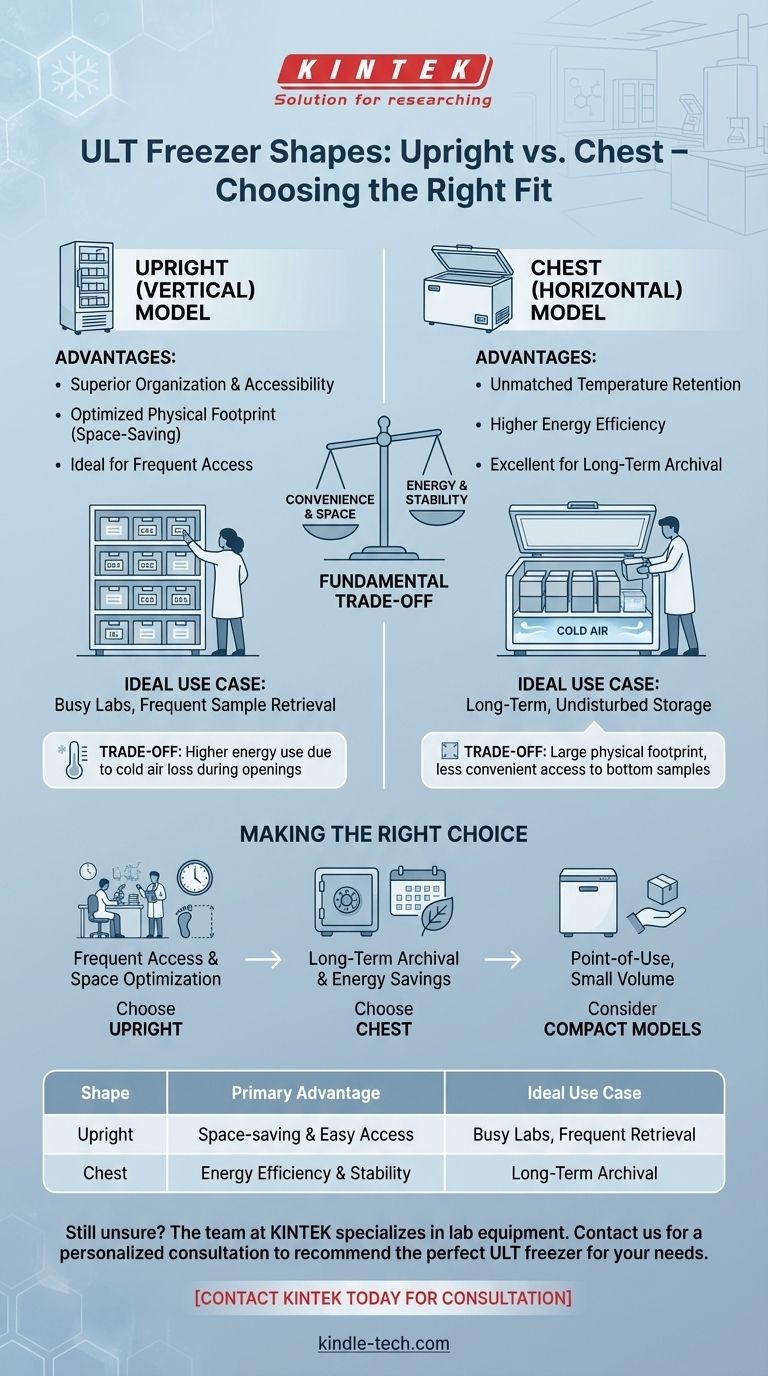
The two primary shapes for ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers are the upright (vertical) model and the chest (horizontal) model. Upright freezers are prized for their space-saving footprint and easy access to organized samples, making them common in busy labs. Chest freezers are valued for their superior energy efficiency and temperature stability, which is ideal for long-term archival.
The choice between an upright and a chest ULT freezer is not about which is universally better, but about a fundamental trade-off: balancing the daily convenience and space efficiency of an upright model against the long-term energy savings and temperature stability of a chest model.

The Upright Freezer: Designed for Access
Upright freezers are the most common configuration found in modern laboratories. Their design prioritizes workflow efficiency and maximizing the use of limited floor space.
