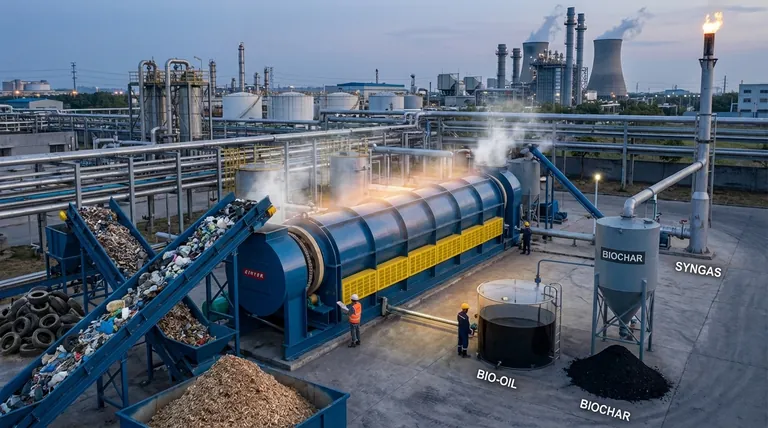
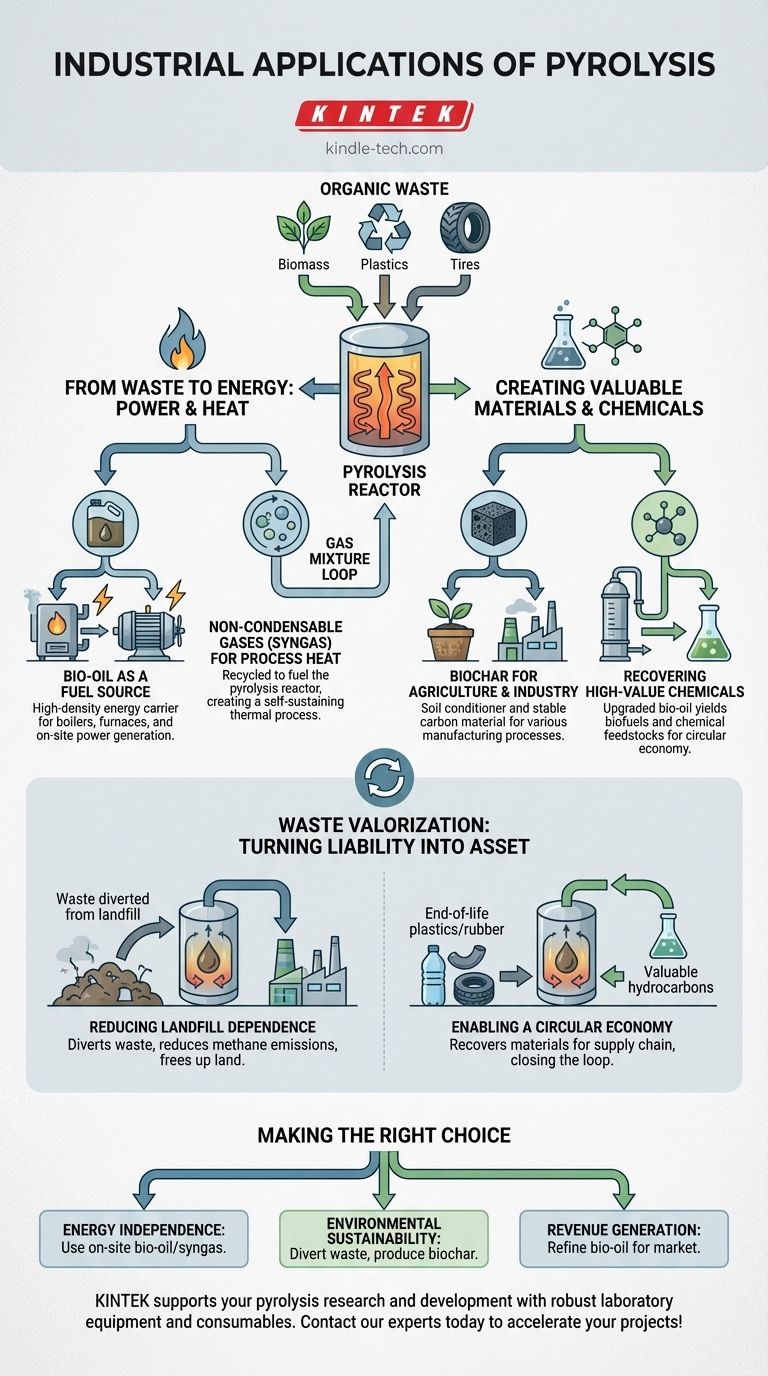
In an industrial context, pyrolysis is a transformative process that converts organic waste materials into valuable energy products and marketable goods. It is primarily applied to turn low-value inputs like biomass, plastics, and tires into three core outputs: a liquid fuel known as bio-oil, a solid residue called biochar, and a combustible gas mixture.
