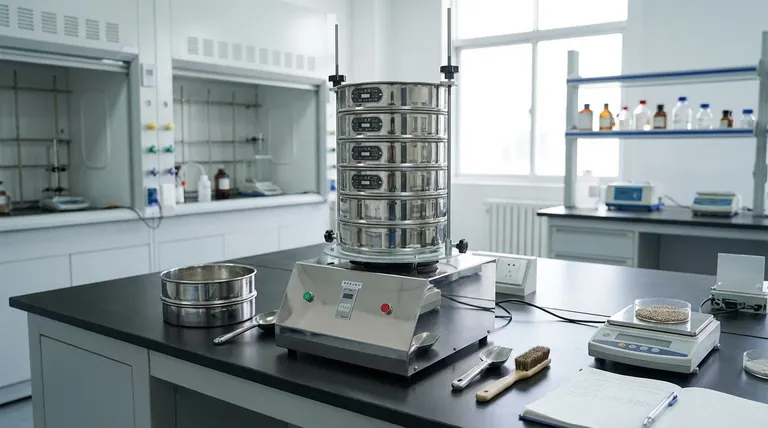
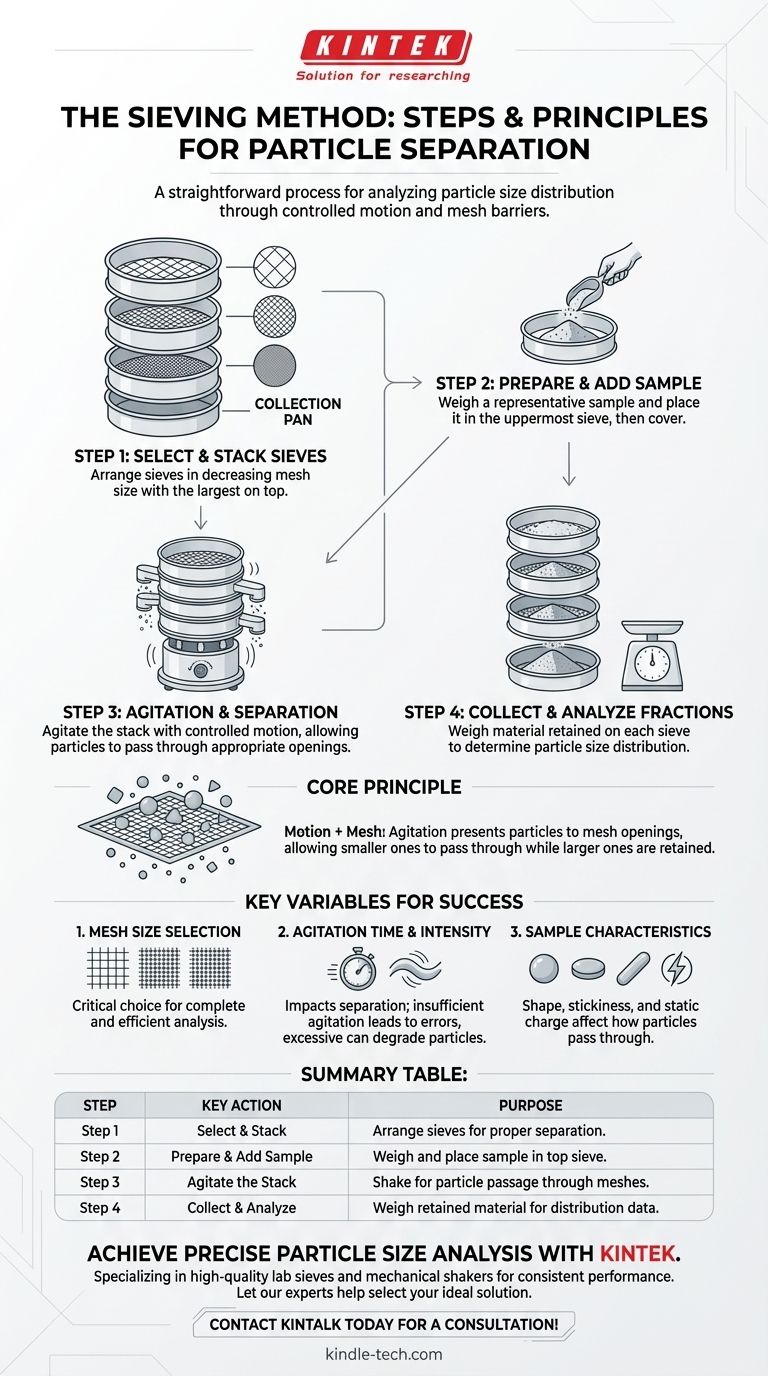
The sieving method is a straightforward process for separating particles of different sizes. It involves preparing a stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings, placing a sample in the top sieve, agitating the stack to allow particles to fall through, and then collecting the separated material from each level.
