedstock for your pyrolysis goals?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for analyzing and processing pyrolysis feedstocks. Whether you're researching biomass conversion, plastic recycling, or waste valorization, our reliable tools help you characterize materials and optimize your process for maximum yield and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and help you achieve your project objectives.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What is a sputtering system? Achieve Unmatched Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What are sputtering systems used for? A Guide to Advanced Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the types of induction melting furnace? Coreless, Channel, and VIM Explained



















