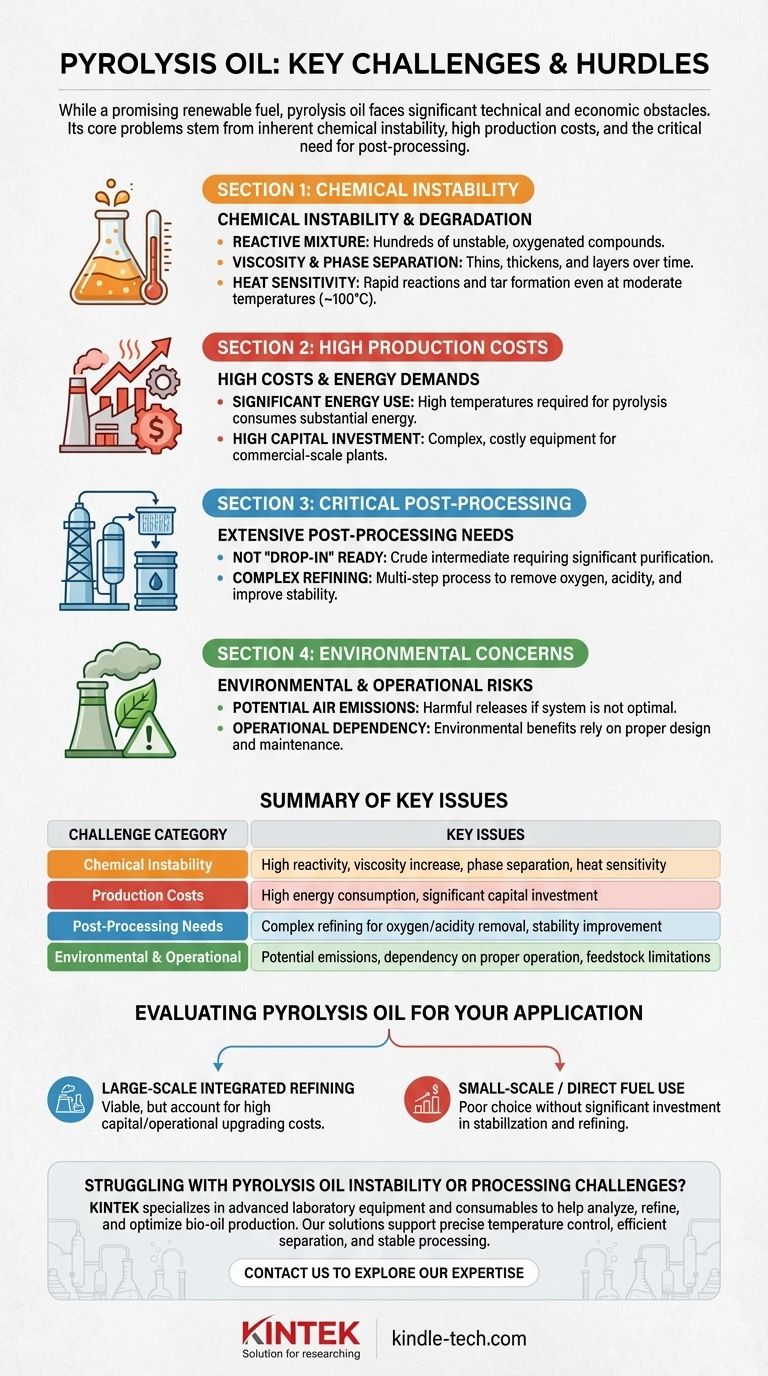
While a promising renewable fuel, pyrolysis oil is plagued by several significant challenges. Its core problems stem from its inherent chemical instability, the high energy and capital costs of its production, and the critical need for extensive post-processing before it can be used as a conventional fuel. These factors combine to create significant technical and economic hurdles to its widespread adoption.
The central issue is that pyrolysis oil is not a finished, "drop-in" fuel. It is a reactive, intermediate product whose instability and complex composition make it difficult to store, handle, and use without costly and energy-intensive refinement.
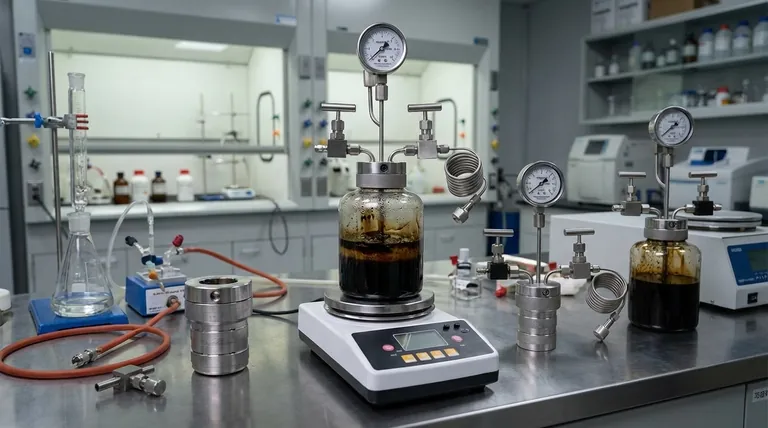

The Challenge of Chemical Instability
The most fundamental problem with pyrolysis oil, also known as bio-oil, is that it is not a stable substance. It begins to degrade almost as soon as it is produced.
