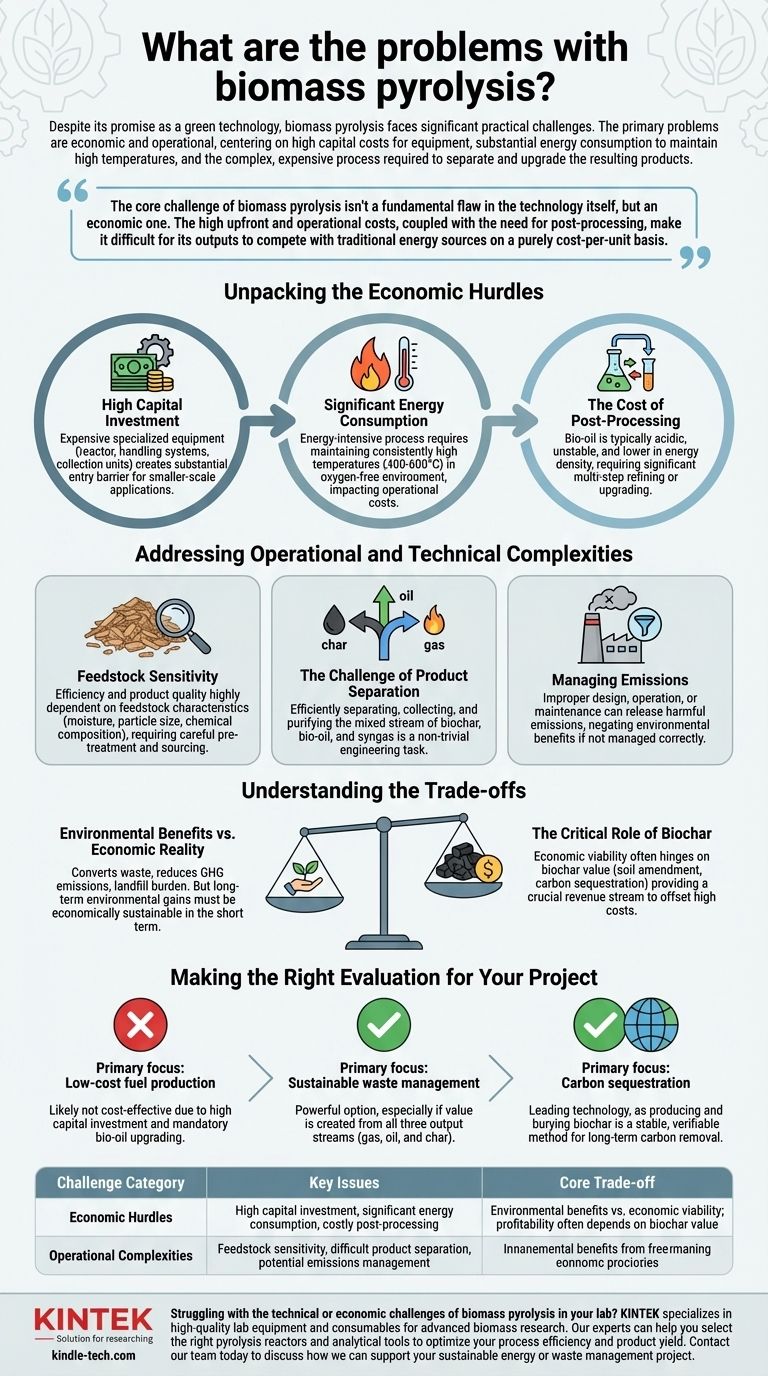
Despite its promise as a green technology, biomass pyrolysis faces significant practical challenges. The primary problems are economic and operational, centering on high capital costs for equipment, substantial energy consumption to maintain high temperatures, and the complex, expensive process required to separate and upgrade the resulting products.
The core challenge of biomass pyrolysis isn't a fundamental flaw in the technology itself, but an economic one. The high upfront and operational costs, coupled with the need for post-processing, make it difficult for its outputs to compete with traditional energy sources on a purely cost-per-unit basis.
