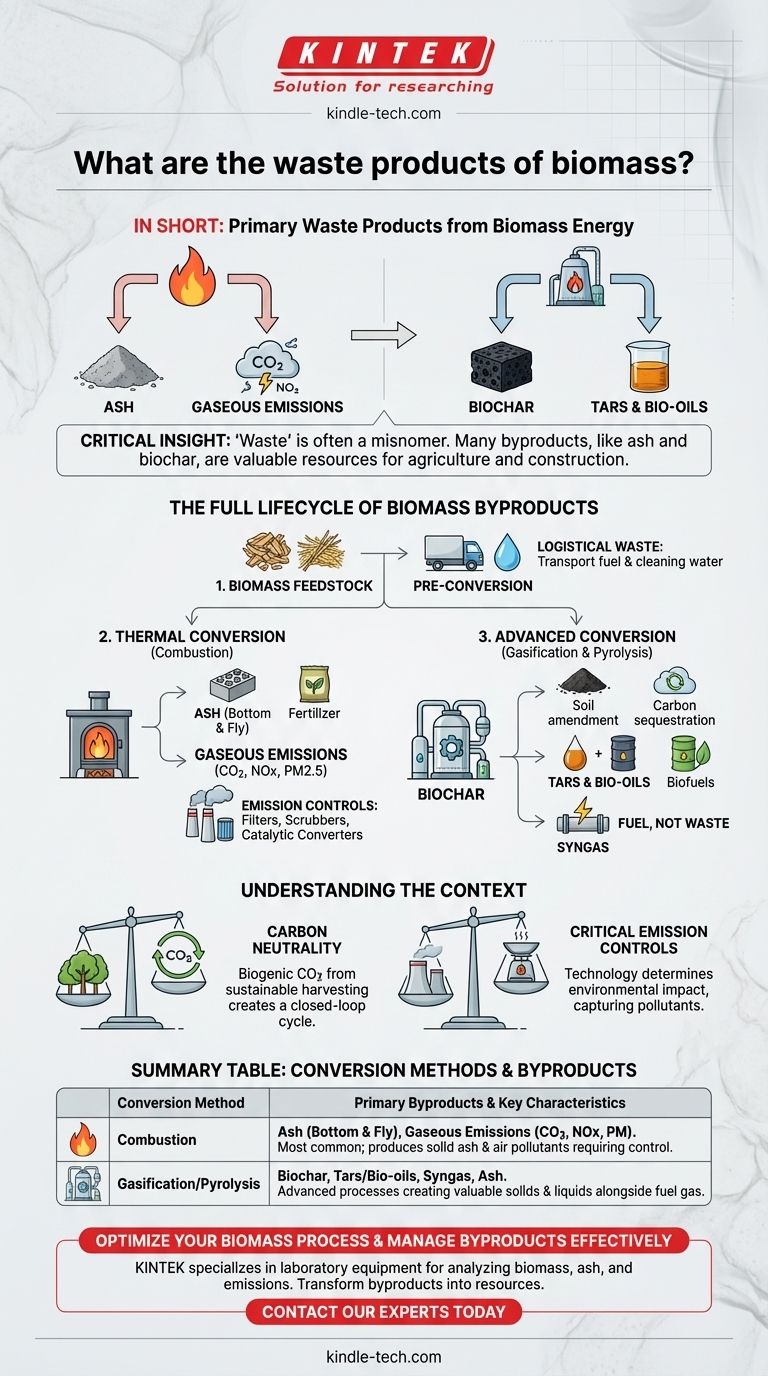
In short, the primary waste products from using biomass for energy are ash, gaseous emissions like carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides, and in some processes, biochar and tars. The exact byproducts depend entirely on the type of biomass used and the conversion technology, such as direct combustion versus gasification.
The most critical insight is that "waste" from biomass is often a misnomer. Many byproducts, like ash and biochar, are valuable resources for agriculture and construction, while the most significant environmental challenge lies in managing gaseous emissions.
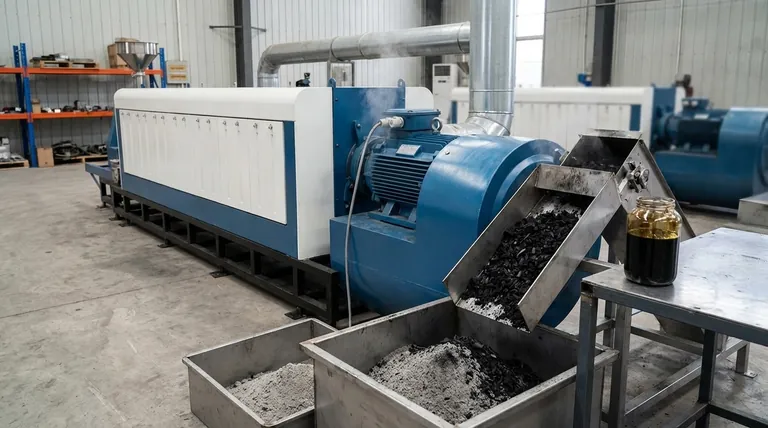

The Full Lifecycle of Biomass Byproducts
To understand the waste, you must look at the entire process, from the raw material to the final energy conversion. The output is fundamentally dictated by the input and the method.
