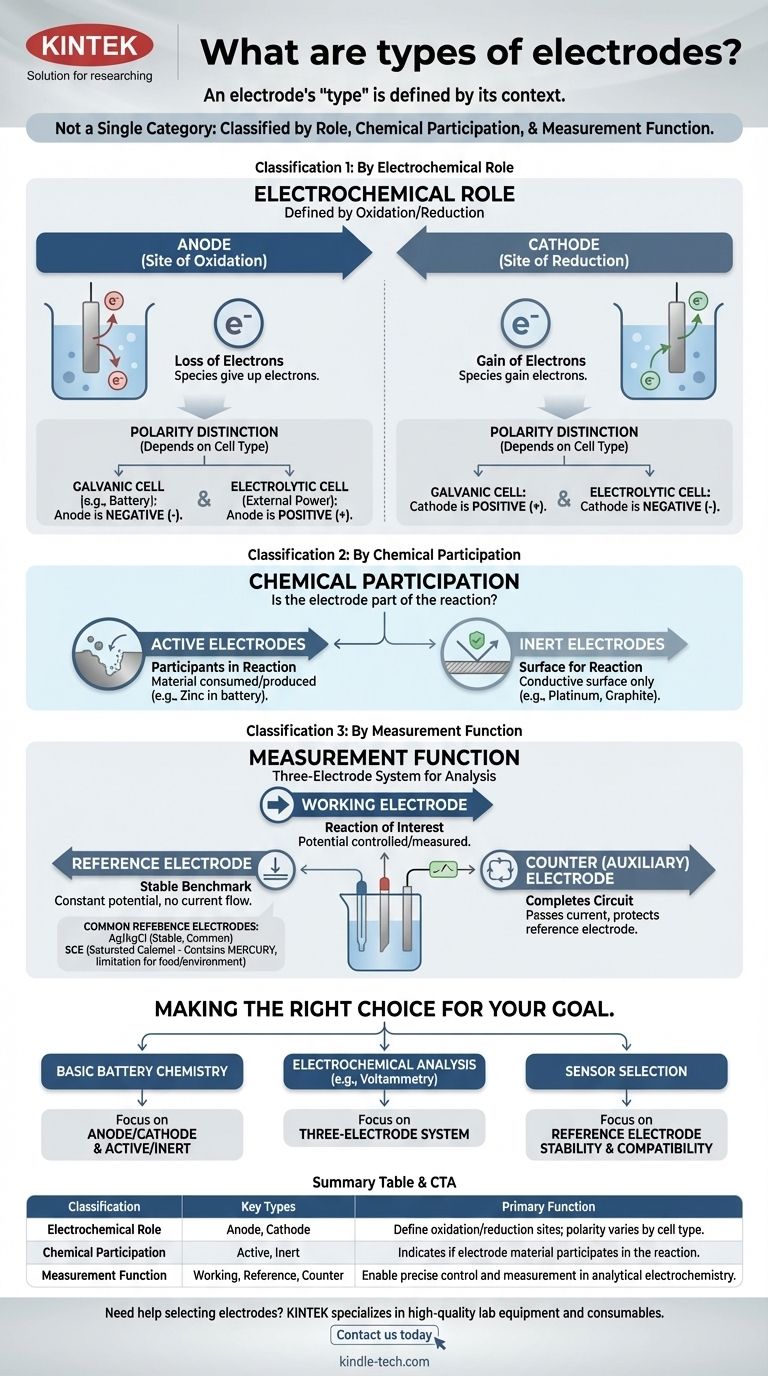
The term "electrode" is not a single category. Instead, electrodes are classified in several distinct ways based on their role in a reaction, their chemical participation, and their function within a measurement system. Understanding these different classification systems is the key to grasping their purpose in any electrochemical cell.
The most critical insight is that an electrode's "type" is defined by its context. The same piece of metal can be an anode or a cathode, active or inert, depending entirely on the electrochemical system you place it in.
Classification 1: By Electrochemical Role
The most fundamental classification defines an electrode by its role in the two halves of an electrochemical reaction: oxidation and reduction.
The Anode: The Site of Oxidation
The anode is, by definition, the electrode where oxidation occurs—the loss of electrons. Species at the anode give up their electrons to the electrode.
