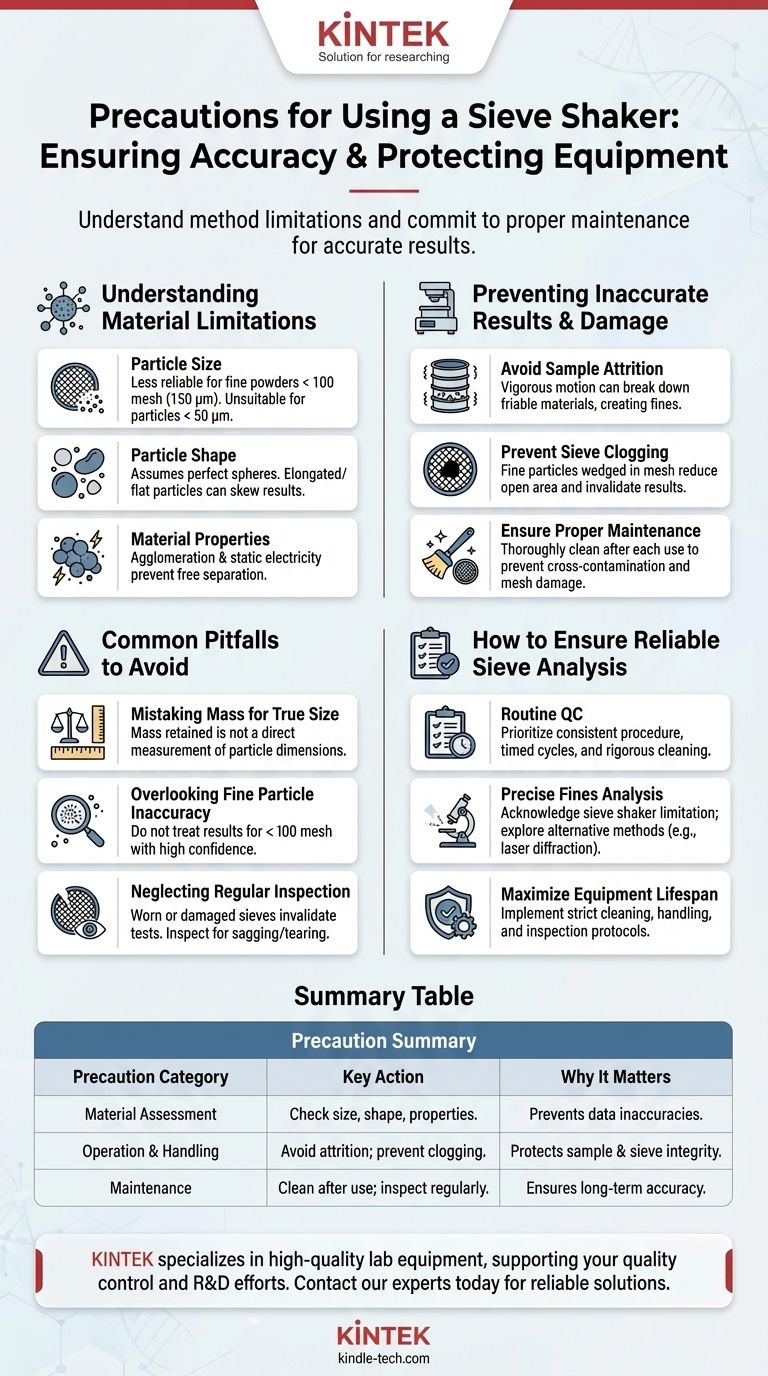
To ensure accurate results and protect your equipment, the primary precautions for using a sieve shaker involve understanding the limitations of the method itself and committing to proper operational maintenance. Key risks include generating inaccurate data due to particle shape or size, and damaging the sieves through clogging or distortion if they are not cared for correctly.
The core challenge with sieve shaker analysis is not the operation, but the interpretation. The main precaution is to recognize that its effectiveness is strictly limited by the physical characteristics of your sample and the physical condition of your sieves.

Understanding Material and Particle Limitations
The most significant errors in sieve analysis often occur before the machine is even turned on. They stem from a mismatch between the sample's characteristics and the shaker's capabilities.