The fundamental industrial value of pyrolysis is its ability to "valorize" waste. It's not simply a disposal method; it's a manufacturing process that creates marketable products from materials that would otherwise end up in a landfill, addressing both environmental and economic objectives.

From Waste to Energy: Power and Heat Generation
One of the most direct applications of pyrolysis is the creation of energy products that can replace or supplement traditional fossil fuels. This allows industries to lower energy costs and reduce their carbon footprint.
Bio-oil as a Fuel Source
The liquid bio-oil produced during pyrolysis is a high-density energy carrier. It can be burned directly in industrial boilers and furnaces to generate heat for various processes.
This oil can also be used to power engines and turbines, enabling on-site electricity production for facilities looking to become more energy independent.
Non-Condensable Gases for Process Heat
Pyrolysis also generates a mixture of non-condensable gases, often called syngas. A common industrial practice is to loop this gas back into the system.
This syngas is used to fuel the pyrolysis reactor itself, creating a highly efficient and often self-sustaining thermal process that minimizes the need for external energy inputs.
Creating Valuable Materials and Chemicals
Beyond energy, pyrolysis is a key technology for material recovery and the production of valuable chemical feedstocks. This aligns with the principles of a circular economy, where waste is repurposed as a new raw material.
Biochar for Agriculture and Industry
The solid, carbon-rich residue known as biochar has significant industrial value. Its primary application is as a soil conditioner in agriculture to improve soil health and water retention.
Beyond farming, biochar is also used as a stable carbon material in various manufacturing processes or as a carrier for industrial catalysts.
Recovering High-Value Chemicals
Bio-oil is not just a fuel; it's a complex mixture of chemical compounds. Through a refining process, this oil can be upgraded into more valuable products.
These include transportation-grade biofuels, specialty chemicals, and additives used in the production of materials like plastics, reducing the reliance on virgin petroleum feedstocks.
Understanding the Strategic Driver: Waste Valorization
The underlying goal of industrial pyrolysis is to turn a liability (waste) into an asset (products). This has profound implications for both environmental compliance and business profitability.
Reducing Landfill Dependence
By diverting organic materials, plastics, and used tires from landfills, pyrolysis directly addresses a major environmental and logistical challenge. This reduces methane emissions from decomposing waste and frees up valuable land.
Enabling a Circular Economy
Pyrolysis is a cornerstone of circular economic models. It enables the recovery of valuable hydrocarbons from end-of-life plastics and rubber, allowing them to be reintroduced into the supply chain as new raw materials. This closes the loop and reduces the need for resource extraction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal application of pyrolysis depends entirely on your strategic objective.
- If your primary focus is energy independence: Utilize the bio-oil and syngas on-site to power your boilers, furnaces, and electrical generators, significantly reducing your reliance on the grid.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Emphasize the diversion of waste from landfills and the production of biochar, which can be used for soil improvement and long-term carbon sequestration.
- If your primary focus is generating new revenue streams: Invest in the capability to refine bio-oil into higher-value specialty chemicals or biofuels for sale on the open market.
Ultimately, pyrolysis provides a flexible and powerful tool for transforming waste streams into strategic industrial assets.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Product | Key Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Generation | Bio-oil & Syngas | Fuel for industrial boilers, furnaces, and on-site power generation. |
| Material Production | Biochar | Soil conditioner in agriculture and a stable carbon material for industry. |
| Chemical Recovery | Refined Bio-oil | Feedstock for biofuels and specialty chemicals, supporting a circular economy. |
| Waste Valorization | All Products | Diverting waste from landfills and creating revenue from waste streams. |
Ready to turn your waste stream into a strategic asset?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables to support your pyrolysis research and development. Whether you are exploring bio-oil refinement, biochar applications, or optimizing syngas production, our products are designed for precision and reliability.
Let us help you achieve your goals of energy independence, environmental sustainability, or new revenue generation.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your pyrolysis projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields



















