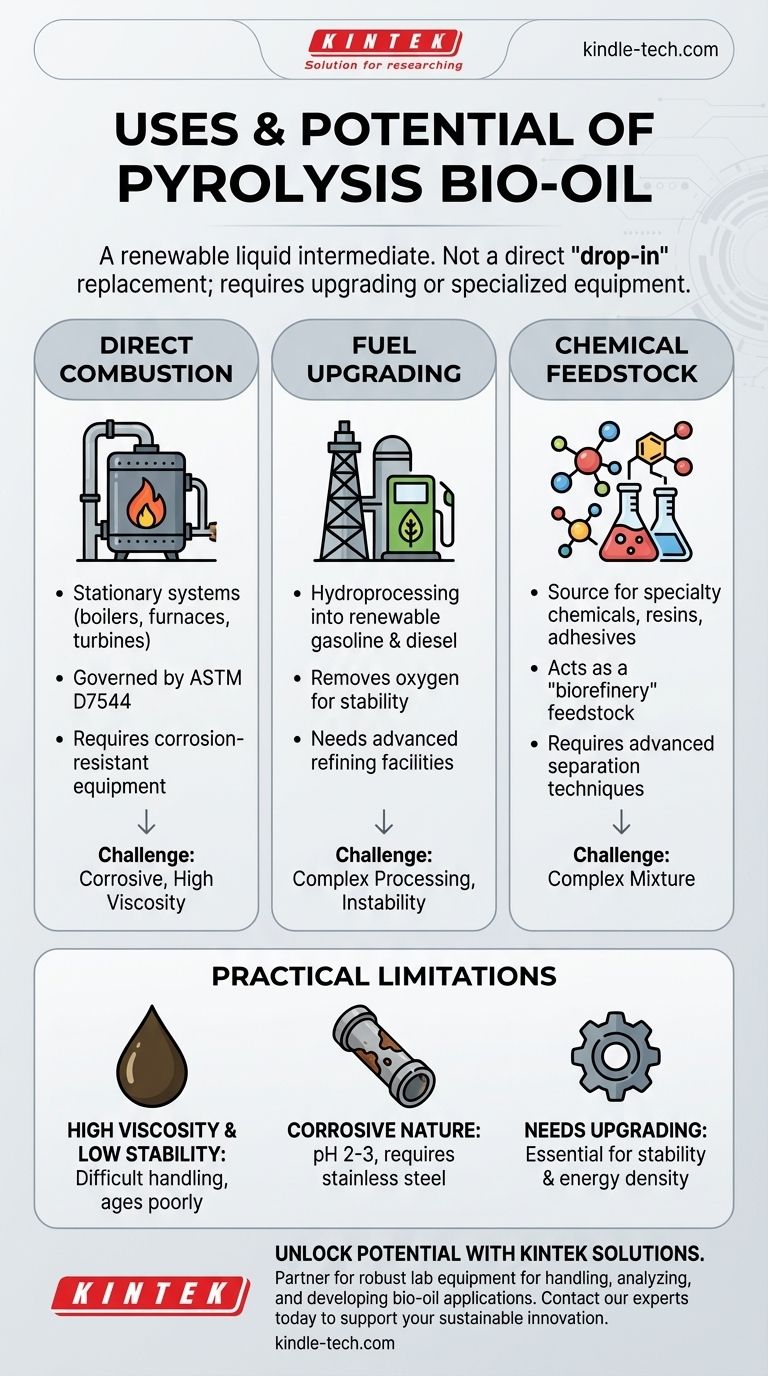
At a high level, pyrolysis bio-oil is primarily used as a substitute for conventional fuel oil in stationary applications like boilers and furnaces. It also serves as a potential feedstock for upgrading into transportation fuels or for the extraction of valuable specialty chemicals and materials.
While bio-oil is a promising renewable resource, it is not a direct "drop-in" replacement for fossil fuels. Its challenging properties mean it must either be refined through an upgrading process or used in equipment specifically designed or modified to handle it.

The Primary Applications of Bio-Oil
Pyrolysis bio-oil occupies a unique space as a liquid intermediate derived from biomass. Its uses are divided between direct application and further processing into higher-value products.
Direct Combustion in Stationary Systems
The most straightforward use for bio-oil is as a combustion fuel in stationary systems. This includes industrial boilers, furnaces, and turbines for generating heat and electricity.
This application is mature enough to be governed by its own standard, ASTM D7544, which regulates its use as an alternative to heating oil.
Upgrading to Transportation Fuels
A significant area of development is upgrading bio-oil into hydrocarbon fuels compatible with existing infrastructure. This involves processing it within a refinery, often through hydroprocessing.
This process uses hydrogen to remove oxygen and stabilize the molecules, converting the bio-oil into products like renewable gasoline and diesel.
Feedstock for Chemicals and Materials
Bio-oil is a complex mixture of hundreds of organic compounds. This makes it a rich potential source for extracting platform chemicals, resins, adhesives, and other bio-based materials.
This application treats bio-oil not as a fuel, but as a "biorefinery" feedstock, similar to how crude oil is the basis for the petrochemical industry.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
The widespread industrial use of raw, unrefined bio-oil is limited by several inherent chemical and physical properties. Understanding these challenges is critical to its successful application.
High Viscosity and Low Stability
Raw bio-oil is significantly thicker than conventional diesel or heating oil. It also tends to age poorly, increasing in viscosity and even solidifying over time, which complicates storage, pumping, and injection.
Corrosive Nature
Bio-oil is highly acidic, with a pH typically between 2 and 3. This makes it corrosive to common construction materials like carbon steel, requiring specialized stainless steel tanks, pumps, and engine components.
The Inevitable Need for Upgrading
These limitations—corrosiveness, instability, and high viscosity—are the primary reasons bio-oil must be "upgraded." Processes like stabilization, hydrotreating, and esterification are used to create a more stable, less corrosive, and more energy-dense fuel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing how to leverage bio-oil depends entirely on your available infrastructure, technical capabilities, and end goals.
- If your primary focus is immediate power generation: Plan to use the bio-oil in dedicated or heavily modified stationary boilers and be prepared to manage the material handling and corrosion challenges.
- If your primary focus is producing high-value transportation fuels: The path is to invest in or partner with facilities that have upgrading technologies, like hydroprocessing, to refine the raw bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is sustainable chemical production: View bio-oil as a complex chemical feedstock that requires advanced separation and purification techniques to isolate valuable compounds.
By understanding bio-oil as a valuable intermediate rather than a finished fuel, you can navigate its challenges and unlock its true potential.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Combustion | Fuel for boilers & furnaces (ASTM D7544) | Requires corrosion-resistant equipment |
| Fuel Upgrading | Feedstock for renewable gasoline/diesel | Needs hydroprocessing or other refining |
| Chemical Feedstock | Source for specialty chemicals & materials | Requires advanced separation techniques |
Unlock the potential of pyrolysis bio-oil in your lab or process development.
KINTEK specializes in providing the robust lab equipment and consumables needed to safely handle, analyze, and develop applications for challenging materials like bio-oil. Whether you are researching fuel upgrading processes, chemical extraction, or combustion properties, our reactors, corrosion-resistant components, and analytical tools are designed for reliability and precision.
Let KINTEK be your partner in sustainable innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your bio-oil research and development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
