Assess Particle Size
A sieve shaker is highly effective for coarse materials, but its accuracy diminishes significantly for very fine powders. Be aware that results can be less reliable for materials finer than 100 mesh (150 µm) and generally unsuitable for particles smaller than 50 µm.
Account for Particle Shape
Sieve analysis fundamentally assumes all particles are perfect spheres that pass through a square opening. This is a critical point of failure for materials containing elongated or flat particles.
These non-spherical particles may be retained on a sieve that is much larger than their actual mass or volume would suggest, skewing the final mass-based results.
Consider Material Properties
The inherent nature of your material dictates sieving success. Materials prone to agglomeration (clumping) or those affected by static electricity will not separate freely, leading to inaccurate distribution measurements.
Verify Liquid Compatibility for Wet Sieving
If you are performing a wet sieve analysis, you must confirm that the dispersion liquid will not react with or dissolve your sample material. Any adverse reaction will fundamentally alter the particles you are trying to measure.
Preventing Inaccurate Results and Equipment Damage
Once you've qualified your material, operational diligence is essential to protect both your data integrity and your hardware investment.
Avoid Sample Attrition
The vigorous, three-dimensional motion of a sieve shaker can be aggressive. For friable or brittle materials, this action can cause size reduction errors, where the shaking itself breaks down particles, creating more fines and distorting the results.
Prevent Sieve Clogging
Fine particles can become wedged in the mesh openings, a phenomenon known as clogging or blinding. This effectively reduces the open area of the sieve, preventing other particles from passing through and invalidating the results for that screen.
Ensure Proper Sieve Maintenance
Clogging is often a symptom of poor maintenance. After each use, sieves must be thoroughly cleaned. Failure to do so not only leads to cross-contamination but also risks permanent sieve distortion or damage when trying to remove impacted material.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Beyond the basic operation, several common oversights can undermine the value of your analysis.
Mistaking Mass for True Particle Size
Always remember you are measuring the mass retained on each sieve, not directly measuring individual particle dimensions. For materials with varying densities or non-spherical shapes, this mass-based result can be a poor representation of the true particle size distribution.
Overlooking Fine Particle Inaccuracy
Do not treat results for particles under 100 mesh with the same confidence as those for coarser materials. If precise analysis of fines is your goal, a sieve shaker is likely the wrong instrument; methods like laser diffraction may be more appropriate.
Neglecting Regular Inspection
Sieves are precision instruments that wear out over time. Regularly inspect the mesh for any signs of sagging, tearing, or distortion. A single damaged sieve in the stack can invalidate the entire test.
How to Ensure Reliable Sieve Analysis
Your approach should be guided by your ultimate analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control on granular materials: Prioritize consistent procedure, timed shaking cycles, and rigorous post-use cleaning to prevent sieve clogging.
- If your primary focus is precise analysis of fine or non-spherical particles: Acknowledge that a sieve shaker is likely inappropriate and explore alternative particle analysis methods.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment lifespan: Implement a strict protocol for cleaning, handling, and inspecting sieves to prevent permanent distortion and damage to the mesh.
By treating the process with this level of diligence, you ensure your sieve shaker remains a reliable and valuable tool for particle analysis.
Summary Table:
| Precaution Category | Key Action | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Material Assessment | Check particle size, shape, and properties. | Prevents inaccurate data from fines, non-spherical particles, or agglomeration. |
| Operation & Handling | Avoid sample attrition; prevent sieve clogging. | Protects sample integrity and sieve mesh from damage. |
| Maintenance | Clean sieves thoroughly after each use; inspect regularly. | Ensures long-term accuracy and prevents cross-contamination. |
Maximize the accuracy and lifespan of your particle analysis equipment.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories. Whether you require durable sieve shakers, reliable test sieves, or expert advice on particle analysis methods, we are here to support your quality control and R&D efforts.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the right solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- How is a vibrating sieve shaker used to classify atomized Al-Fe-Ni powders? Expert Guide to Particle Size Control
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- What is the use of vibrating sieve machine? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis



