The Cathode: The Site of Reduction
The cathode is the electrode where reduction occurs—the gain of electrons. The cathode gives its electrons to species in the solution.
The Critical Distinction: Anode/Cathode Polarity
A common point of confusion is the charge (+ or -) of the anode and cathode. This polarity depends on the type of cell:
- In a galvanic cell (like a battery), the spontaneous reaction generates energy. The anode is the negative terminal, and the cathode is the positive terminal.
- In an electrolytic cell, an external power source drives a non-spontaneous reaction. The anode is the positive terminal, and the cathode is the negative terminal.
Classification 2: By Chemical Participation
This classification describes whether the electrode material itself is part of the chemical reaction.
Active Electrodes: Participants in the Reaction
An active electrode is made from a material that is either consumed or produced during the cell's reaction. For example, in a zinc-copper battery, the zinc anode dissolves, actively participating in the oxidation half-reaction.
Inert Electrodes: A Surface for Reaction
An inert electrode does not participate in the chemical reaction. It serves only as a conductive surface where oxidation or reduction can take place. Platinum and carbon (graphite) are common inert electrodes used to facilitate reactions involving gases or dissolved ions.
Classification 3: By Measurement Function
In analytical electrochemistry, a three-electrode system is often used for precise measurements. This gives rise to a functional classification.
The Working Electrode
This is the electrode where the reaction of interest is occurring. Its potential is the primary variable being controlled or measured.
The Reference Electrode: The Stable Benchmark
A reference electrode provides a stable, constant potential against which the working electrode's potential is measured. Its own potential does not change regardless of the current flowing or the composition of the bulk solution.
The Counter (or Auxiliary) Electrode
This electrode's sole purpose is to complete the electrical circuit. It passes all the current needed by the working electrode, ensuring that negligible current flows through the sensitive reference electrode, thereby protecting its stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Common Reference Electrodes
The choice of reference electrode is critical for accurate measurements and depends on the chemical environment.
Ag/AgCl: The Common Workhorse
The Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode is the most common reference electrode. It is stable, inexpensive, and generally reliable, making it a default choice for many aqueous solutions.
Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE): The Classic Alternative
The Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) is an older, highly stable standard. It is often used in situations where the sample solution is incompatible with silver or chloride ions, which could interfere with the Ag/AgCl electrode.
The Mercury Problem: A Key Limitation
The major drawback of the SCE is that it contains mercury. This makes it unsuitable for applications involving food, beverages, or environmental testing where mercury contamination is a significant concern.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application determines which classification is most important.
- If your primary focus is understanding basic battery chemistry: Master the concepts of anode/cathode and active/inert electrodes.
- If your primary focus is performing electrochemical analysis (like voltammetry): The three-electrode system (working, reference, counter) is the essential framework.
- If your primary focus is selecting a sensor for a specific environment: Your main concern will be the chemical compatibility and stability of your reference electrode, such as choosing between Ag/AgCl and an alternative.
Understanding these overlapping classifications empowers you to control and interpret the behavior of any electrochemical system.

Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Types | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical Role | Anode, Cathode | Define oxidation/reduction sites; polarity varies by cell type (galvanic/electrolytic) |
| Chemical Participation | Active, Inert | Indicates if electrode material participates in the reaction or acts as a surface only |
| Measurement Function | Working, Reference, Counter | Enable precise control and measurement in analytical electrochemistry |
Need help selecting the right electrodes for your lab's electrochemical applications? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your research needs. Whether you're working on battery development, sensor design, or analytical measurements, our expertise ensures you get the optimal electrodes for accuracy and performance. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and enhance your electrochemical workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is a common application for the platinum wire/rod electrode? The Essential Guide to Counter Electrodes
- What are the performance characteristics of platinum wire/rod electrodes? Unmatched Stability for Your Lab
- What is the rotating ring disk electrode method? Unlock Real-Time Reaction Analysis
- How should a platinum wire/rod electrode be cleaned before use? A Guide to Reliable Electrochemical Data
- What is the common role of a platinum disk electrode? A Guide to Its Primary Use as a Working Electrode



















