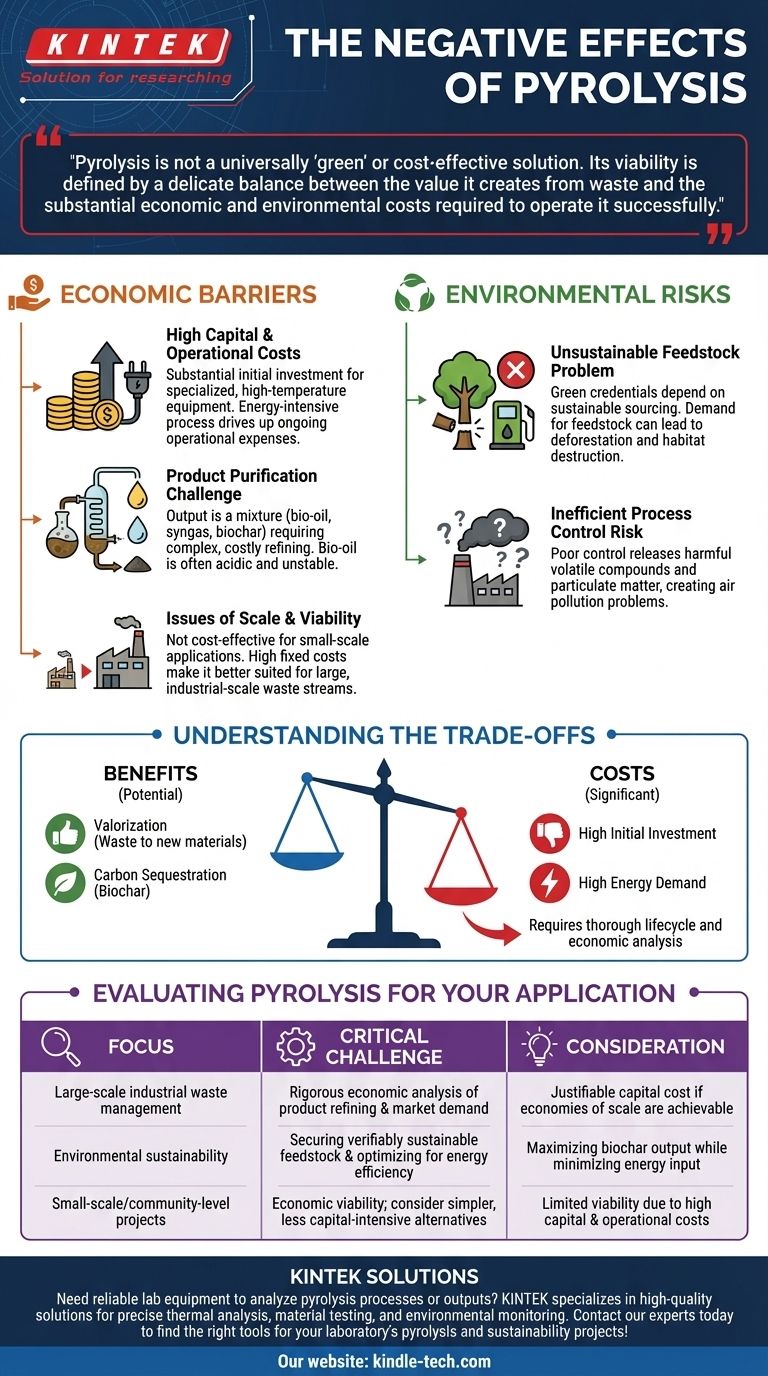
While promising in principle, the practical application of pyrolysis is often hampered by significant negative effects. The primary drawbacks are high capital and energy costs, the technical difficulty of refining its products, and the potential for serious environmental harm if the process is not managed with rigorous control and sustainable sourcing.
Pyrolysis is not a universally "green" or cost-effective solution. Its viability is defined by a delicate balance between the value it creates from waste and the substantial economic and environmental costs required to operate it successfully.