A Reactive and Unstable Mixture
Pyrolysis oil is not like crude oil. It is a complex mixture of hundreds of different oxygenated organic compounds, which are intermediate products of thermal decomposition. These components are highly reactive.
Over time, these compounds undergo condensation reactions, causing the oil's properties to change.
Viscosity and Phase Separation
This inherent reactivity leads to a gradual increase in the oil's viscosity, meaning it becomes thicker and harder to pump.
In some cases, the reactions can become so advanced that the oil undergoes phase separation, separating into distinct layers that are unusable without further processing.
Sensitivity to Heat
The instability is accelerated by heat. Even moderate heating to around 100°C can cause rapid reactions, producing a solid, tar-like residue and volatile organic compounds. This makes storage and upgrading processes difficult to manage.
High Costs and Energy Demands of Production
Creating pyrolysis oil is an expensive and energy-intensive undertaking, which presents a major barrier to its economic viability.
Significant Energy Consumption
The pyrolysis process requires heating biomass to very high temperatures in the absence of oxygen. Maintaining these temperatures for the required residence times consumes a substantial amount of energy.
High Capital Costs
The equipment and machinery needed for a commercial-scale pyrolysis plant are complex and costly. This high initial investment, or capital cost, can make projects difficult to finance, especially for smaller-scale applications.
The Critical Need for Post-Processing
Raw pyrolysis oil is rarely usable as-is. It is a crude intermediate that requires significant purification and refining to become a valuable product.
A Complex, Mixed Product
The liquid that exits the pyrolysis reactor is a mixed stream that requires efficient separation and purification. This multi-step process adds considerable time, complexity, and expense to the overall production chain.
Essential Refining for Fuel Use
To be used as a transportation fuel, bio-oil must undergo significant refining to remove oxygen, reduce its acidity, and improve its stability. This upgrading process is a major technical and economic challenge that makes pyrolysis less cost-effective than conventional fuel production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Environmental Concerns
While often positioned as a "green" technology, the pyrolysis process itself has potential downsides that must be managed carefully.
Potential for Air Emissions
The high temperatures involved in pyrolysis can produce harmful emissions if the system is not designed or operated correctly. These emissions can negatively impact local air quality, undermining the technology's environmental benefits.
Operational Dependency
The process's environmental friendliness is not guaranteed. It is entirely dependent on the proper design, operation, and maintenance of the furnace and gas handling systems to minimize unwanted emissions.
Feedstock and Location Limitations
Finally, the pyrolysis process is not a universal solution. It may not be suitable for all types of biomass feedstock or for all geographic locations, limiting its applicability.
Evaluating Pyrolysis Oil for Your Application
Understanding these challenges is key to determining if pyrolysis is the right pathway for your goals.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, integrated refining: Pyrolysis can be a viable feedstock source, but you must account for the high capital and operational costs of the required upgrading facilities.
- If your primary focus is small-scale or direct fuel use: The inherent instability and extensive need for post-processing make raw pyrolysis oil a poor choice without significant investment in stabilization and refining technology.
Ultimately, the viability of pyrolysis oil hinges on overcoming its inherent chemical instability and the economic hurdles of its production and refinement.
Summary Table:
| Challenge Category | Key Issues |
|---|---|
| Chemical Instability | High reactivity, viscosity increase, phase separation, sensitivity to heat |
| Production Costs | High energy consumption, significant capital investment for equipment |
| Post-Processing Needs | Requires complex refining to remove oxygen, reduce acidity, and improve stability |
| Environmental & Operational | Potential air emissions, dependency on proper system operation, feedstock limitations |
Struggling with pyrolysis oil instability or processing challenges? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables designed to help you analyze, refine, and optimize bio-oil production. Our solutions support precise temperature control, efficient separation, and stable processing—ensuring your research or production meets the highest standards of efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can enhance your pyrolysis workflow and overcome these critical hurdles. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- 100L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- What are the technical characteristics of PTFE (Teflon) lined hydrothermal reactors? Comparing α-ZrP Synthesis Methods
- Why use high-pressure reactors for food waste pretreatment? Boost Hydrogen Production Efficiency Today!
- What role does a high-pressure reactor play in the hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of bio-oil? Drive Deep Fuel Upgrading
- Why must SCWG reactors maintain a specific heating rate? Protect Your High-Pressure Vessels from Thermal Stress
- What role does a PTFE-lined stainless steel autoclave play in the synthesis of BiOBr precursor nanosheets?



















