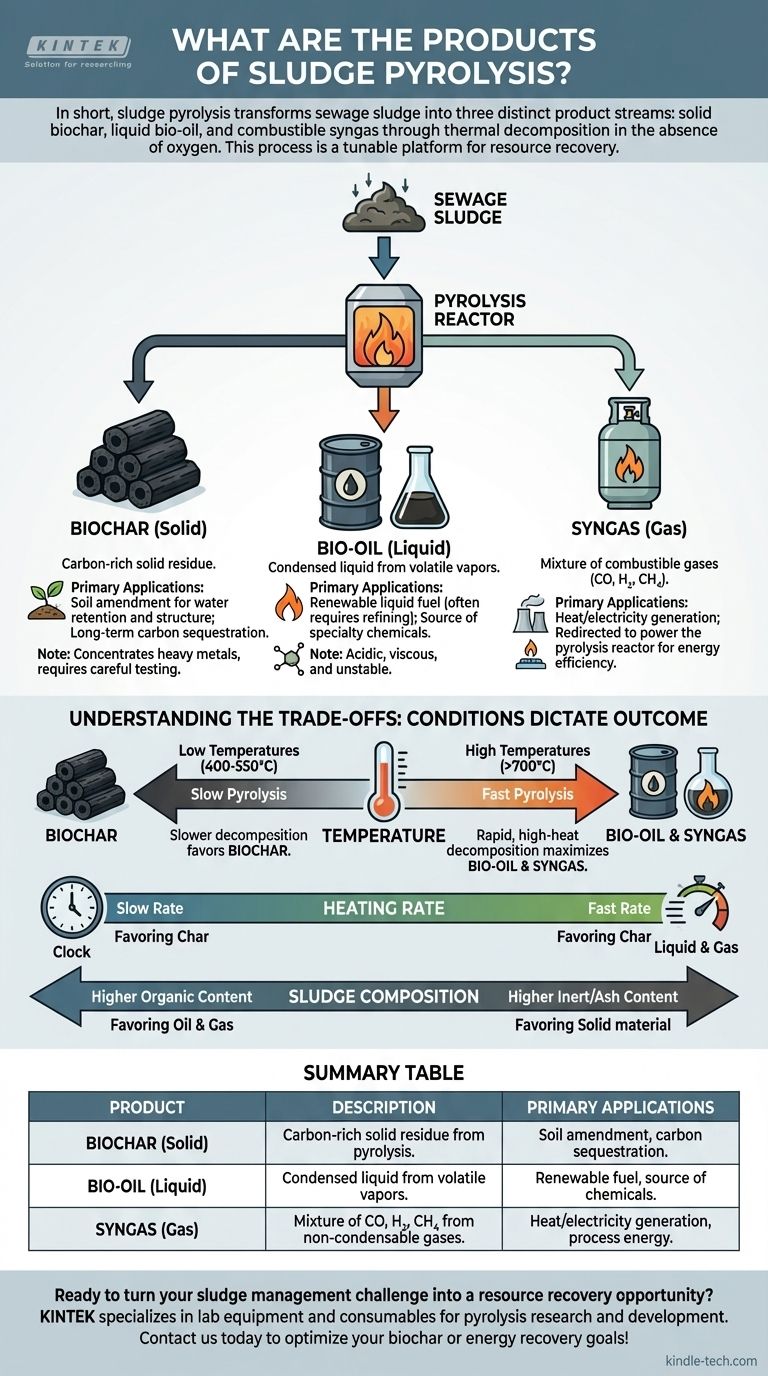
In short, sludge pyrolysis transforms sewage sludge into three distinct product streams: a solid known as biochar, a liquid called bio-oil, and a combustible gas referred to as syngas. The process thermally decomposes the sludge in the absence of oxygen, ensuring that the material breaks down into these components rather than burning away.
Pyrolysis is best understood not as a single process, but as a tunable platform for resource recovery. By controlling factors like temperature, you can dictate whether the process primarily yields solid biochar for soil applications or liquid and gaseous fuels for energy.