Superior Organization and Accessibility
The vertical design of an upright freezer allows for internal shelving and racks, much like a standard refrigerator. This makes it easy to organize samples into specific compartments and retrieve them quickly.
This model is ideal for environments where researchers need frequent access to various samples throughout the day. The clear organization reduces search time and minimizes how long the door stays open for any single retrieval.
Optimized Physical Footprint
By building vertically, upright freezers occupy significantly less floor space than chest freezers of the same internal volume. This is a critical advantage in crowded labs where every square foot is valuable.
Their shape also makes them easier to position alongside other lab equipment and benches.
The Chest Freezer: Engineered for Stability
Chest freezers are the classic workhorses for long-term, secure sample storage. Their design is fundamentally rooted in the physics of cold air.
Unmatched Temperature Retention
The key advantage of a chest freezer is its top-opening lid. Because cold air is denser than warm air, it naturally settles at the bottom. When you open the lid, very little cold air escapes.
This design results in exceptional temperature stability and faster temperature recovery after the lid is closed, protecting valuable samples stored for long durations.
Higher Energy Efficiency
By minimizing the loss of cold air during openings, chest freezers are inherently more energy-efficient than upright models. They require less energy to maintain their ultra-low setpoint, leading to lower operational costs over the freezer's lifespan.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is perfect for every situation. Understanding their inherent limitations is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your lab's primary goals.
Upright Freezer: The Cost of Convenience
When you open the door of an upright freezer, the dense, cold air immediately "falls out" and is replaced by warmer, ambient air. This forces the compressor to work harder to return to its setpoint, consuming more energy and creating temporary temperature fluctuations inside the unit.
Chest Freezer: The Challenge of Space and Organization
The primary drawback of a chest freezer is its large physical footprint. It requires more floor space and can be difficult to integrate into a tightly packed lab.
Furthermore, accessing samples can be cumbersome. Items at the bottom are hard to reach, often requiring the removal of upper layers of boxes or racks, which can be difficult for some users.
A Note on Smaller Form Factors
For labs with minimal storage needs or those requiring point-of-use storage, smaller under-counter or table-top ULT freezers exist. These compact units offer convenience for daily work but lack the volume for significant archival purposes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your lab's specific workflow, storage strategy, and physical constraints.
- If your primary focus is frequent sample access and optimizing lab space: An upright freezer is the most practical choice for your daily operations.
- If your primary focus is long-term, undisturbed archival and minimizing energy costs: A chest freezer provides the best performance for sample integrity and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is storing a small number of critical samples at a specific workstation: A compact under-counter or table-top model offers targeted, convenient storage.
Ultimately, selecting the right freezer shape is a strategic decision that directly supports your research goals and operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Shape | Primary Advantage | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Upright (Vertical) | Space-saving footprint & easy sample access | Busy labs requiring frequent sample retrieval |
| Chest (Horizontal) | Superior energy efficiency & temperature stability | Long-term, undisturbed archival storage |
Still unsure which ULT freezer shape is best for your laboratory's workflow and storage strategy?
The team at KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and can help you analyze your specific needs—from daily access frequency to long-term archival requirements—to recommend the perfect ultra-low temperature freezer. We provide reliable, energy-efficient solutions to protect your valuable samples and optimize your lab's operational costs.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and ensure your samples are stored with the utmost integrity and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 158L Precision Vertical Ultra Low Freezer for Laboratory Applications
- 608L Essential Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Freezer For Critical Sample Preservation
- 708L Ultra Low Temperature Freezer High Performance Laboratory Freezer
- 208L Advanced Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Cold Storage
- 808L Precision Laboratory Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers? Preserve Critical Biological Samples
- What are the different types of ultra-low temperature freezers available? Choose the Right ULT Freezer for Your Lab
- How is temperature controlled in ultra low temperature freezers? A Guide to Stable -80°C Storage
- Why are ultra-low temperature freezers important in scientific research? Ensure Sample Integrity and Reproducibility
- How do ultra-low temperature freezers work? Unlocking the Secrets of -86°C Sample Preservation



















