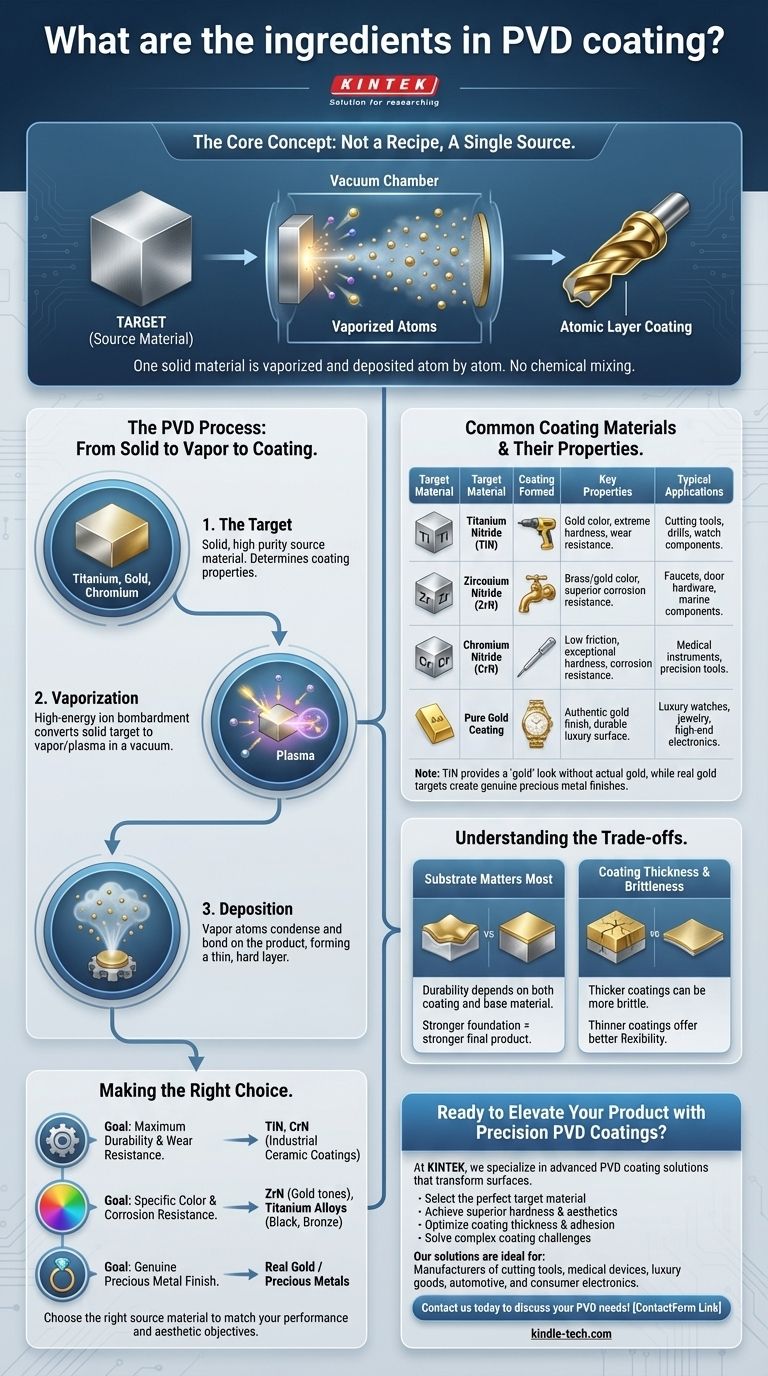
The "ingredients" of a PVD coating are not mixed like a recipe, but rather consist of a single, solid source material that is vaporized and deposited atom by atom. This source material, called a "target," can be a pure metal like titanium, zirconium, or chromium, a precious metal like gold, or a specific alloy. The choice of target material directly determines the final coating's color, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
The central concept to grasp is that PVD is not a single formula. The "ingredient" is the source material you choose to vaporize, and it is the atomic properties of that specific material that bond to your product's surface to create the desired outcome.
The Core Principle: From Solid Target to Atomic Layer
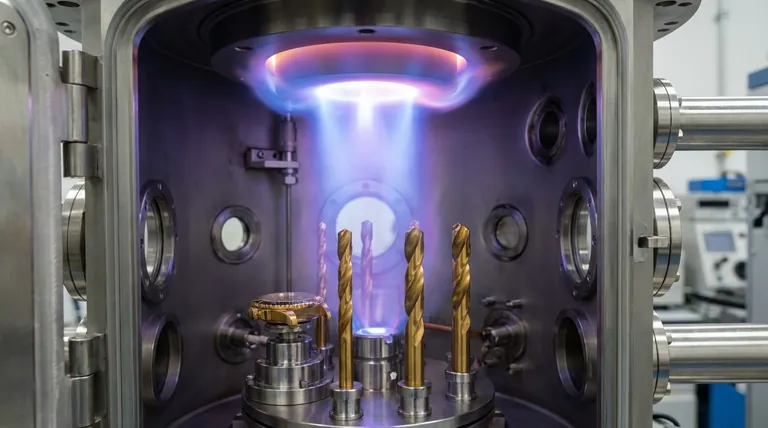
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is fundamentally a process of transferring a material on a molecular level. It's more akin to 3D printing with atoms than it is to painting.
