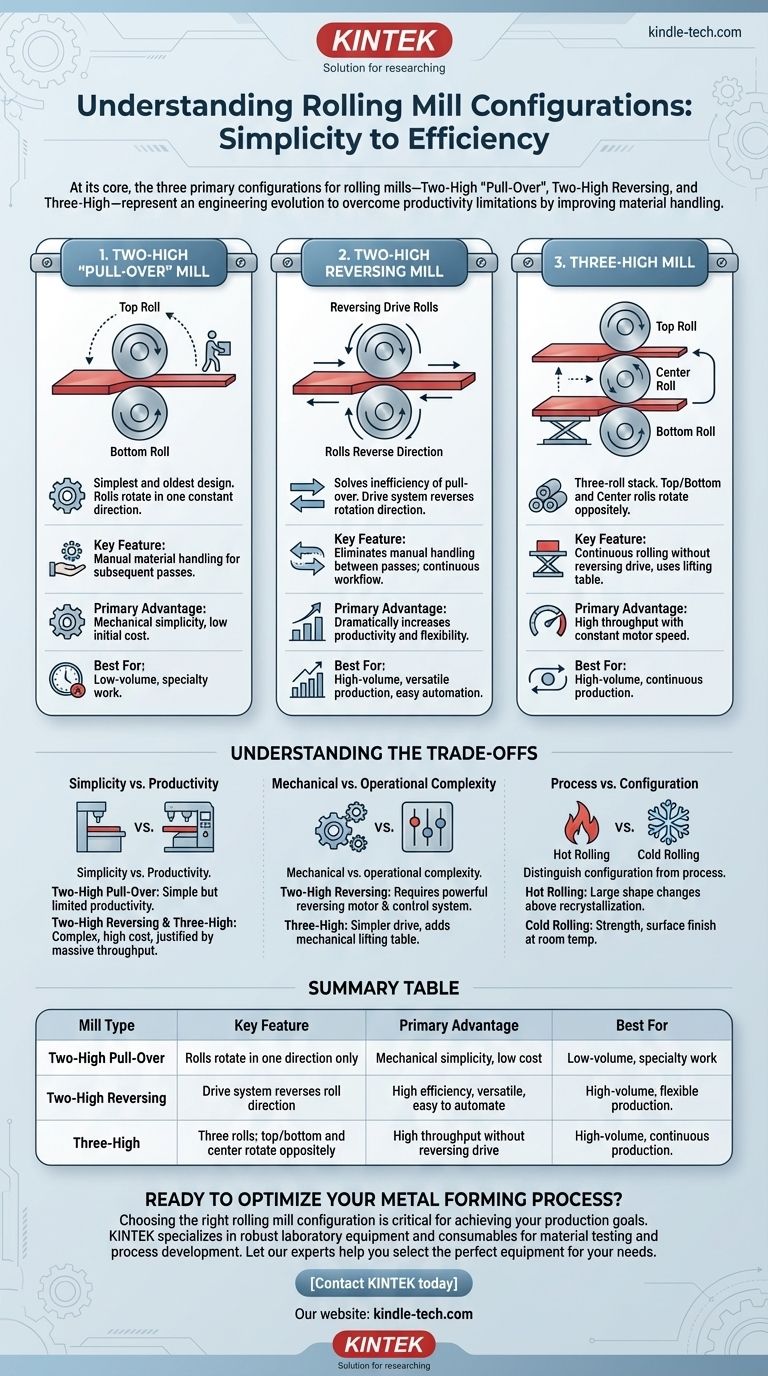
At its core, the three primary configurations for rolling mills are the Two-High "Pull-Over" Mill, the Two-High Reversing Mill, and the Three-High Mill. These designs represent an engineering evolution, with each subsequent type developed to overcome the productivity limitations of its predecessor by improving how material is handled between passes.
The choice between different rolling mill configurations is not arbitrary; it is a direct trade-off between mechanical simplicity, operational cost, and production efficiency. Understanding these designs reveals the fundamental challenge of metal rolling: performing multiple reduction passes as quickly as possible.

The Fundamental Rolling Mill Configurations
The classification of a rolling mill is determined by the number and arrangement of its rolls. This configuration dictates the mill's operational workflow, speed, and overall efficiency.