The Three Core Products of Sludge Pyrolysis
The transformation of sludge through pyrolysis results in a predictable set of outputs, each with its own distinct characteristics and potential applications. The yield and quality of each product are not fixed; they are a direct result of the process conditions employed.
The Solid Product: Biochar
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components have been driven off. It resembles charcoal in appearance and composition.
Its primary value lies in its use as a soil amendment, where it can improve water retention and soil structure. Because its carbon is highly stable, it also serves as a method for long-term carbon sequestration.
A critical consideration with sludge-derived biochar is that it concentrates the heavy metals present in the original sludge. This means its use in agriculture requires careful testing and may be restricted depending on contamination levels.
The Liquid Product: Bio-oil
Bio-oil, also known as pyrolysis oil or tar, is a complex mixture of water, organic acids, alcohols, and other compounds. It is the condensed form of the volatile vapors produced during the process.
The primary potential for bio-oil is as a renewable liquid fuel. However, it is typically acidic, viscous, and unstable, requiring upgrading or refining before it can be used in standard engines or boilers.
It can also be a source for extracting valuable specialty chemicals, though this is often a more complex and costly endeavor.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
The non-condensable gases released during pyrolysis are collectively known as syngas (synthesis gas). This is a mixture of combustible gases, primarily carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), and methane (CH₄).
Syngas has a moderate energy value and can be combusted to generate heat or electricity.
A key advantage is that the syngas produced can be redirected to provide the heat for the pyrolysis reactor itself. This creates a more energy-efficient, self-sustaining system and reduces reliance on external fuel sources.
Understanding the Trade-offs: How Conditions Dictate the Outcome
You are not a passive observer of the pyrolysis process; you are the operator who controls the outcome. The relative yield of char, oil, and gas is determined almost entirely by the process parameters you set.
The Decisive Role of Temperature
Temperature is the single most important control lever. The relationship is straightforward:
- Low Temperatures (400-500 °C): Slower decomposition favors the formation of solid biochar. This is often called "slow pyrolysis."
- High Temperatures (>700 °C): Rapid, high-heat decomposition cracks the larger organic molecules into smaller volatile compounds, maximizing the yield of bio-oil and syngas. This is known as "fast pyrolysis."
The Influence of Heating Rate
How quickly the sludge reaches the target temperature also plays a critical role.
A slow heating rate gives large molecules time to rearrange and form stable char. A fast heating rate, often achieved by injecting small particles into a very hot reactor, instantly vaporizes the material, favoring liquid and gas production.
The Impact of Sludge Composition
Finally, the nature of the initial sludge feedstock matters. Higher organic content will naturally yield more oil and gas, while higher inert or ash content will result in more solid material, though not necessarily high-quality biochar. The water content must also be managed, as evaporating water consumes a significant amount of energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" pyrolysis strategy depends entirely on your objective. By aligning process conditions with your desired output, you can optimize the system for maximum value.
- If your primary focus is soil improvement and carbon sequestration: Employ slow pyrolysis with lower temperatures (400-550 °C) and slower heating rates to maximize the production of stable biochar.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy generation: Use fast pyrolysis with higher temperatures (>600 °C) and rapid heating rates to maximize the yield of combustible bio-oil and syngas.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Any pyrolysis approach achieves a significant reduction, but fast pyrolysis generally provides the greatest mass and volume decrease by converting solids to liquids and gases.
By understanding these fundamental principles, you can effectively transform a waste management problem into a targeted resource production opportunity.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | Carbon-rich solid residue from pyrolysis. | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration. |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Condensed liquid from volatile vapors. | Renewable fuel, source of chemicals. |
| Syngas (Gas) | Mixture of CO, H₂, CH₄ from non-condensable gases. | Heat/electricity generation, process energy. |
Ready to turn your sludge management challenge into a resource recovery opportunity? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're optimizing for biochar production or energy recovery, our solutions help you achieve precise control over temperature and process conditions. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and support your sustainability goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