What is a "Target"?
The "ingredient" in any PVD process begins as a solid, high-purity block of material known as the target. This is the source of the coating.
If you want a titanium-based coating, you start with a solid target of titanium. If you want a true gold coating, you use a solid target of gold.
The Vaporization Process
Inside a high-vacuum chamber, the target is bombarded with high-energy ions. This bombardment is so powerful it knocks atoms loose from the solid target, converting them into a vapor or plasma.
This is a physical process, not a chemical one. The material is simply transitioned from a solid to a vapor phase without altering its fundamental chemistry.
Deposition on the Substrate
This cloud of vaporized atoms travels through the vacuum and condenses on the objects being coated (the "substrates").
Because this happens atom by atom, the coating forms an incredibly thin, dense, and well-adhered layer on the substrate's surface, typically between 0.5 and 5 microns thick.
Common Coating Materials and Their Properties
The choice of target material is dictated entirely by the desired properties of the final product.
Industrial Workhorses: Nitrides and Carbides
For most industrial applications, the target metal is vaporized in the presence of a reactive gas like nitrogen or carbon. This forms even harder ceramic compounds on the substrate surface.
The most common is Titanium Nitride (TiN), known for its gold color, extreme hardness, and excellent wear resistance. It's frequently used on cutting tools and drills.
Other popular options include Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) for a brass or pale-gold look with superior corrosion resistance, and Chromium Nitride (CrN) for exceptional hardness and a low coefficient of friction.
The Case of "Gold" PVD
This is a frequent point of confusion. A "gold" PVD finish can refer to two very different things.
Most often, it is a coating like Titanium Nitride (TiN) which has a brilliant gold color but contains no actual gold. This is chosen for its durability and cost-effectiveness on items like faucets or watches.
However, for luxury goods, the target material can be real gold (e.g., 18k or 24k). This process vaporizes genuine gold, depositing a thin, hard layer that is far more durable than traditional gold plating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A PVD coating's performance is not determined by the ingredient alone. It's part of a system, and understanding its limitations is critical for success.
The Substrate Matters Most
The final durability of a product is a combination of the coating and the base material. A hard PVD coating on a soft substrate like plastic will protect against scratches but will still dent easily because the underlying material gives way.
The same coating on hardened steel will result in a dramatically more durable surface. The coating is only as strong as the foundation it's applied to.
Coating Thickness vs. Brittleness
While a thicker coating (closer to 5 microns) can provide more wear resistance, it can also become more brittle and prone to chipping on impact.
Thinner coatings (around 1 micron) often provide a better balance of scratch resistance and flexibility, adhering better to parts that may experience minor flexing.
Line-of-Sight Application
The PVD process is "line-of-sight," meaning the vaporized atoms travel in a straight line from the target to the substrate.
This makes it very difficult to coat complex internal channels or the backsides of intricate parts without complex rotation within the chamber. It is best suited for external surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct PVD "ingredient" means matching the material's properties to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and wear resistance: Choose an industrial ceramic coating like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Chromium Nitride (CrN).
- If your primary focus is a specific color with corrosion resistance: Use materials like Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) for gold tones or other titanium alloys for black, bronze, and gunmetal finishes.
- If your primary focus is a genuine precious metal finish: Use a target made of real gold or other precious metals for a durable, authentic coating on luxury goods.
Ultimately, understanding the PVD "ingredient" is about choosing the right source material to achieve the precise performance and aesthetic your project demands.
Summary Table:
| Target Material | Common Coating Formed | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium (Ti) | Titanium Nitride (TiN) | Gold color, extreme hardness, wear resistance | Cutting tools, drills, watch components |
| Zirconium (Zr) | Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) | Brass/gold color, superior corrosion resistance | Faucets, door hardware, marine components |
| Chromium (Cr) | Chromium Nitride (CrN) | Low friction, exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance | Medical instruments, precision tools |
| Gold (Au) | Pure Gold Coating | Authentic gold finish, durable luxury surface | Luxury watches, jewelry, high-end electronics |
Ready to Elevate Your Product with Precision PVD Coatings?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced PVD coating solutions that transform ordinary surfaces into high-performance assets. Whether you need industrial-grade durability for cutting tools or authentic precious metal finishes for luxury goods, our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures your coating process delivers exceptional results.
We help you:
- Select the perfect target material for your specific application
- Achieve superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal
- Optimize coating thickness and adhesion for maximum performance
- Solve complex coating challenges with our technical expertise
Our solutions are ideal for: Manufacturers of cutting tools, medical devices, luxury goods, automotive components, and consumer electronics.
Contact us today to discuss how our PVD coating expertise can enhance your product's performance and value!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