The core principle of sieving is not just about filtering; it's about using controlled motion to create opportunities for smaller particles to pass through a specific mesh size while larger particles are retained.

The Fundamental Principle of Sieving
Before detailing the steps, it's crucial to understand the mechanism that makes sieving effective. The entire process relies on the interaction between particle size, sieve mesh size, and movement.
The Role of Motion
Sieving requires agitation, either through vertical or horizontal motion. This shaking ensures that particles don't just sit flat on the mesh surface.
The movement creates a relative difference in motion between the particles and the sieve itself. This causes particles to be repeatedly presented to the mesh openings in different orientations, maximizing the chance for smaller particles to pass through.
The Sieve Mesh as a Gatekeeper
Each sieve is essentially a screen made of wire-mesh with precisely sized openings. This mesh acts as a physical barrier.
Particles smaller than the mesh openings can pass through to the next level, while particles larger than the openings are retained on the mesh surface.
A Step-by-Step Guide to the Sieving Process
Whether performed manually or with a machine, the core steps of a standard sieve analysis are consistent.
Step 1: Selecting and Stacking the Sieves
First, a set of sieves with various mesh sizes is selected based on the material being analyzed.
These sieves are stacked in order of decreasing mesh size, with the largest openings on top and the smallest on the bottom. A solid collection pan is always placed at the very bottom of the stack.
Step 2: Preparing and Adding the Sample
A representative sample of the material is weighed accurately.
The entire sample is then carefully placed into the uppermost sieve (the one with the largest mesh openings), and a lid is placed on top to prevent loss of material during agitation.
Step 3: Agitation and Separation
The entire stack of sieves is agitated for a predetermined amount of time. This can be done by hand or, for more consistent results, with a mechanical sieve shaker.
During agitation, particles work their way down the stack, passing through meshes until they reach a sieve with openings too small for them to fit through. The very finest particles will collect in the bottom pan.
Step 4: Collecting and Analyzing the Fractions
After the shaking is complete, the stack is disassembled.
The material retained on each individual sieve is carefully removed and weighed. The sum of the weights from each sieve should closely match the initial total weight of the sample.
Understanding Key Variables for Success
Achieving accurate and repeatable results depends on controlling several factors. Simply shaking a screen is not enough for a precise analysis.
Mesh Size Selection
The choice of mesh sizes is critical. Using too few sieves may provide an incomplete picture of the particle size distribution, while using too many can be inefficient.
Agitation Time and Intensity
The duration and force of the shaking directly impact separation. Insufficient agitation will result in incomplete separation, leaving smaller particles trapped on upper sieves. Conversely, excessive agitation can, in some cases, cause particle degradation.
Sample Characteristics
The shape and properties of the particles matter. Elongated or flat particles may not pass through a mesh as easily as spherical ones, even if their volume is smaller. Materials that are sticky or carry a static charge can also clump together, preventing effective separation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The required precision of the sieving process depends entirely on your final objective.
- If your primary focus is precise particle size analysis: Use a standardized set of sieves and a mechanical shaker with controlled time and intensity to ensure results are repeatable.
- If your primary focus is simple bulk material segregation: Manually sieving with one or two mesh sizes is often sufficient to separate a material into coarse and fine fractions for processing.
Ultimately, mastering the sieving method is about controlling motion and mesh size to achieve your desired separation.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Select & Stack Sieves | Arrange sieves by mesh size for proper separation. |
| 2 | Prepare & Add Sample | Weigh and place a representative sample in the top sieve. |
| 3 | Agitate the Stack | Shake to allow particles to pass through appropriate meshes. |
| 4 | Collect & Analyze | Weigh the material retained on each sieve for distribution data. |
Achieve precise and reliable particle size analysis in your lab. The accuracy of your sieving results depends on using the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves and mechanical sieve shakers designed for consistent performance and repeatable data. Let our experts help you select the ideal sieving solution for your specific materials and accuracy requirements.
Contact KINTALK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis



