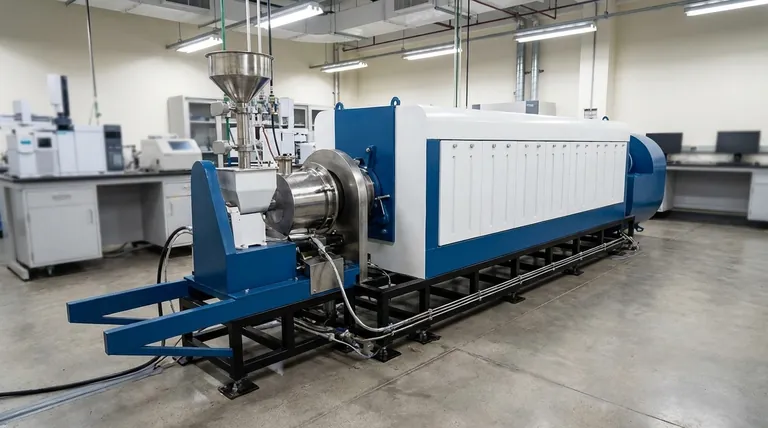

Unpacking the Economic Hurdles
The financial viability of a pyrolysis project is often the most significant barrier to its adoption. These costs are present in every phase of the operation.
High Capital Investment
The specialized equipment required—including the reactor, feedstock handling systems, and product collection units—is expensive. This high initial capital expenditure creates a substantial barrier to entry, particularly for smaller-scale agricultural or municipal applications.
Significant Energy Consumption
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process. It requires maintaining consistently high temperatures, often between 400°C and 600°C, in an oxygen-free environment. This continuous energy demand directly impacts operational costs and can erode the net energy gain of the system.
The Cost of Post-Processing
The outputs of pyrolysis are not immediately usable. The liquid bio-oil is typically acidic, unstable, and has a lower energy density than petroleum fuels, requiring significant refining or upgrading before it can be used in standard engines. This multi-step upgrading process adds another layer of complexity and cost.
Addressing Operational and Technical Complexities
Beyond the economics, the day-to-day operation of a pyrolysis plant presents several engineering and logistical challenges.
Feedstock Sensitivity
The process is not a "one-size-fits-all" solution for biomass waste. The efficiency of the reaction and the quality of the end products are highly dependent on the feedstock's characteristics, such as moisture content, particle size, and chemical composition. This requires careful pre-treatment and sourcing.
The Challenge of Product Separation
Pyrolysis produces a mixed stream of outputs: a solid (biochar), a liquid (bio-oil), and a gas (syngas). Efficiently separating, collecting, and purifying these distinct product streams is a non-trivial engineering task that adds to the system's complexity and cost.
Managing Emissions
While often presented as an environmentally friendly process, pyrolysis can produce harmful emissions if not managed correctly. Improper design, operation, or maintenance can release volatile organic compounds and other pollutants, negating some of the environmental benefits.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To properly evaluate pyrolysis, one must weigh its considerable challenges against its unique benefits. The technology's value is often found in its co-products, not just the fuel.
Environmental Benefits vs. Economic Reality
The clear advantages of pyrolysis are its ability to convert waste into energy, reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, and reduce landfill burden. However, these long-term environmental gains must be economically sustainable in the short term.
The Critical Role of Biochar
Often, the economic viability of a pyrolysis plant hinges on the value of its solid co-product: biochar. When a strong market exists for biochar—as a potent soil amendment or as a method for long-term carbon sequestration—it can provide a crucial revenue stream that offsets the high costs and makes the entire process profitable.
Making the Right Evaluation for Your Project
The suitability of biomass pyrolysis depends entirely on your primary goal. Use these points to frame your evaluation.
- If your primary focus is low-cost fuel production: Pyrolysis is likely not the most direct or cost-effective path due to the high capital investment and mandatory upgrading of its bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is sustainable waste management: Pyrolysis is a powerful option, especially if you can create value from all three output streams (gas, oil, and char).
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: Pyrolysis is a leading technology, as producing and burying biochar is one of the most stable and verifiable methods for long-term carbon removal.
Ultimately, viewing pyrolysis not just as a fuel production method but as a complete resource conversion system is the key to overcoming its inherent challenges.
Summary Table:
| Challenge Category | Key Issues |
|---|---|
| Economic Hurdles | High capital investment, significant energy consumption, costly post-processing of bio-oil |
| Operational Complexities | Feedstock sensitivity, difficult product separation, potential emissions management |
| Core Trade-off | Environmental benefits vs. economic viability; profitability often depends on biochar value |
Struggling with the technical or economic challenges of biomass pyrolysis in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced biomass research. Our experts can help you select the right pyrolysis reactors and analytical tools to optimize your process efficiency and product yield. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your sustainable energy or waste management project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output



