The Economic Barriers to Pyrolysis
While pyrolysis can transform low-value waste into higher-value products, the financial path to achieving this is often steep and complex. These economic hurdles are a primary reason the technology has not seen more widespread adoption.
High Capital and Operational Costs
The initial investment for pyrolysis equipment and machinery is substantial. These systems must safely operate at very high temperatures, which requires specialized materials and engineering.
Furthermore, the process itself is energy-intensive. Achieving and maintaining the necessary high temperatures over long residence times consumes a significant amount of energy, driving up operational costs and impacting the overall energy balance of the system.
The Challenge of Product Purification
Pyrolysis does not produce a single, clean output. Instead, it creates a mixture of bio-oil, syngas, and biochar, which must be separated.
The bio-oil, in particular, is often acidic, unstable, and contains impurities. It typically requires significant and costly refining before it can be used as a viable transportation fuel, adding another layer of expense and complexity to the overall process.
Issues of Scale and Viability
The combination of high capital costs and the need for complex downstream processing means that pyrolysis is often not cost-effective for small-scale applications.
For smaller organizations or communities, the initial investment and ongoing operational expenses can be prohibitive, making it a technology better suited for large, industrial-scale waste streams where economies of scale can be achieved.
Environmental Risks and How They Emerge
The environmental friendliness of pyrolysis is conditional. Poor planning and execution can negate its potential benefits, leading to negative ecological consequences.
The Problem of Unsustainable Feedstock
The "green" credentials of pyrolysis hinge on using sustainable biomass or waste materials. If the demand for feedstock leads to deforestation or the destruction of natural habitats, the process becomes a net negative for the environment.
Using unsustainable biomass sources simply shifts the environmental burden from fossil fuels to land use, undermining the core purpose of the technology.
The Risk of Inefficient Process Control
A poorly controlled pyrolysis process can fail to properly capture and convert materials, leading to pollution.
If the system is inefficient, it can release harmful volatile compounds and particulate matter into the atmosphere. This not only represents a loss of valuable product but also creates a direct air pollution problem, turning a potential solution into a new environmental hazard.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Evaluating pyrolysis requires an objective look at its inherent compromises. The benefits do not come without significant costs and considerations.
Value Creation vs. Initial Investment
Pyrolysis is unique in its ability to thermally decompose waste into new, often superior, materials. It is a powerful tool for valorization.
However, this potential must be weighed against the very high capital costs. An organization must be certain that the market value of the end products (biochar, refined oils) can justify the initial and ongoing financial outlay.
Potential for Carbon Sequestration vs. Energy Demand
The creation of biochar is a major environmental benefit, as it serves as a stable method of sequestering carbon in the soil.
This positive outcome is counterbalanced by the high energy input the process demands. A thorough lifecycle analysis is needed to ensure the energy consumed does not outweigh the carbon sequestration and fossil fuel displacement benefits.
Evaluating Pyrolysis for Your Application
To determine if pyrolysis is the right technology, you must align its specific challenges with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial waste management: The high capital cost may be justifiable, but success depends on a rigorous economic analysis of product refining and market demand.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Your critical challenges will be securing a verifiably sustainable feedstock and optimizing the process to maximize biochar output while minimizing energy input.
- If your primary focus is small-scale or community-level projects: The economic viability is a major hurdle, and simpler, less capital-intensive waste-to-energy technologies may be more practical.
A successful pyrolysis initiative depends on a clear-eyed assessment of its economic realities and a steadfast commitment to sustainable operation.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Negative Effects |
|---|---|
| Economic | High capital & operational costs, complex product purification, limited small-scale viability |
| Environmental | Air pollution from inefficient control, unsustainable feedstock sourcing (e.g., deforestation) |
| Technical | Energy-intensive process, unstable outputs requiring costly refinement |
Need reliable lab equipment to analyze pyrolysis processes or outputs? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal analysis, material testing, and environmental monitoring. Whether you're researching bio-oil refinement, biochar properties, or process efficiency, our solutions help you achieve accurate, repeatable results. Contact our experts today to find the right tools for your laboratory's pyrolysis and sustainability projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process


