Pre-Conversion and Feedstock Waste
Before any energy is produced, the biomass itself is often a repurposed waste stream. Using materials like forestry residue, sawdust, or agricultural straw prevents them from decomposing and releasing methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
The primary waste at this stage is logistical, involving fuel for transport and any water used for cleaning the feedstock.
Byproducts of Thermal Conversion (Combustion)
Direct combustion—burning biomass in the presence of oxygen—is the most common conversion method. It produces heat to drive turbines or warm buildings.
- Ash: This is the solid, non-combustible mineral content left after burning. It comes in two forms: bottom ash, which collects at the bottom of the furnace, and fly ash, which is a fine powder carried away in the exhaust gas.
- Gaseous Emissions: This is the most complex category. Key emissions include Carbon Dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O), Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Particulate Matter (PM2.5).
Byproducts of Advanced Conversion (Gasification & Pyrolysis)
These methods involve heating biomass with little or no oxygen, which chemically converts it rather than simply burning it.
- Biochar: Pyrolysis produces a stable, carbon-rich solid called biochar. Far from being waste, it is a highly valuable soil amendment that improves water retention and sequesters carbon for centuries.
- Tars and Bio-oils: These complex liquid hydrocarbons are also produced. They can be challenging byproducts that require further refining or can be upgraded into valuable biofuels and chemicals.
- Syngas: Gasification produces a "synthesis gas" (syngas), which is a fuel, not a waste product. The waste stream from this process is typically the ash and the cleanup of tars.
Understanding the "Clean Energy" Context
Biomass is often called a "clean" or "carbon-neutral" fuel, but this depends entirely on context and technology. Ignoring the nuances is a common and costly pitfall.
The Carbon Neutrality Debate
The CO2 released from burning biomass is considered biogenic, meaning it was recently captured from the atmosphere by the plant. In theory, if the biomass is harvested sustainably, this creates a closed-loop carbon cycle.
However, this neutrality is compromised if harvesting practices are not sustainable or if the timescale for regrowth is very long (e.g., clear-cutting old-growth forests).
The Critical Role of Emission Controls
The most significant environmental "waste" from biomass is uncontrolled air pollution. A simple wood stove releases high levels of particulate matter and carbon monoxide.
In contrast, a modern biomass power plant uses sophisticated filters, scrubbers, and catalytic converters to capture the vast majority of harmful pollutants like NOx, SOx, and particulates before they are released. The technology determines the true environmental impact.
How Feedstock Changes the Waste Profile
The type of biomass is critical. Clean, untreated wood or crop residue produces predictable ash and emissions.
Conversely, burning treated or contaminated wood (e.g., construction debris with paint, glue, or preservatives) can release heavy metals and toxic organic compounds, creating hazardous waste that requires special disposal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy for managing biomass byproducts should align directly with your primary objective, as there is no single "best" approach.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Prioritize technologies like pyrolysis that create biochar for carbon sequestration, and insist on advanced emission controls for any combustion process.
- If your primary focus is economic return: Analyze the local market for selling byproducts. High-quality ash can be sold as agricultural fertilizer, and biochar is a valuable product for farming and landscaping.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy output: Focus on high-efficiency combustion or gasification systems, and view byproduct management as a necessary operational cost to be optimized.
Ultimately, harnessing the full potential of biomass requires viewing its byproducts not as waste to be discarded, but as resources to be managed and valorized.
Summary Table:
| Conversion Method | Primary Byproducts | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion | Ash (Bottom & Fly), Gaseous Emissions (CO2, NOx, PM) | Most common method; produces solid ash and air pollutants requiring control. |
| Gasification/Pyrolysis | Biochar, Tars/Bio-oils, Syngas, Ash | Advanced processes creating valuable solids (biochar) and liquids alongside fuel gas. |
Ready to optimize your biomass process and manage byproducts effectively? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment for analyzing biomass feedstocks, ash content, and emissions. Our solutions help you characterize your materials, ensure process efficiency, and turn byproducts into valuable resources. Contact our experts today to find the right tools for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis oil the same as crude oil? No, and here’s why the difference matters.
- How do magnetic stirrers and vacuum drying ovens work together to optimize catalyst performance? Expert Prep Guide
- What is the cycle of heat treatment? Master the 3 Stages to Control Metal Properties
- Why is deposition technology good? Unlock Atomic-Level Control for Superior Materials
- What is the principle of reactive sputtering? Create High-Performance Ceramic Coatings
- What is sputtering in plasma treatment? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between VAR and ESR? A Guide to Understanding Tail Risk in Financial Modeling
- What is the difference between a lab furnace and a lab oven? Choose the Right Heating Tool for Your Lab