The Two-High "Pull-Over" Mill
This is the simplest and oldest design, consisting of two horizontally mounted rolls that rotate in a single, constant direction.
The workpiece is passed through the rolls in one direction to reduce its thickness. To make another pass, the material must be physically lifted and carried back over the top roll to the entry side, a process known as "pulling over."
This design is defined by its simplicity but suffers from extremely low productivity due to the significant downtime and manual labor required to return the workpiece for subsequent passes.
The Two-High Reversing Mill
To solve the inefficiency of the pull-over mill, the reversing mill was developed. It also uses two rolls, but its key innovation is a drive system that can reverse the direction of rotation.
After the material passes through in one direction, the rolls are stopped and their rotation is reversed. The workpiece is then passed back through in the opposite direction for another reduction.
This eliminates the need for manual handling between passes, dramatically increasing productivity and enabling a more continuous workflow on a single piece of equipment.
The Three-High Mill
The three-high mill is another clever solution to the same productivity problem. It consists of a stack of three rolls. The top and bottom rolls rotate in one direction, while the center roll rotates in the opposite direction.
A workpiece is passed through the gap between the bottom and middle rolls. Then, a lifting table raises the workpiece to the upper gap, where it is passed back through between the middle and top rolls.
This design allows for continuous rolling in both directions without needing to reverse the powerful and heavy machinery, offering high throughput with constant motor speed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each configuration presents a different set of advantages and disadvantages. The optimal choice depends entirely on the production goal.
Simplicity vs. Productivity
The Two-High Pull-Over mill is mechanically simple and has a low initial cost. However, its productivity is severely limited by the manual handling required, making it suitable only for small-scale or specialized work.
In contrast, both the Two-High Reversing and Three-High mills are designed for high-volume production. Their higher mechanical complexity and cost are justified by a massive increase in throughput.
Mechanical vs. Operational Complexity
The Two-High Reversing mill requires a powerful, specialized motor and control system capable of rapid and repeated reversals under heavy load. This adds electrical and control complexity.
The Three-High Mill uses a simpler, single-direction drive but requires a separate mechanical system (a lifting table) to move the heavy workpiece between the lower and upper roll gaps. This adds mechanical complexity to the material handling.
Process vs. Configuration (Hot vs. Cold Rolling)
It is critical to distinguish the mill's configuration (like two-high or three-high) from the rolling process (hot or cold).
Hot rolling is done above the metal's recrystallization temperature to allow for large shape changes, while cold rolling is done at room temperature to increase strength and improve surface finish. Any of these mill configurations can be engineered for either hot or cold rolling applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right mill is about aligning the equipment's capabilities with your specific manufacturing needs.
- If your primary focus is simple, low-volume, or specialty work: The Two-High "Pull-Over" mill is the most cost-effective solution due to its mechanical simplicity.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: The Three-High mill provides excellent throughput without the need for a reversing drive system, making it a robust workhorse.
- If your primary focus is versatile, high-efficiency production: The Two-High Reversing mill offers great flexibility for various reduction schedules and is often easier to automate than a three-high system with its lifting table.
Ultimately, understanding these foundational designs is the first step toward optimizing any metal forming process for cost, speed, and quality.
Summary Table:
| Mill Type | Key Feature | Primary Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Two-High Pull-Over | Rolls rotate in one direction only | Mechanical simplicity, low cost | Low-volume, specialty work |
| Two-High Reversing | Drive system reverses roll direction | High efficiency, versatile, easy to automate | High-volume, flexible production |
| Three-High | Three rolls; top/bottom and center rotate oppositely | High throughput without reversing drive | High-volume, continuous production |
Ready to Optimize Your Metal Forming Process?
Choosing the right rolling mill configuration is critical for achieving your production goals in cost, speed, and quality. KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables, including solutions for material testing and process development that rely on precise metal forming.
Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment for your needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Ten-Body Horizontal Jar Mill for Lab Use
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.
- What is the ball mill based on the principle of? Impact and Attrition for Efficient Grinding
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination



















